The Comprehensive Guide to Rivet Nut Technology

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China
In the modern manufacturing field, rivet nut technology is being widely used in many industries such as automotive, sheet metal, electronics, electrical cabinets, home appliances, etc. due to its efficient, reliable and adaptable connection. This guide will comprehensively analyze the development history, structural principles, application advantages and selection tips of rivet nut technology to help engineers, purchasers and manufacturers gain an in-depth understanding of this key fastening solution, so as to achieve higher efficiency and stronger connection strength in product design and production.
Table of Contents
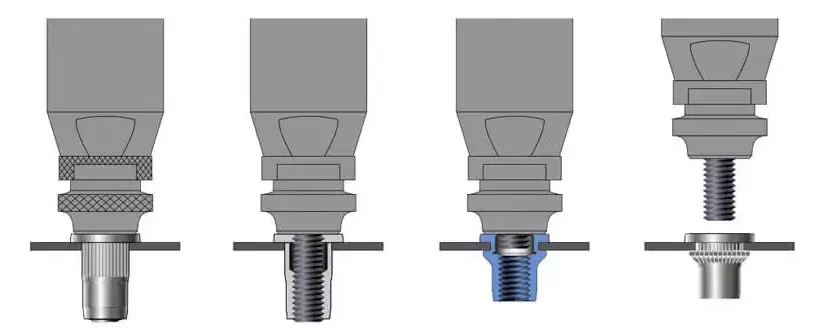
What Is Rivet Nut Technology?
In modern manufacturing, Rivet Nut Technology is a highly effective fastening solution for creating threaded joints in thin plates, tubes or structures with non-contactable backs. It is used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, sheet metal, electrical, aerospace, home improvement and many others, by stretching the end of the rivet nut in a pre-determined hole to create a plastic deformation, which creates a solid “blind” threaded point in the workpiece.

Rivet Nuts, also known as Rivet Nuts, are a metal sleeve structure with internal threads, similar in shape to a solenoid, with a plastically deformable tail. It can in scenarios where it is not possible to operate from the back, complete the installation of threaded holes in a single pass, and is particularly suitable for:
- Areas where the plate thickness is too thin to be tapped;
- Hollow or closed structures such as aluminum profiles, square tubes;
- Work stations where a removable connection (screw assembly) is still required subsequently.
a. Core Principle
The core principle is to use a special rivet nut gun to apply tension to the end of the nut from the front side, prompting the tail end to bulge outward and backwrap the substrate, thus forming a clamping and fixing structure on the front and back sides of the plate at the same time. This process requires no welding, has no heat effects, and does not damage the base material structure, creating a stable, reusable threaded joint.
b. Explanation of critical deformation and force areas:
| Zones | Functions | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tail Bulge | Anchor Structure | “Flanging” locking effect on the backside of the workpiece |
| Flange Heads | Support and Reaction | Restricted deformation zones, fitting to the front side of the workpiece |
| Internal Threads | Threaded Joints | Maintained intact, for subsequent bolting |
| Bulge Contact surfaces | Friction fixing | Increase shear and tensile forces to avoid loosening |
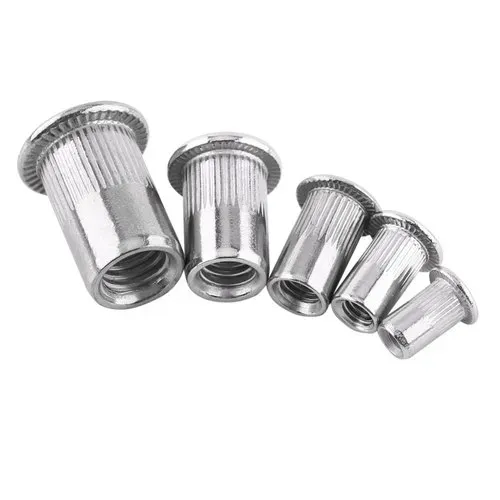
History of Rivet Nut Technology

Rivet Nut (Rivet Nut, also known as pull cap, pull rivet nut) as a single-sided operation and have the function of internal thread fasteners, its technology since the early 1900s since the birth of the technology, has experienced nearly a century of development and evolution. It is widely used in automotive, aviation, sheet metal, electrical equipment and many other industries, and is one of the indispensable threaded connection solutions in modern industry.
