Rivet Nut vs Pop Rivet: Which One Is Best for You?

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China
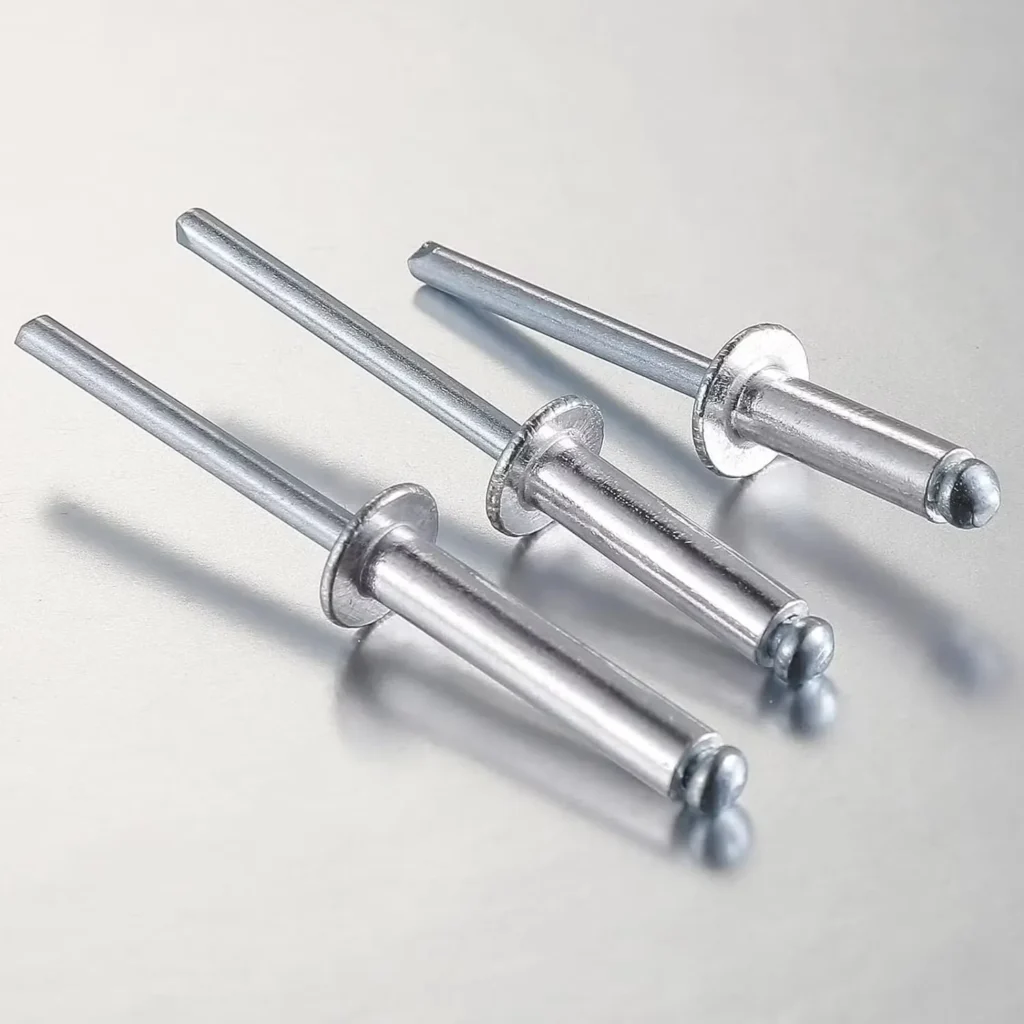

