Plus Nut vs Rivet Nut: Key Differences and Best Applications

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China

When it comes to fastening solutions, understanding the key differences between a plus nut vs rivet nut is essential for selecting the right component for your project. Both offer unique benefits, but their applications vary depending on material type, load capacity, and installation requirements. In this blog, we’ll explore the key differences between plus nut vs rivet nut , helping you determine which is best suited for your specific needs.
Table of Contents

1. Definition and Features
A Plus Nut (also called slotted rivet nut, multi-grip rivet nut, cross nut) is a special type of rivet nut designed to enhance clamping force and pull-out resistance. Its name comes from its unique shape and the “lantern-like” expanded structure that forms after installation. Compared to regular rivet nuts, the slotted rivet nut has a larger expansion range, providing a firmer connection on thin plates, soft materials, or irregular surfaces.
2. Material Options
Plus Nuts are typically made from several types of metal materials to suit various usage environments and load requirements:
- Carbon Steel: High strength, suitable for heavy-duty applications, but requires additional corrosion protection (such as galvanizing).
- Stainless Steel: Strong corrosion resistance, suitable for wet or corrosive environments, such as marine and chemical industries.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, ideal for weight-sensitive applications, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
3. Design Features

- Expansion Design: During installation, the tail of the Plus Nut expands outward, forming multiple curved support points. This design allows it to tightly fit the installation material and provides higher pull-out strength and resistance to rotation.
- Internal Threads: After installation, the multi-grip nut creates a strong threaded connection inside, allowing bolts to securely fasten other components.
- Suitable for Thin and Soft Materials: Due to its expansion capability, the Plus Nut is particularly suited for installation in thinner metal sheets, composite materials, plastics, or other soft substrates without damaging the material itself.
4. Common Applications and Industries
Due to its high strength and excellent fastening performance, Plus Nuts are widely used in the following fields:
- Automotive Industry: Used for fastening thin sheet structures such as vehicle bodies, interiors, and dashboards, providing reliable threaded connections.
- Industrial Equipment: Used on metal frames, thin-walled pipes, and other components to ensure high-strength connections.
- Aerospace: Used for fastening lightweight structural components, ensuring stability in vibration-prone environments.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Used for assembling wooden or composite material furniture, providing durable threaded fixing points.
- Rail Transportation: Used in applications such as train carriages and seating structures, ensuring long-term durability and safety.