Initial period (1930s-1950s): the birth of the military industry drive
- In the 1930s, American companies such as AVK and Rivnut found that traditional threaded connections could not meet the demands of “blind holes”, “thin walls” or “one-sided operation” in the aircraft manufacturing process. The traditional threaded connection cannot meet the demand of “blind hole”, “thin wall” or “one-side operation” working conditions.
- To solve the problem of connecting aircraft skins to structural components, the first rivet nuts (such as the Rivnut) were created to provide a stable internal threaded connection in locations where tapping was not possible.
- The first generation of rivet nut is mostly open cylindrical design, the material is mainly steel, aluminum.
Representative Scenario: U.S. Army fighter and transport aircraft skin structure.
Industrialization period (1960s-1980s): batch manufacturing and multi-industry expansion
- With the development of industrial automation, rivet nuts gradually entered automotive, home appliances, machinery assembly and other fields, and began to batch manufacturing;
- Processes began to appear knurling, hexagonal, slotted and other anti-spin design;
- Tool end also developed manual rivet gun, pneumatic tools, such as primary mechanical equipment;
- Countries have developed their own riveting system, such as Germany GESIPA, Japan Honsel and other manufacturers to enter the market.
Iconic development:
- Introduction of stainless steel to enhance corrosion resistance;
- The degree of tool standardization has increased, adapting to different specifications.
Technology diversification period (1990s-2010s): system upgrade and automation integration
- Expansion of rivet nut technology towards higher precision and diversification:
- Countersunk head type, closed type, thin flange type, extended shank type and many other structures were born;
- Material introduction brass, alloy steel and other special metals;
- Rapid evolution of riveting equipment:
- The emergence of electric rivet nut gun, servo control tools ;
- Promote the application of automated production lines, such as robot integration riveting;
- Accelerated standardization process, ISO, DIN, IFI and other standards to establish a unified specification.
Intelligent Manufacturing Period (2010s-present): Intelligent Control and Green Manufacturing
- With the rise of Industry 4.0, rivet nut technology is upgraded in the direction of intelligent, digital and green:
- Electro-hydraulic system can accurately control the tension and stroke;
- Some systems support data collection, quality tracking;
- Lighter and stronger new materials (such as 7075 aluminum alloy) are used in the production of rivet nuts;
- In terms of green manufacturing, the rivet nut connection method no spark, no welding, no pollution, in line with the global trend of environmental protection.
Technology Trends
| Development Direction | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation and Intelligence | Tools will integrate data return, quality monitoring, and remote setting functions |
| Material Innovation | Development of lighter, stronger, and more corrosion-resistant alloys |
| Connection Optimization | Launch of multi-station integrated tooling to improve line efficiency |
| Sustainability | Use of recycled materials and support of green manufacturing standards |
What Are the Key Benefits of Rivet Nut Technology?
Rivet Nut Technology is widely used in the modern manufacturing industry because of its obvious advantages in terms of joining efficiency, mechanical properties, and applicability, which make it particularly suitable for dealing with a wide range of actual working conditions such as thin plate joining, space constraints, and one-sided operation.
Fast & One-Side Installation
- Rivet nuts can be installed from one side only, which is especially suitable for structures such as pipes and boxes where it is not possible to work from the back side;
- The entire process requires no tapping, welding or nut holding, greatly reducing process time;
- Particularly suitable for high-volume production lines, which can significantly improve assembly efficiency.
- Rivet nut molding after the tail bulge anti-wrap, can effectively withstand the screw torque and axial tension;
- With good resistance to pull-out force, shear force and torsion, the connection is durable and stable;
- Can withstand vibration, load changes and other harsh working conditions, widely used in automotive, machinery, aviation and other areas with strict requirements for structural strength.
- Rivet nuts can be installed on different base materials such as metal (aluminum, carbon steel, stainless steel), plastic, composite boards, etc.;
- Different material nuts (such as aluminum, brass, stainless steel, etc.) can be selected to match the performance of the workpiece;
- Suitable for a wide range of structural requirements such as sheet metal, electrical cases, appliance housings, lightweight components, etc.