Rivet nut vs pop rivet, which fastening solution is right for your project? Choosing the right fastening solution—rivet nut or pop rivet—depends on the specific needs of your project. Understanding their distinct differences can help you make an informed decision.
Table of Contents
Rivet nuts are internally threaded fasteners used to create strong connections in materials like metal, plastic, and composites. They are installed by expanding or deforming the nut inside a material to form a secure threaded hole.
Originally developed in the 1950s, rivet nuts were created to address the need for strong threaded connections in thin or brittle materials that couldn’t hold traditional threads. Over time, the demand for lightweight, durable fasteners in industries like aerospace and automotive led to improvements in rivet nut designs and materials.
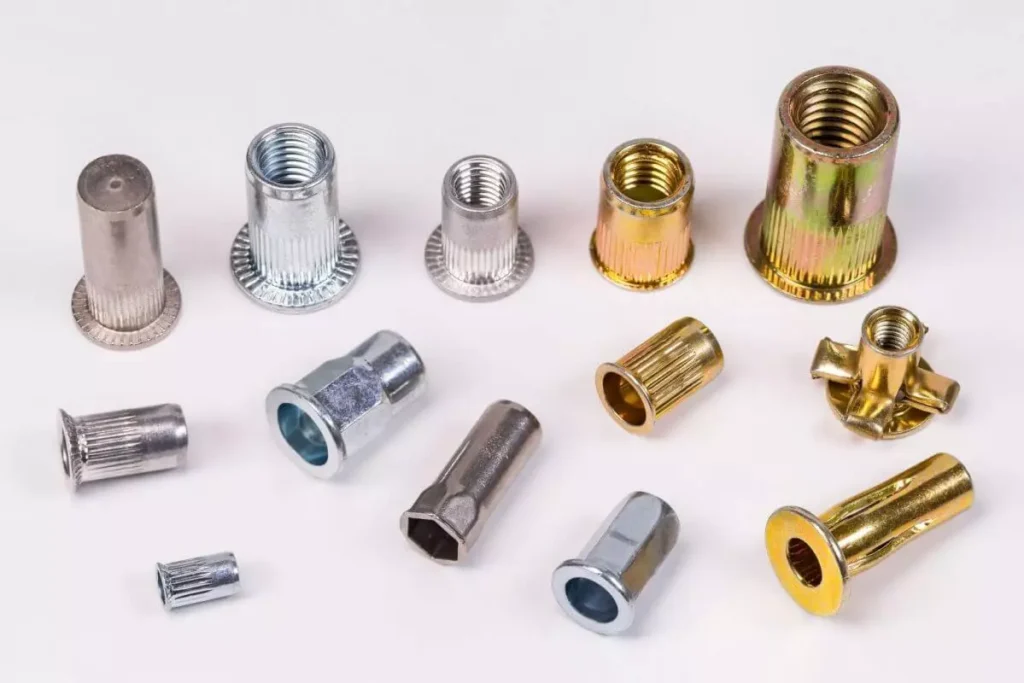

The structural composition of a rivet nut typically consists of a body, internal threads, and a flange. The body is usually made of materials like steel, aluminum, or stainless steel, offering different levels of strength and corrosion resistance.
The internal threads allow for the attachment of bolts, screws, or other fasteners, while the flange provides a larger surface area to distribute load and prevent damage to the material. The rivet nut expands during installation, creating a secure, strong grip in the material, ensuring the connection remains intact even under stress or vibration.
6 Common Types of Rivet Nuts
Choosing the right type of rivet nut depends on your application’s material, strength requirements, environmental conditions, and the type of connection needed. Here we introduce the common 6 types of rivet nuts, so that you have a preliminary understanding of rivet nuts.

Material: Made from lightweight aluminum, these rivet nuts offer corrosion resistance and are easy to install.
Applications: Ideal for applications requiring moderate strength, such as in the automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries.
Advantages: Aluminum rivet nuts are cost-effective, offer easy installation with hand tools, and are suitable for light-duty applications.
Limitations: They may not be suitable for high-load or high-temperature applications.