1. Definition and Features
A Rivet Nut is a threaded fastener that can be installed on thin plates or hollow structures, providing a strong threaded connection when regular nuts cannot be used. It is fixed to the substrate through a riveting process, allowing it to offer a stable threaded connection even when access is available only from one side. This feature makes rivet nuts widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing.
2. Material Options
Rivet Nuts are mainly made from three types of metal materials to meet different usage requirements:
- Aluminum Rivet Nut: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for weight-sensitive applications, such as aerospace and lightweight equipment.
- Carbon Steel Rivet Nut: High strength, suitable for industrial and automotive applications requiring higher load capacity, but needs additional corrosion protection like galvanizing.
- Stainless Steel Rivet Nut: Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for wet or corrosive environments, such as marine engineering and chemical equipment.
3. Design Features
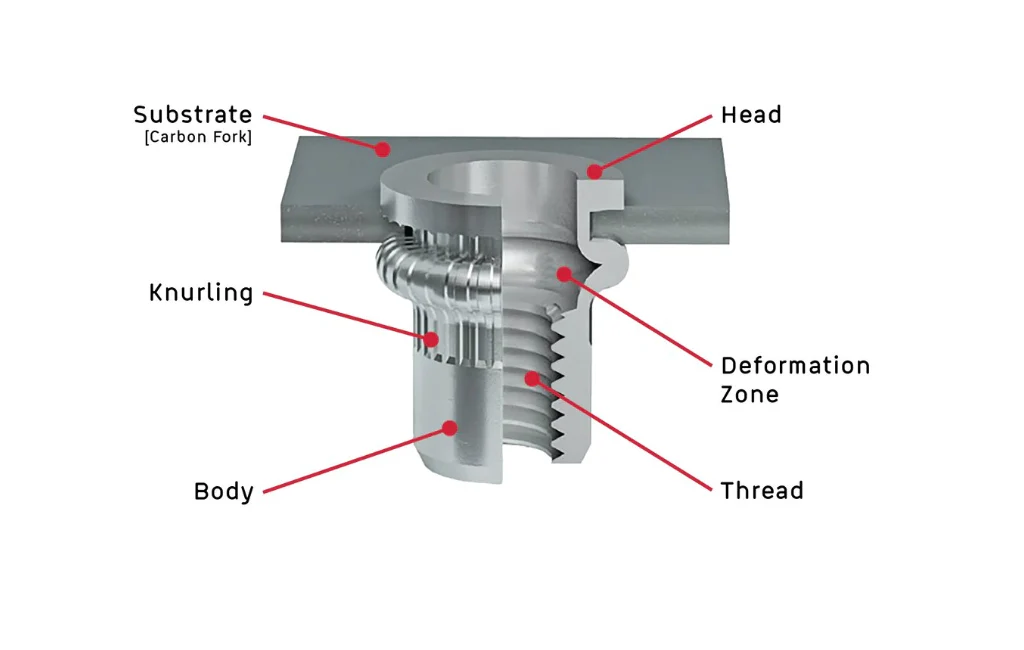
- Open-End vs. Closed-End
- Open-End: Suitable for most applications, where bolts can pass through the entire rivet nut after installation.
- Closed-End (Blind Rivet Nut): The bottom is sealed, suitable for applications needing waterproofing, dustproofing, or preventing bolts from protruding too far, such as in electronic devices or precision machinery.
- Pull-Style vs. Knurled-Style
- Pull-Style: Secures through deformation during riveting, suitable for most thin-wall materials.
- Knurled-Style: The outer surface has a knurled texture, providing additional anti-rotation resistance, ideal for softer or more deformable materials.
4. Common Applications and Industries
Due to its high strength, ease of installation, and ability to adapt to various materials, Rivet Nuts are widely used in the following industries:
- Automotive Industry: Used for thin sheet connections in car bodies, seats, bumpers, dashboards, providing stable threaded fastening points.
- Aerospace: Suitable for lightweight structures such as aircraft skins and internal components, ensuring reliable fastening while reducing weight.
- Machinery Manufacturing: Used in various machinery equipment, such as metal frames, enclosures, and pipe connections.
- Rail Transportation: Used in train carriages, seat fixation, and control panels, enhancing structural strength and vibration resistance.
- Electronics: Provides strong threaded connections in electrical cabinets, server enclosures, and other applications, with the option of using closed-end rivet nuts to prevent foreign matter from entering.
Plus Nut vs Rivet Nut: Key Differences
To better understand the differences between Slotted Rivet Nut and Rivet Nut, we will compare them in terms of installation mechanism, material compatibility, load strength, vibration resistance, installation requirements, and typical applications.
1. Installation Mechanism
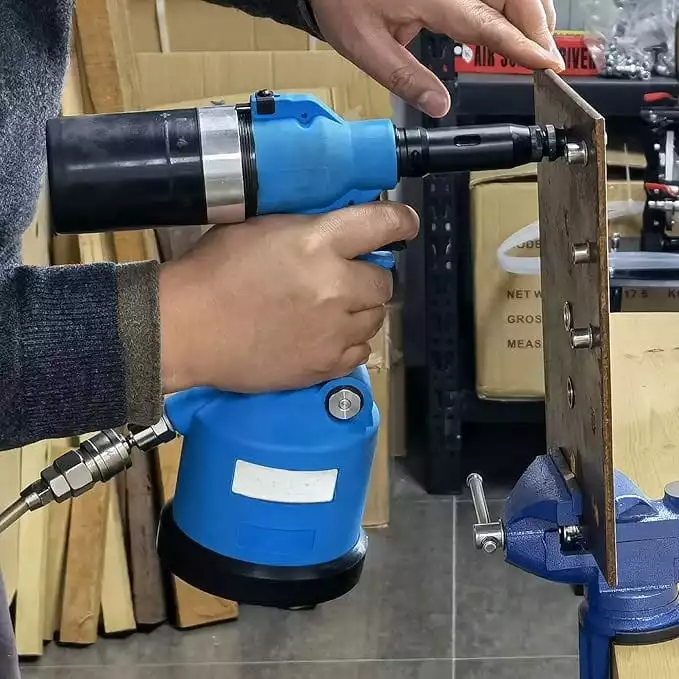