Automation-Friendly
- The rivet nut installation process is standardized and controllable, easy to integrate with robotic arms, automatic feeding systems, and CNC tools;
- Suitable for automatic riveting in robotic assembly lines, improving production tempo and consistency;
- High-end factories widely use electric, pneumatic or servo type rivet nut guns for intelligent control.
Eco-Friendly & Clean Process
- The installation process has no sparks, no high temperature, no smoke and dust, and does not affect other processes;
- More environmentally friendly and safer than traditional welding/tapping connection;
- In line with the trend of green manufacturing, meets the requirements of RoHS, REACH and other environmental regulations.
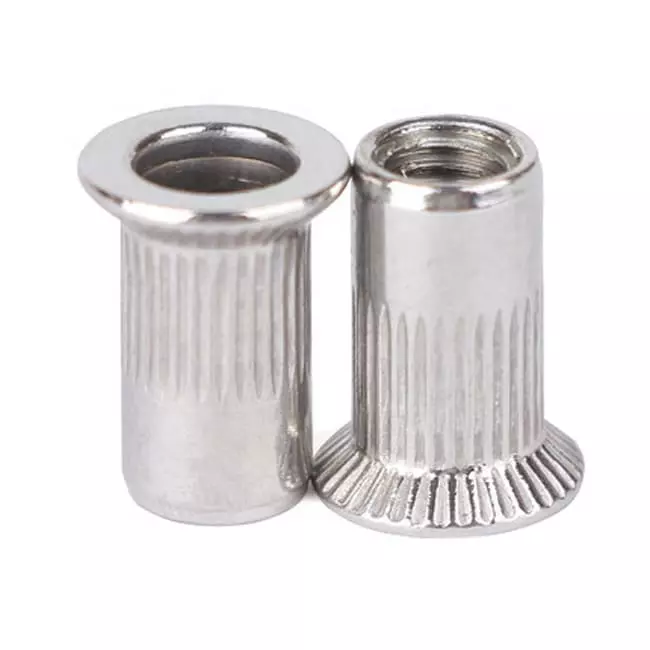
What Are the Different Types of Rivet Nuts ?
Rivet nuts can be subdivided into various types depending on the structure, head shape, profile type and material. Correct selection can significantly improve assembly strength, spin resistance and adaptability. The following is a detailed analysis of common rivet nut types.
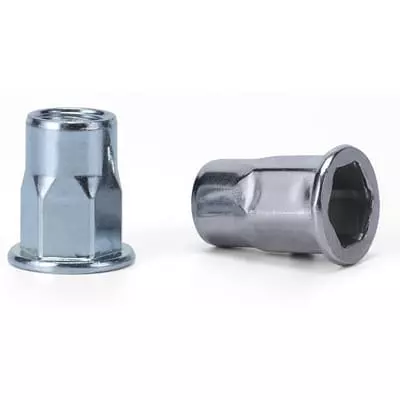
a. Open-End vs Closed-End
Open-End Rivet Nut
- Open-end, allowing bolts to penetrate to the bottom;
- Highly versatile, suitable for most through-hole connection structures;
- Used in mechanical housings, electrical control boxes, sheet metal plates, etc.
- Closed-end to prevent water, dust or oil from entering the inside of the thread;
- Particularly suitable for applications where sealing is required, such as automobile chassis and outdoor equipment;
- Also prevents screws from penetrating the back of the workpiece, protecting the internal space.
b. Round Body vs Hex Body
Round Body
- Round shape, easy to install, generally anti-rotation by friction;
- Requirements for hole accuracy are low, suitable for non-high-torque applications;
- Suitable for soft or low-strength substrates, such as plastic plates and aluminum plates.
- Hexagonal shape, requires matching hexagonal punch for installation;
- Provides stronger anti-rotation capability and is suitable for high torque and high vibration environments;
- Commonly used in heavy machinery, automobile chassis and other structures.
c. Flat Head vs. Countersunk Head
Flat head
- Flange edge protrudes and is mounted slightly above the surface of the workpiece;
- Suitable for most general-purpose installations for easy stress dispersion;
- Easy to install, no chamfering of the workpiece is required.
- The countersunk head is flush with the surface of the workpiece after installation, which is aesthetically pleasing and does not affect subsequent assembly;
- Suitable for workpieces with high appearance requirements or limited structural space;
- The holes need to be chamfered 90° before mounting.
d. Material Options
Choosing the right material for the rivet nut is critical to ensuring a balance of joint strength, corrosion resistance and cost effectiveness. Common rivet nut materials include aluminum alloy, carbon steel, stainless steel and brass. Different materials are suitable for different usage environments and load requirements.