Material: Made from carbon steel, these rivet nuts offer high tensile strength and durability.
Applications: Best for heavy-duty applications, such as machinery or construction, where a strong and robust connection is needed.
Advantages: High strength, resistance to wear, and affordable compared to other materials.
Limitations: They may require coatings (such as zinc or chrome) to protect against corrosion in outdoor or moist environments.
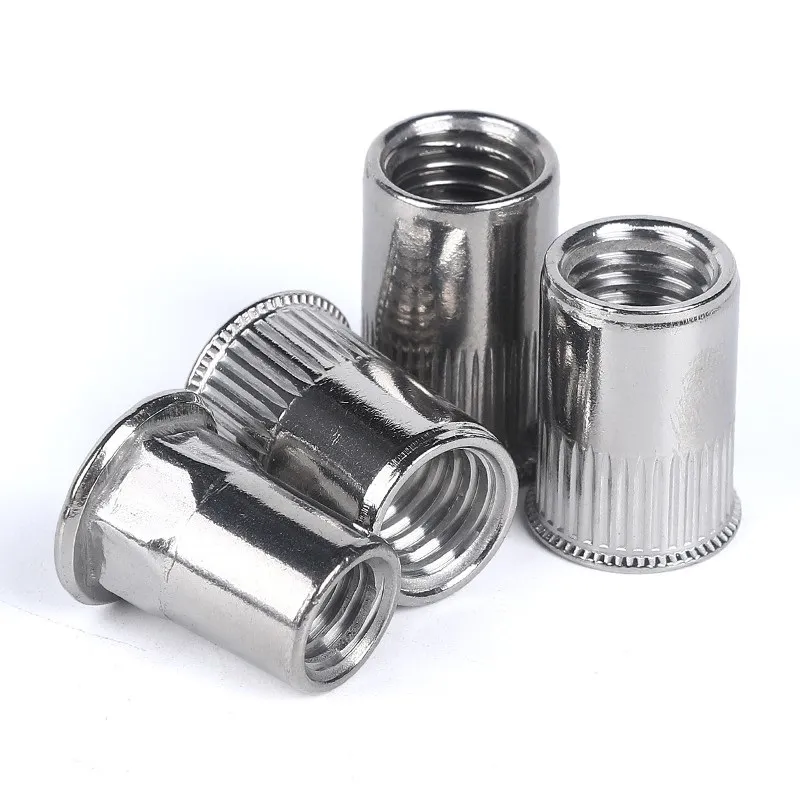

Material: Made from stainless steel, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance.
Applications: Ideal for marine, food processing, outdoor, and aerospace applications, where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures is common.
Advantages: High durability, corrosion resistance, and long service life in harsh environments.
Limitations: Stainless steel rivet nuts tend to be more expensive than aluminum or carbon steel options.

Shape: These rivet nuts have a hexagonal body design, offering better grip and preventing rotation during installation.
Applications: Ideal for automotive or construction applications, where a secure connection is needed in areas subject to high torque or vibration.
Advantages: Increased torque resistance, prevents rotation during tightening, and provides a more secure fit in applications with thicker materials.
Limitations: Hex body rivet nuts may require specialized installation tools due to their shape.
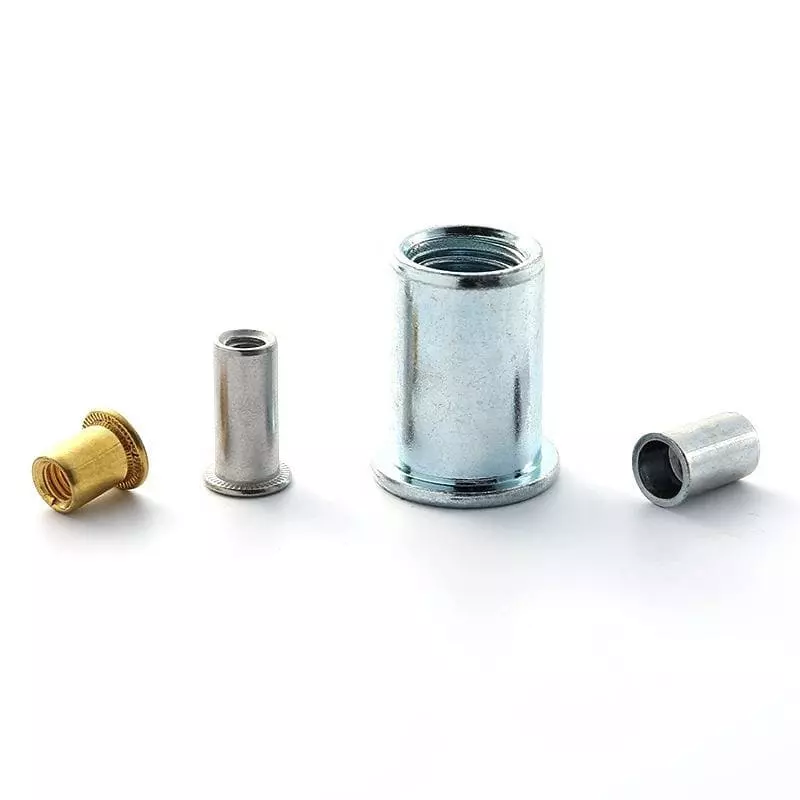

