How Thick of Steel Can You Use a Rivet Nut?

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China

When working with steel components, rivet nuts (also known as Rivnuts) offer a reliable way to create strong, threaded connections—especially in applications where only one side of the material is accessible. However, choosing the right rivet nut isn’t just about thread size or head style—the thickness of the steel plays a critical role in ensuring a secure and lasting installation. So, how thick of steel can you actually use a rivet nut on? In this article, we’ll break down the answer based on rivet nut types, grip ranges, and alternative solutions for thicker materials.
Table of Contents
How Does a Rivet Nut Work?
A rivet nut, also known as a rivnut or blind nut, is a fastener specially designed for thin-walled materials. It provides a strong internal thread in base materials where traditional tapping is not feasible, such as sheet metal or tubing. Rivet nuts are widely used in industries like automotive manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication, electrical enclosures, and machinery.
A rivet nut is a hollow metal sleeve with internal threads, typically made from aluminum, steel, or stainless steel. The outer body can be round, knurled, or hexagonal to meet different anti-rotation requirements and installation conditions. Its internal design allows it to function as a standard threaded insert once installed.

b. How Does It Create Threads in Thin-Walled Materials?
During installation, the rivet nut is inserted into a pre-drilled hole and pulled using a special rivet nut tool or manual setter. As the tool pulls the threaded shaft, the unthreaded portion of the rivet nut undergoes plastic deformation, bulging or flaring on the blind side of the workpiece, which securely clamps the material. This creates a strong mechanical lock. Once deformed, the rivet nut remains permanently fixed within the panel and offers a usable internal thread for a bolt.
This process is similar to how a blind rivet works, so rivet nuts are often referred to as “blind nuts”, meaning they can be installed from only one side of the material.
Blind-side Installation: Requires access to only one side of the workpiece—ideal for enclosed spaces or unreachable areas;
No Tapping Required: Can create strong internal threads in thin metal, plastic, or composites without cutting threads;
Fast and Efficient: With the appropriate tool, installation takes just seconds—perfect for high-volume production;
Versatile Compatibility: Works with a wide range of materials and thicknesses; available in various anti-rotation, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant designs;
Easy Maintenance: If damaged, the rivet nut can be removed and replaced without needing to replace the entire workpiece.
How Does Steel Thickness Affect Rivet Nut Installation?
Rivet nuts are internal-threaded fasteners designed specifically for thin metal sheets ranging from 0.5mm to 5mm. Their installation relies on plastic deformation inside a pre-drilled hole to form a mechanical lock on the back side of the material. When the steel thickness exceeds the intended grip range, the rivet nut may not install properly, compromising safety and structural integrity.
Below are four key aspects explaining how steel thickness affects the installation of rivet nuts:
1. Grip Range Limitations
The grip range is one of the most critical parameters of a rivet nut, indicating the thickness of the base material it can be properly installed into. Only within this range can the rivet nut deform correctly and form a secure lock.
a. Principle:
Rivet nuts install by expanding at the tail section on the back of the workpiece, forming an umbrella-like bulge that clamps the material securely. If the base material is too thin or too thick, installation fails:
Too thin: The rivet nut may over-deform, damaging the internal threads or causing instability.
Too thick: The rear end cannot fully deform, leading to weak installation or even detachment.
b. Example Comparison:
| Rivet Nut Spec | Recommended Grip Range | Application Material Thickness |
| M4 Flat Head Open-End | 0.5 – 2.5 mm | ≤ 2.5 mm ✔️ |
| M6 Flat Head Open-End | 0.5 – 3.0 mm | 4.0 mm ❌ (Too thick) |
| M8 Extended Type | 2.0 – 5.0 mm | 4.0 mm ✔️ |
| M10 Ultra-Long Closed-End | 4.0 – 7.0 mm | 6.5 mm ✔️ |
Using an M6 rivet nut on a 4.0mm steel plate exceeds its maximum grip range (3.0mm), preventing proper deformation and increasing the risk of loosening or detachment.
c. Consequences of Improper Use:
- Failure to complete installation.
- Rivet nut may spin or fall out during use.
- Deformed or damaged mounting holes, increasing rework costs.
- Major safety risks in load-bearing or vibrating applications.
d. Best Practices:
- Accurately measure material thickness before design and selection.
- Choose rivet nuts with matching grip ranges.
- Use extended or custom types for thicker plates.
- Conduct a sample test before mass production.