Aluminum
- Characteristics: Lightweight, easy to mold, corrosion-resistant;
- Applicable Scenarios: suitable for light-loaded structures, such as electronic equipment housings, household appliances, and thin aluminum panels;
- Advantages:
- Low density, reducing the overall weight;
- Surface oxide layer provides basic corrosion resistance;
- Cautions: Low tensile and shear strengths, not suitable for heavy-duty structures.
Carbon Steel
- Characteristics: Moderate strength and economical price;
- Applicable Scenarios: Widely used in general-purpose sheet metal structures, mechanical assemblies, and electric appliance brackets;
- Advantages:
- Rust resistance can be enhanced by surface galvanization and nickel plating;
- Lower cost, suitable for bulk purchase and daily industrial application;
- Precautions: Protective treatment must be done in humid or corrosive environments, otherwise it is easy to rust.
Stainless Steel
- Features: high strength, high corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance;
- Applicable Scenario: suitable for outdoor, high humidity, high salt environment, such as ships, rail transportation, food equipment;
- Advantages:
- Stable material, acid and alkali resistant, oxidation resistant;
- Excellent tensile and shear performance, suitable for high strength connection;
- Commonly used models:
- 304: general-purpose, stable performance, cost-effective;
- 316: stronger corrosion resistance, suitable for seashore and chemical environment;
- Note: high cost, more difficult to process and mold.
Brass

- Features: excellent electrical conductivity, good self-lubrication, smooth assembly;
- Applicable Scenarios: mostly used for electrical connections, precision instruments, decorative components;
- Advantages:
- Not easy to jam, suitable for repeated disassembly;
- Good electromagnetic compatibility and electrical conductivity;
- Cautions: Mechanical strength is not as good as steel, suitable for low and medium strength occasions.
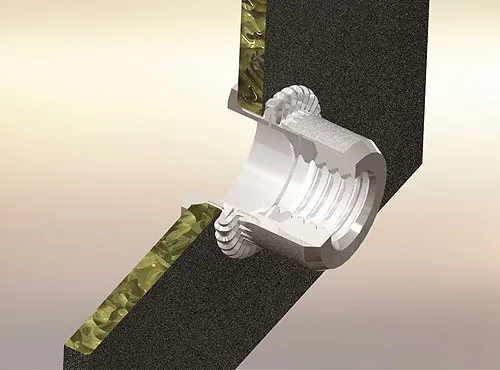
Rivet Nut (Rivet Nut) as a kind of threaded fasteners designed for thin-walled materials or blind hole structure, the core of its working principle lies in the controlled plastic deformation of the tail and structural clamping mechanism. Compared with traditional welded nuts or self-tapping screws, rivet nuts have outstanding advantages such as single-sided operation, stable molding and efficient installation.
A. Rivet deformation principle and clamping mechanism
The core installation mechanism of Rivet Nut (Rivet Nut) is a process of generating plastic deformation by stretching the tail to achieve reliable clamping under preset constraints. This process does not rely on welding, tapping, or double-sided work, and enables a permanent, reusable threaded joint to be achieved by operation on one side only.

① Controlled bulging and deformation of the tail section
- At the start of riveting, the rivet nut is threaded onto the tie rod of the rivet nut gun;
- After the rivet nut is inserted into the pre-drilled hole, the gun is activated and the drawbar exerts an axial tension force;
- This pulling force stretches the tail of the rivet nut outward, but because the nut is embedded in the substrate, the space in the tail is limited, so the tail distends radially in the mold limitations or material reaction;
- The bulging area eventually forms an “umbrella” or “flap” structure.
- The bulging area eventually forms an “umbrella” or “flap” structure.
② Double sided clamping structure
- The flange head at the front of the rivet nut presses against the front side of the substrate, while the bulging tail wraps around and presses against the back side of the substrate;
- Together, they form a “front-pressing and back-supporting ” clamping structure;
- This double-sided clamping method effectively disperses stress and prevents pulling off, rotation and loosening.
- This double-sided clamping method effectively disperses stresses and prevents pull-off, rotation and loosening.