Shape: These rivet nuts have a smooth, cylindrical body without any external ridges or knurling, making them more aesthetically pleasing in visible areas.
Applications: Commonly used in electronic enclosures, consumer products, and other applications where appearance is important.
Advantages: Provides an even load distribution, often used in applications requiring higher aesthetic value.
Limitations: Less grip strength compared to knurled or hex body rivet nuts, making them unsuitable for high-vibration applications.
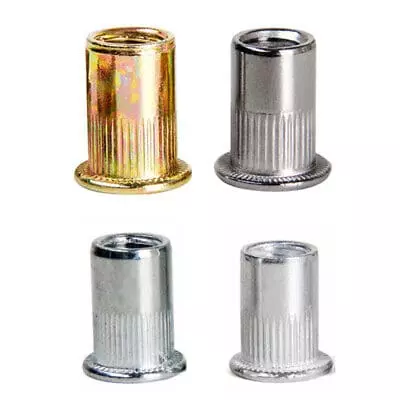

Shape: These rivet nuts feature a textured surface (knurling) on the body, which provides enhanced grip and prevents slippage during installation.
Applications: Used in vibration-prone or dynamic environments, such as automotive, railway, or industrial machinery.
Advantages: Improved pull-out resistance, better torque retention, and enhanced grip in materials that may experience vibrations or high stresses.
Limitations: May not be necessary for low-stress applications, as the knurling can increase the cost.
Conclusion
Aluminum rivet nuts offer lightweight and cost-effective solutions, while carbon steel rivet nuts provide durability for heavy-duty applications. Stainless steel rivet nuts excel in harsh environments, while hex body and knurled body rivet nuts offer better grip and torque resistance for high-stress and vibration-sensitive environments.
Pros and Cons of Rivet Nuts
Rivet nuts are an excellent fastening solution for many applications, especially where a strong, reusable threaded connection is needed in thin or soft materials. However, they do have limitations, particularly in terms of material choice, installation costs, and load-bearing capacity. Understanding the specific requirements of your project will help determine if rivet nuts are the right choice.
Pros of Rivet Nuts
- Strong and Reliable Connections: Rivet nuts provide a secure, durable threaded connection that can withstand high loads, vibrations, and stress.
- Versatility: They can be used in a wide range of materials, including metal, plastic, composite, and thin-walled materials that cannot hold traditional threads.
- Easy Installation: Rivet nuts are typically installed using simple tools (manual, pneumatic, or hydraulic), making them quick and easy to install, even in tight spaces.
- Wide Grip Range: Rivet nuts come in a variety of grip ranges, allowing them to be used in materials of different thicknesses, providing flexibility for different applications.
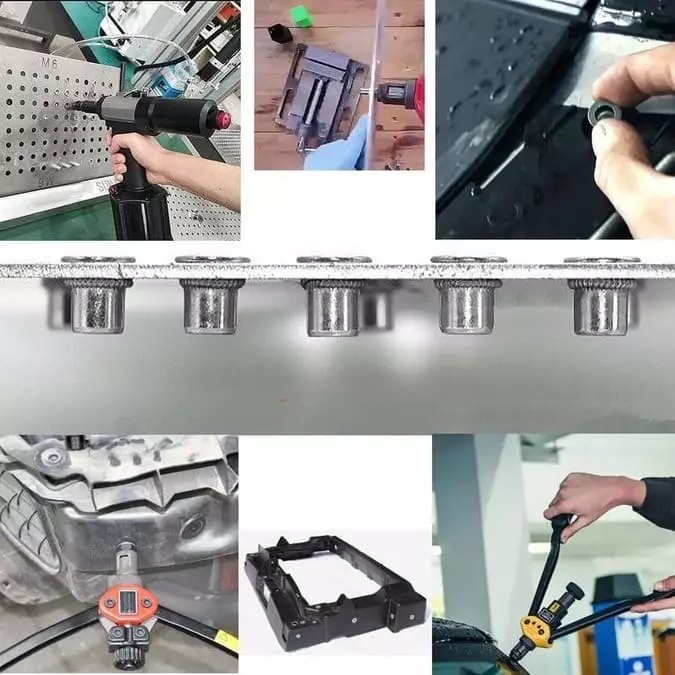