2. Performance Loss Due to Incomplete Deformation
In rivet nut installation, metal bulging at the rear is the key to structural strength. The tail section expands under axial force to tightly clamp the backside of the material, forming a reliable mechanical lock.
Insufficient deformation is one of the most common failure causes—often due to material thickness exceeding the grip range or incorrect installation settings.
a. Performance with Proper Deformation
Taking an M6 steel rivet nut installed in 1.5mm to 4.0mm thick steel:
- Tensile strength reaches 6.5–10.0 kN, handling most mechanical loads.
- Shear strength ranges from 5.0–8.0 kN.
- Rear bulge thickness is typically 1.5–2.0 mm, ensuring tight contact.
b. Effects of Over-Thickness
When the steel exceeds the grip range (usually >6mm):
- Rear deformation shrinks to 0.5–0.8 mm or less—insufficient to clamp the material.
- Mechanical lock weakens, reducing tensile and shear strength.
- Tensile strength drops 30%–50%, with risks of rotation or detachment.
- Severe safety concerns for structural reliability.
c. Real-World Example
- Using an M6 rivet nut in 6mm thick steel: tensile force was only 3.0–4.5 kN—well below standard.
- Repeat installation widened the hole, increasing looseness.
- Under vibration, the rivet nut detached, leading to equipment malfunction.
d. Conclusion
Using rivet nuts beyond the grip range leads to:
- Weak rear support and locking force.
- Connection instability and thread damage.
- Significant risk to structural safety.

3. Hole Clearance Affects Stability
Rivet nuts rely on tight clamping during deformation. Installation quality directly affects the joint’s stability and longevity. When the material is too thick, clearance between the nut and hole becomes a major threat.
a. Ideal Installation State
- Material within grip range ensures full deformation and secure clamping.
- Hole is tightly filled—no play between the rivet nut and material.
- Internal threads tightly engage the bolt.
b. Excessive Thickness Creates Gaps
- When the material exceeds the grip range, deformation is incomplete.
- A measurable gap >0.1mm often forms between the nut and hole.
- The rivet nut gains room to move, reducing lock effectiveness.
c. Negative Effects of Clearance
- Loosening under vibration due to micro-movement in the hole.
- Thread mismatch, causing thread stripping or torque failure.
- Unreliable joints that fail to meet structural safety standards.
d. Practical Observations
- Noisy joints or looseness in vibrating machines.
- Bolts repeatedly come loose; holes grow oversized.
- Torque wrenches fail to meet design specs—locking force insufficient.
e. Summary & Advice
Summary:
Clearance from excessive thickness results in:
- Reduced locking power.
- Loosening under cyclic load or vibration.
- Decreased structural reliability.
Recommendations:
- Measure material thickness precisely.
- Use extended rivet nuts or backing washers to reduce clearance.
- Design for safety margins in grip range selection.
How Thick of Steel Can You Use a Rivet Nut?
Depending on the design and deformation mechanism of the rivet nut, different types are suitable for different steel thicknesses. Selecting the right type not only improves the fastening strength but also ensures stable installation and long-term performance.
- Recommended Material Thickness: 0.5mm ~ 3.5mm
- This is the most common rivet nut type, featuring a smooth cylindrical body. After installation, the back side expands into a “bulge” to clamp the base material.
- Suitable for general applications such as automotive sheet metal, light-duty steel structures, and appliance housings.
- As it lacks an anti-rotation feature, the hole diameter must be precise to prevent spinning after installation.
- Moderate adaptability to material thickness and hardness—excessively thick material may hinder full deformation, while overly thin material may be crushed during installation.
- Recommended Material Thickness: 0.5mm ~ 3.5mm
- Similar in design to the open-end type but with a sealed tail, which prevents moisture, dust, or other contaminants from entering through the threaded hole.
- Commonly used in applications requiring sealing, such as marine equipment, outdoor electronics, and fluid containers.
- Its mechanical performance is generally similar to the open-end type; however, adequate rear space must be ensured for full expansion.
- For high sealing requirements, consider using O-rings or thread sealants for enhanced protection.
- Recommended Material Thickness: 1.0mm ~ 4.0mm
- Features longitudinal knurls or splines on the surface that create a strong frictional lock against the hole wall after installation, effectively preventing rotation.
- Especially suitable for high-strength or hardened steel sheets, such as structural steel, electrical enclosures, or stainless-steel panels.
- Recommended for high-vibration or high-load environments, such as construction machinery, railway systems, and elevator panels.
- The knurled design requires precise hole quality—excessive diameter tolerance can significantly reduce anti-rotation performance.
- Recommended Material Thickness: 1.5mm ~ 6.0mm
- Features a standard hexagonal exterior, designed for installation in hex-shaped holes to create a mechanical interlock and eliminate rotation.
- Ideal for thick steel plates and high-stress connections, such as automotive chassis, heavy equipment brackets, and structural steel joints.
- Provides excellent resistance to loosening, even under strong impact or vibration.
- Requires precise hexagonal punching equipment, and the base material must be strong enough to withstand localized pressure during installation.
Summary Recommendations:
- For steel thickness <1mm, use open-end or closed-end round body types.
- For steel thickness 1.5mm–3.5mm, choose knurled body for better anti-rotation performance.
- For thick steel or high locking strength applications (>3mm), hex body rivet nuts are strongly recommended.
- If hole size cannot be precisely controlled, prefer knurled or hex body types to enhance anti-rotation reliability.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
How Do You Choose the Right Rivet Nut for Steel Thickness?
Before using a rivet nut, correctly matching its grip range with the steel thickness is key to ensuring a secure fastening and long-term safety.
1. Select the Appropriate Model Based on Grip Range
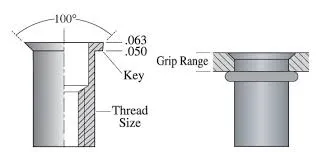
Each rivet nut model comes with a specified grip range, which is the effective material thickness range it can properly fasten. For example:
An M6 open-end round rivet nut may have a grip range of 0.5mm–3.5mm;
An M8 hex body rivet nut may have a grip range of 1.5mm–6.0mm.
You must ensure the base material thickness falls within this range, otherwise the joint may fail due to insufficient deformation or clamping force.
2. Accurately Measure the Steel Thickness
Use a caliper or electronic thickness gauge to measure the target steel plate, with precision to at least one decimal place (e.g., 1.8mm, 3.2mm), to select a rivet nut model that matches the thickness.
For stacked or layered materials, sum the thickness of all contacting layers;
If the steel has coatings or paint, exclude the thickness of surface layers when measuring.
3. Avoid Installing Rivet Nuts Outside Their Grip Range
If the rivet nut’s grip range is smaller than the material thickness:
Insufficient bulging deformation → Unable to provide effective clamping force;
Gaps inside the hole → May cause slipping after installation or loosening under vibration;
Uneven load distribution or reduced strength → Early rivet nut failure.
Conversely, if the steel thickness is much less than the minimum grip range, over-expansion may occur, potentially bursting the hole and damaging the base material.
Conclusion: Always match the steel thickness to the rivet nut’s grip range to guarantee joint quality and avoid safety risks. When uncertain, consult the supplier for recommended specifications or request sample installations before final purchase.
What Are the Alternatives to Rivet Nuts for Thick Steel?
When the steel thickness exceeds 6mm, standard rivet nuts often fail to provide reliable fastening. In such cases, the following alternative solutions can be considered to ensure connection strength and long-term stability:
1. Tapping Threads Directly
For steel plates with sufficient thickness, internal threads can be directly tapped into the hole without using additional fasteners:
Suitable when steel thickness ≥ minimum thread engagement depth (typically 1.5 to 2 times the thread pitch);
Provides excellent mechanical strength;
Requires no backside access, ideal for space-restricted applications.
2. Weld Nut
Weld nuts are attached to the steel plate via spot welding and offer the following advantages:
High load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy-duty applications;
Secure and stable even under vibration or impact;
Requires access to both sides of the workpiece and welding equipment.