③ Threads remain intact and can be used repeatedly
- During the riveting process, the internal threaded portion of the rivet nut is not involved in deformation;
- After riveting is completed, the internal threads remain intact, allowing repeated screwing in and out of bolts or screws;
- Compared with welded nuts, they are not affected by heat and do not have problems such as thread galling and burnout.
Summary: Principles of riveting deformation
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Clamping method | Flange pressure on the front side + bulge area support on the back side, forming a mechanical locking |
| Plastic deformation parts | Riveted nut tail (does not affect the thread) |
| Core drive | Tie rods to provide axial tension |
| Connection stability | Tensile, torsion and vibration resistance, solid structure |
| Applicable working conditions | Thin plate Thin Plates, Blind Holes, Soft Materials, Unable to Weld or Tap |
B. Why Use Rivet Nuts for Blind Hole Fastening?
① What is a Blind Hole Connection?
A Blind Hole is a hole that can only be accessed and operated from one side and the other side is closed or inaccessible. This type of structure is very common in actual product design, such as the inside of boxes, closed cavities in profiles, thin-walled sheet metal parts, pipe ends, and so on. This type of scenario cannot be connected by clamping using the normal nut-and-bolt method.
② Rivet Nuts Provide the Ideal Solution for Blind Hole Connections
The Rivet Nut is perfectly suited for blind holes due to its single sided mounting, without the need for a counter support. Simply inserted into a pre-drilled hole from one side and deformed by pulling with a Rivet Nut gun, it creates a strong, reusable threaded joint in the substrate.
③ Advantages over conventional methods
| Comparison Dimension | Riveted Nut Connection | Ordinary Nut + Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable Locations | Blind Hole on One Side | Requires Double Sided Operation |
| Operational Efficiency | Fast, Automation Supported | Slow, Labor Dependent |
| Mounting Methods | No Welding, No Tapping Required | Usually Tapping or Fitting Gaskets |
| Substrate Requirements | Suitable for Thin Plates, Pipes, Etc. | Needs to Be Supported by a Certain Thickness |
| Cost Control | Simple, labor-saving process | Complicated, costly operation |
What Are the Common Installation Methods for Rivet Nuts?
Rivet Nuts can be installed in a variety of ways, and different types of installation tools are usually selected based on application scenarios, installation batches, and budget requirements. Below are several common installation methods and their applicable characteristics:
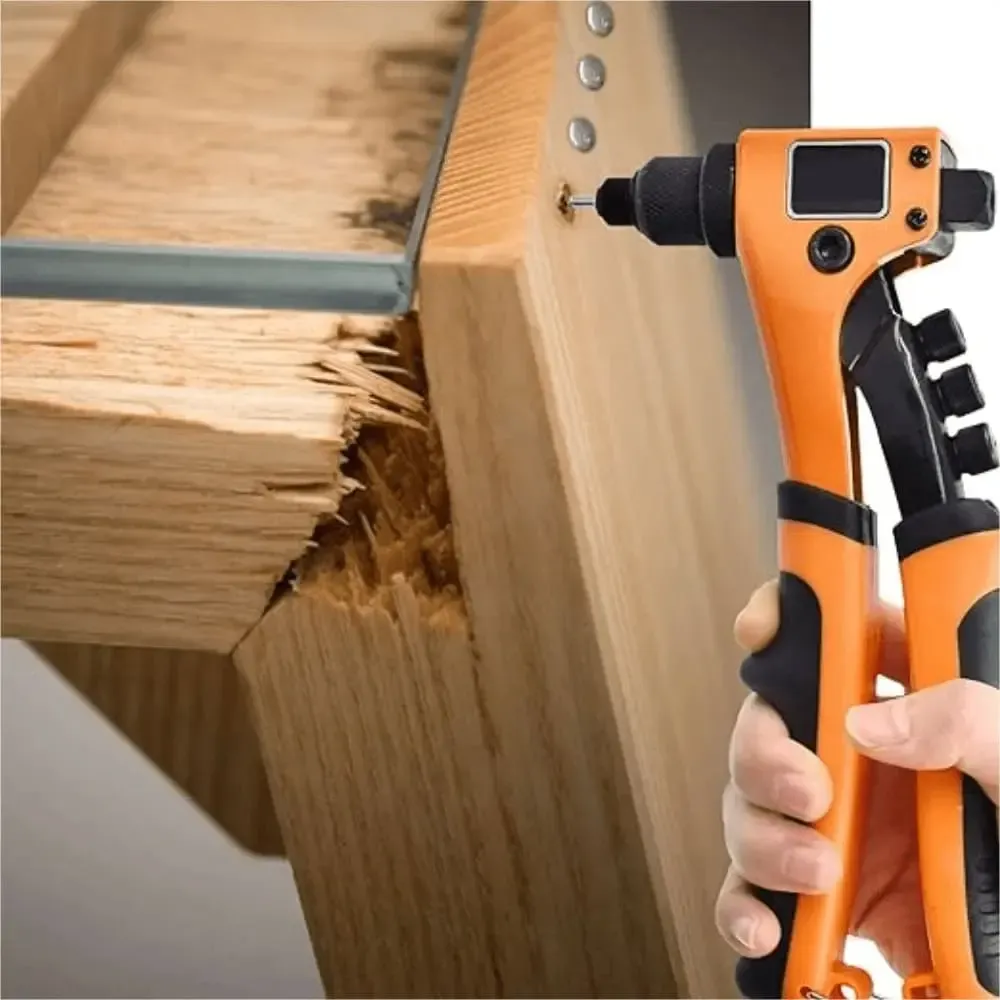
The Hand Rivet Nut Gun is a simple construction and flexible basic tool for entry level or small job scenarios in nut riveting. It is used to clamp and secure by manually applying force to actuate a pull rod, which causes plastic deformation of the end of the rivet nut. Widely used in maintenance, home DIY, sample making, start-up assembly line, etc.
Working Principle:
- The tool applies pressure through the combined force of two handles;
- The tie rod pulls backward on the inner thread of the rivet nut;
- The end of the nut gradually expands and presses against the back of the workpiece;
- When the riveting is complete, the tie rod is rotated out to form a solid threaded connection.
- –Riveting is completed and the tie bar is rotated out to form a solid threaded connection.
Main advantages:
- Easy to operate: no need for electricity or gas source, plug and play;
- Low cost: relatively inexpensive, suitable for projects with limited budget;
- Easy to carry: small size and light weight, suitable for outdoor or mobile operation;
- Strong adaptability: supports a variety of nut specifications (usually M3~M8).
Main limitations:
- High labor intensity: requires greater hand strength, easy to fatigue with long time use;
- Lower efficiency: not suitable for batch and large-volume continuous assembly;
- Repeatability accuracy is limited: human operation differences will lead to slight fluctuations in riveting results.
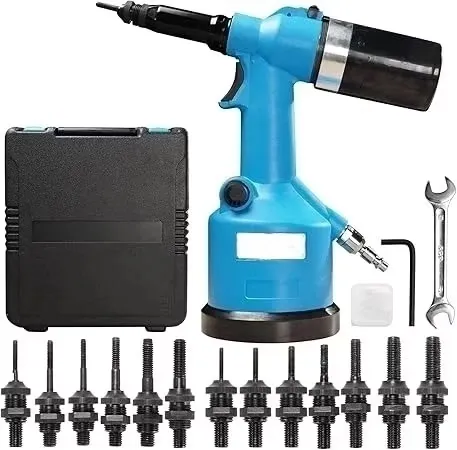
2. Electric & Pneumatic Rivet Nut Guns
Electric & Pneumatic Rivet Nut Guns are mid-to-high-end tools that improve assembly efficiency and consistency and are widely used in mid-volume to high-volume production scenarios. They use electric motors or compressed air to drive the pull rod to complete the riveting action, dramatically reducing the amount of force applied manually, improving the pace of work and riveting quality, and are suitable for industrial applications where efficiency, strength and precision are required.
a. Electric Rivet Nut Gun
Principle of operation:
- Driven by built-in motor to rotate and return the pull rod;
- Automatically complete the rivet nut pulling and riveting deformation process;
- One-button operation, some models support automatic reversal, adjustable stroke and torque control.
Advantages:
- Easy to operate: only push button control, no need to apply force manually;
- Good consistency: high accuracy of each riveting, suitable for standardized process;
- Higher portability: wireless battery model is suitable for mobile operation;
- Applicable to a wide range of nut sizes: such as M3~M10, some models support M12.