Cons of Rivet Nuts
- Material and Design Limitations: Not all rivet nuts are suitable for extreme temperatures or highly corrosive environments, so the right material must be selected based on the application.
- Pull-Out Resistance: If installed improperly or in the wrong material, rivet nuts can have poor pull-out resistance or fail under stress. This is especially true if the material is too soft or thin.
- Higher Cost Compared to Other Fasteners: For some applications, rivet nuts may be more expensive compared to other types of fasteners, especially if only a few are needed.
- Limited Load-Bearing Capacity in Some Designs: While rivet nuts offer good strength, some designs (like aluminum rivet nuts) may have a lower load-bearing capacity compared to stronger materials like carbon steel or stainless steel.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
What Are Pop Rivets?
Pop rivets are a type of blind fastener used to join two materials by deforming the rivet body. They consist of rivet body, rivet mandrel, and rivet head. The mandrel is pulled, expanding the rivet body and securing the materials together.

Pop rivets were first developed in the 1930s to simplify fastening in inaccessible or tight spaces. They became widely used in industries like automotive and aerospace, where quick, permanent fastening was required.
4 Common Types of Pop Rivets
Each type of pop rivet is designed to meet specific application needs. The choice depends on factors like material thickness, environmental conditions, and load requirements.

- Description: Open-type pop rivets are the standard and most commonly used rivets. They are composed of a hollow cylindrical body with a mandrel inside. When the mandrel is pulled, it deforms the rivet body, which then expands to securely hold the materials together.
- Applications: These rivets are widely used in industries like automotive, construction, and sheet metal fabrication. They are ideal for applications that do not require a sealed or watertight connection.
- Advantages: Quick to install, cost-effective, and ideal for low to medium-strength applications.
- Limitations: Not suitable for applications requiring waterproof or airtight seals.