Ideal for situations where tapped threads are damaged or need reinforcement:
Can restore damaged threads and enhance reusability;
Some metal inserts (such as helical inserts) feature self-locking properties;
Installation is more complex but offers high reliability.

4. Extra-Long Grip Range Rivet Nut
Some manufacturers offer specially designed rivet nuts for thick steel plates:
Extended body design supports grip ranges greater than 6mm;
Requires high-spec installation tools;
Suitable for applications that demand high strength and only allow one-sided installation.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Conclusion
Rivet Nuts Are Best Suited for Thin Steel Plates (<6mm)
Rivet nuts were originally designed for thin-walled materials, relying on the backside bulge formed during installation to provide clamping force and internal thread support. For thick steel plates, standard rivet nuts may fail due to insufficient grip or incomplete deformation.
Always Refer to Technical Specifications When Choosing Rivet Nuts for Thick Steel
Each type of rivet nut comes with a clearly defined grip range and applicable material thickness. Before use, carefully review the product’s technical data to ensure the selected model can accommodate the current steel thickness and meet the required mechanical performance, such as tensile and shear strength.
If Uncertain, Consult the Manufacturer for Recommendations or Alternative Fastening Solutions
For projects with demanding requirements or complex application conditions, it’s recommended to contact the rivet nut manufacturer or supplier for expert guidance tailored to the specific scenario. When the required thickness exceeds the standard grip range, consider alternatives such as weld nuts, tapping threads, or custom-designed rivet nuts to ensure reliable and long-lasting connections.
Buy Rivet Nuts from Rivetfix

As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, Rivetfix are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world. We offers a wide range of rivet nuts and clinch nuts designed to meet the unique demands of your projects. Rivetfix ensures you have the right solution for every application. Choose Rivetfix for versatile, cost-effective, and durable fastening solutions tailored to your specific needs. In addition, we can also provide customized rivet nuts service and clinch nuts according to your requirements.
Contact us now for more information and customization options on Rivet Nuts!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.