Limitations:
- Relatively high price;
- Limited motor life, need to pay attention to temperature control and maintenance;
- Plug-in models are somewhat dependent on the use environment.
Principle of operation:
- The internal cylinder piston is driven by compressed air;
- Quickly realizes the rivet pulling and releasing action;
- Suitable for continuous operation, usually equipped with automatic nut suction and quick rewind.
Advantages:
- Extremely efficient: single nut riveting time can be as low as 1~2 seconds;
- Strong continuous operation capability: no fatigue, suitable for long time operation;
- Strong pulling force: can cope with stainless steel nuts and thick plates riveting;
- Good riveting stability: suitable for batch production line operation.
Limitations:
- Dependent on air source: need to be equipped with air compressor, air hose, pressure regulator, etc.;
- Loud noise: obvious pneumatic impact sound exists during operation;
- Large equipment volume: weight and volume are usually higher than power tools.
3. Hydraulic / Electric-Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic and Electric-Hydraulic Rivet Nut Systems are a class of specialized riveting tools for heavy-duty, high-strength industrial applications. With hydraulic drive as the core, they have extremely high tensile force output and stable deformation control capability, and are widely used in high strength working conditions such as thick plates, structural steel parts, stainless steel nuts, etc.** They are particularly suitable for applications where reliability, precision and accuracy are of paramount importance. They are especially suitable for use in production lines or automated systems that require high reliability, precision and consistency.
a. Hydraulic Rivet Nut Gun
Principle of operation:
- High pressure hydraulic fluid is used to push a piston to create a pulling force;
- The end of the rivet nut is deformed and backwrapped by the strong force;
- Pressure is supplied by a hydraulic pump, partially operated by a foot pedal or push button control system.
Advantages:
- Large tension output: can easily rivet large-size rivet nuts such as M12~M16;
- Accurate and controllable deformation: suitable for thick metal parts and high strength connection requirements;
- Suitable for ultra-thick/ultra-hard substrates: such as high-strength steel, double-layer structural steel, and heavy workpieces;
- Supports customization and integration with specialized machines: easy to be embedded in automation systems.
Limitations:
- Complicated equipment: requires independent hydraulic pump and oil circuit system;
- Large size and weight: inconvenient to move;
- High initial cost, mainly used for high-volume production line investment.
b. Electro-Hydraulic System
This is an upgraded version of the hydraulic system that integrates electric motors with hydraulic cylinders for automatic control, precise adjustment and simplified operation.
Additional advantages:
- Integrated design: no need for external hydraulic pump, it works when connected to electricity;
- Intelligent control system: parameters such as pulling force, stroke and counter can be set;
- High efficiency + high strength + high consistency: suitable for high-end precision assembly lines.
Typical application scenarios:
- Aviation structural parts assembly;
- Railroad vehicle connection systems;
- Heavy machinery shell/chassis structure;
- Industrial equipment rack and module structure;
- Sheet metal automation production line integration system.
| Type of Application | Recommended Tools | Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Home DIY, small batch assembly | Manual Rivet Nut Guns | Low cost, flexible operation |
| Medium Scale Production Lines | Electric / Pneumatic Rivet Nut Guns | Efficiency, effortless operation |
| High Volume Production / Industrial Installation | Hydraulic / Electric Hydraulics | High tensile force, precise control |
| Mobile Construction Scenarios | Battery operated rivet nut guns | No electrical or pneumatic source of electricity for easy field operation |
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Fasten with Confidence – Choose Rivetfix

🔩 Efficient assembly starts with the choice of Rivetfix rivet nuts!
In high-volume manufacturing, a stable connection is the lifeblood of the production line. Rivetfix rivet nuts are designed for high-strength, fast-paced, automated production environments, and are widely used in automotive, home appliance, machinery, sheet metal and other industries.
✅ High load-bearing capacity, anti-vibration and anti-loosening
✅ Adaptable to a wide range of materials and structures
✅ Precision machining with consistent tolerance
✅ Support customized specifications and fast delivery
📦 Whether you’re a factory that needs millions of pieces per month or a brand manufacturer that demands consistency, Rivetfix can be your trusted fastener partner.
Contact us today for samples or a quote to make your production more efficient and secure!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.