- Description: Sealed-type pop rivets are designed to create a watertight or airtight seal after installation. The sealed end prevents moisture, dirt, or other contaminants from entering the rivet hole. They are similar to the open-type, but the rivet body includes a special sealant at the end. When installed, the seal creates a tight barrier, offering better protection for the materials.
- Applications: Commonly used in electrical enclosures, marine environments, and outdoor equipment where moisture resistance is critical. They are also used in aerospace and automotive industries where seals are required.
- Advantages: Provides a watertight or airtight seal, making them ideal for harsh or moisture-prone environments.
- Limitations: More expensive than open-type rivets due to the additional sealing component.
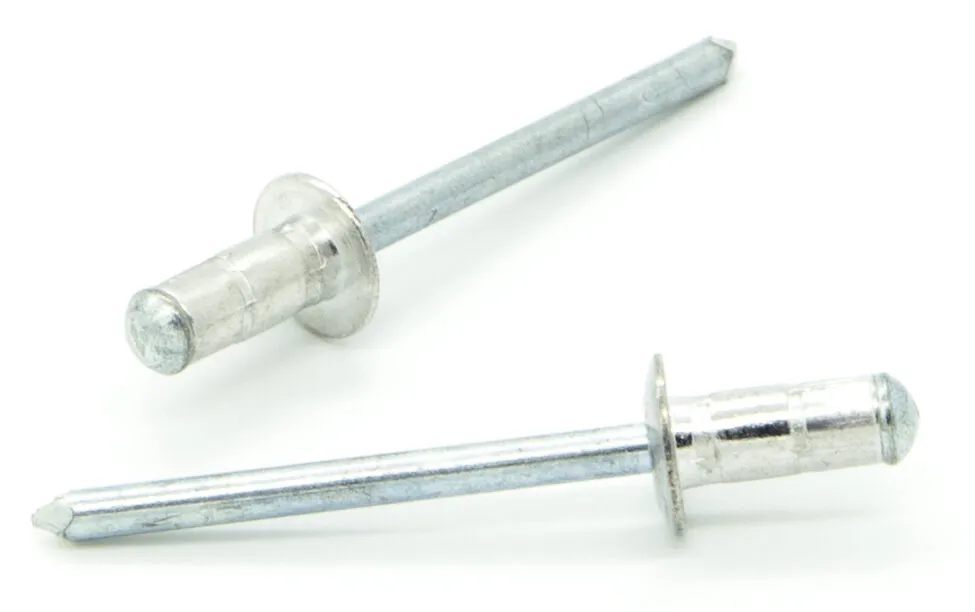
- Description: Multi-grip pop rivets can accommodate a wider range of material thicknesses. This flexibility allows them to be used for applications where the thickness of the materials being joined may vary. The rivet body is be able to expand over a wider grip range. So it can provide a secure fit even when the material thickness differs.
- Applications: Used in industries where materials of varying thicknesses are joined, such as automotive manufacturing, electronics enclosures, and sheet metal fabrication.
- Advantages: Versatile for different material thicknesses, saves time and cost by reducing the need for multiple rivet sizes.
- Limitations: May not offer the same level of strength as standard rivets if used for extreme load-bearing applications.
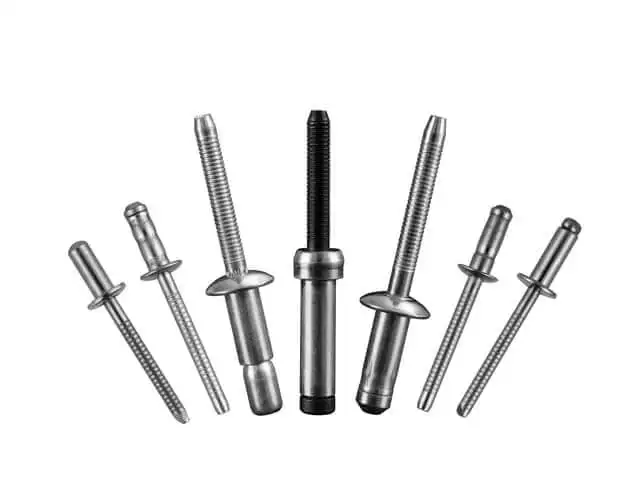

- Description: Structural pop rivets are specifically designed for high-strength applications that require a strong, durable connection. These rivets are typically made from steel, stainless steel, or aluminum and feature a more robust design. The mandrel and rivet body are engineered to handle higher tensile and shear loads.
- Applications: Commonly used in industries that demand high-strength connections. Such as aerospace, automotive, bridge construction, and heavy machinery.
- Advantages: Provides superior strength and load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for demanding applications that require long-lasting, secure connections.
- Limitations: More expensive than standard rivets and may require special tools for installation due to their strength.
Pros and Cons of Pop Rivets
Like any fastener, pop rivets come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding both can help determine whether they are the right choice for a particular project.
Pros of Pop Rivets
Cost-Effective:
Pop rivets are generally inexpensive, making them a budget-friendly fastening solution for many industries and applications.
No Special Tools Required:
Installation typically requires a pop rivet tool, which is simple and easy to use. Special training or equipment is not often necessary.
Variety of Materials:
Pop rivets are available in different materials, including aluminum, steel, and stainless steel, making them versatile for various environments and applications.
Suitable for Thin Materials:
They are ideal for fastening thin or soft materials, such as sheet metal, plastics, and composites, where traditional threading methods might not be effective.

Cons of Pop Rivets
Permanent Connection:
Once installed, pop rivets form a permanent bond, which cannot be undone without damaging the material. This can be a disadvantage when disassembly or adjustments are required. Since pop rivets are permanent, removing them can be challenging, especially if the rivet or surrounding material needs to be preserved.
Limited Strength in High-Stress Applications:
While structural rivets provide good strength, standard pop rivets may not offer enough tensile or shear strength for high-stress or load-bearing applications.
Limited Grip Range:
Pop rivets typically have a limited grip range compared to other fasteners, which can make them unsuitable for materials of significantly varying thickness. Improper installation, such as over-tightening or using the wrong size rivet, can cause material distortion or damage, particularly in softer materials.
Not Ideal for Vibration-Prone Environments:
Pop rivets may not perform well under continuous vibration or cyclical loading. They may loosen over time if not chosen or installed correctly.
Tooling and Maintenance Costs:
While the rivets themselves are inexpensive, pop rivet tools and their maintenance can add to the overall cost, especially for high-volume applications.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Rivet Nut vs Pop Rivet: What's the Difference?
| Feature | Rivet Nut | Pop Rivet |
| Function | Provides a threaded insert for fastening | Used for creating permanent, non-threaded fastenings |
| Material | Typically made from steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or brass | Typically made from aluminum, steel, or stainless steel |
| Thread Type | Can provide internal threads for bolts and screws | No internal threads; used for permanent fastening |
| Installation | Installed with a specialized rivet nut tool that deforms the nut inside the material | Installed using a standard rivet gun to pull and set the rivet |
| Reusability | Can be removed and replaced if necessary | Permanent once installed, cannot be removed easily |
| Applications | Used in structural applications, electronics, automotive, and metalworking | Used in sheet metal, furniture, and non-load-bearing applications |
| Strength | High load-bearing capacity, especially in shear and tensile strength | Moderate strength, primarily used for light to medium-duty applications |
Rivet nut vs pop rivet is a concern for many people. This table highlights the key differences between rivet nut and pop rivet in terms of function, material, application and other characteristics. It is helpful in how you make your choice.
Rivet Nut vs Pop Rivet: How to Choose the Right Riveting Solutions
- Choose rivet nuts when you need a reusable threaded connection, higher strength, or when working with materials that require bolts, screws, or frequent disassembly.
- Choose pop rivets when you’re working with thin materials, need a quick, low-cost solution, and only need access from one side.
Consider factors like material thickness, required strength, accessibility, and whether you need a permanent or reusable connection when making your decision.
Conclusion
Rivet nut vs pop rivet, which one is better for your project? When deciding between rivet nuts and pop rivets, first consider the material thickness to ensure the fastening solution works effectively.
The required strength of the connection is crucial; rivet nuts offer higher load-bearing capacity. Accessibility is another key factor, as pop rivets are ideal when only one side of the material is accessible.
Also, determine whether a permanent or reusable connection is needed; rivet nuts are reusable, while pop rivets provide a permanent bond. Each factor influences which option will be the most suitable for your project’s needs.

As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, Rivetfix are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world. We can select the most suitable fasteners according to your project needs, and provide product customization services.
Contact us for project advice and the latest rivet nut quote!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.