- Plus Nut:
- During installation, when the rivet nut is tightened, the four expansion claws at the bottom spread outward, forming a “lantern” shape. This allows it to provide a stronger grip on softer or thinner materials.
- This expansion mechanism ensures that even with thinner materials, the nut won’t easily pull out, providing higher pull-out resistance and a larger contact area.
- Rivet Nut:
- Rivet nuts are installed using a riveting tool, which applies tension to compress the bottom of the nut against the back of the material, forming a stable threaded connection. So you should choose the best rivet nut tool to install rivet nuts.
- Since it lacks the expansion design of the Plus Nut, it mainly relies on the compressive force to hold the nut in place, rather than friction on the material’s surface.
2. Material Compatibility
- Plus Nut:
- Suitable for softer materials such as plastics, fiberglass, drywall, wood, etc.
- Also works well on thin metal sheets, as its expansion structure provides better fastening without pulling out due to the material’s thinness.
- Rivet Nut:
- More suitable for harder materials such as steel sheets, aluminum alloy plates, composite materials, etc.
- In hard metals, Rivet Nuts provide a stable threaded connection, but may loosen or damage softer materials due to uneven force distribution.
3. Load Strength & Pull-out Resistance
- Plus Nut:
- Due to its four-claw expansion design, cross nut have higher pull-out resistance on softer materials, effectively distributing the load and reducing localized stress.
- On thin sheet materials, Plus Nut offers more reliable fastening than Rivet Nut, and is less likely to be pulled out.
- Rivet Nut:
- On harder materials, Rivet Nuts typically offer higher load strength because they can tightly attach to the back of the material, forming a stable threaded connection.
- For thicker metal sheets or strong materials, Rivet Nuts generally provide superior strength.
4. Vibration Resistance
- Plus Nut:
- The expanded claws increase the contact area, making it less likely to loosen in high-vibration environments.
- Suitable for long-term vibration-resistant applications such as automotive interior structures, ship components, etc.
- Rivet Nut:
- Rivet Nuts rely on the compressive force between the material to stay secure. In high-vibration environments, they may loosen due to material expansion and contraction.
- High-vibration applications usually require additional anti-loosening measures, such as using thread-locking adhesives or locking nuts.
5. Installation Requirements

- Plus Nut:
- Requires pre-drilling a hole in the material and special rivet nut tools for installation.
- Due to its expansion feature, installation requires greater force than Rivet Nuts, making manual tools less suitable for large-scale installations.
- Rivet Nut:
- Also requires pre-drilling a hole, but installation is relatively simple and can be quickly done using pneumatic, electric, or manual rivet nut guns. The correct rivet nut hole size is important for installing rivet nuts.
- Ideal for large-scale production lines or industrial applications, enhancing assembly efficiency.
6. Typical Applications
- Plus Nut:
- Automotive Industry: Used to fasten thin materials, such as plastic interior parts and dashboard fixtures.
- Aerospace: Suitable for composite material structures like aircraft internal panels.
- Shipbuilding: Provides reliable fixation on fiberglass materials without loosening due to vibration.
- Lightweight Material Assembly: Used in furniture, electronics enclosures, and instrument panels.
- Rivet Nut:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Widely used for connecting metal body components, such as doors and hoods.
- Industrial Equipment: Used in machinery manufacturing and steel structure fastening, such as in industrial frames and cabinets.
- Construction Installation: For fixing metal or composite materials for walls, railings, etc.
Plus Nut vs Rivet Nut: Comparison Table
| Comparison Item | Plus Nut | Rivet Nut |
| Installation Mechanism | Four-claw expansion fixation | Compresses material back |
| Material Compatibility | Softer materials, thin plates, plastics, composites | Metals, hard plastics, composites |
| Pull-out Resistance | Strong, ideal for thin sheets and soft materials | Stronger on hard materials |
| Vibration Resistance | Suitable for high-vibration environments | May need additional anti-loosening measures |
| Installation Requirements | Requires greater force, slower installation | Faster installation, suitable for mass production |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, shipbuilding, lightweight material assembly | Automotive, industrial equipment, construction structures |
Plus Nut vs Rivet Nut: How to Choose?
- Choose Plus Nut:
- If you need to install nuts on softer or thin materials (like plastics, fiberglass, wood) and want it to be more vibration-resistant and pull-out resistant, then slotted rivet nut is the better choice.
- Choose Rivet Nut:
- If you need to create threaded connections on metal or hard materials, or you require efficient mass installation, then Rivet Nut is the ideal choice.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Best Applications for Plus Nuts

Plus Nuts, with their unique four-claw expansion structure, are particularly suitable for thin materials, softer materials, or weight-sensitive applications. They provide strong pull-out resistance on fragile or thin substrates and are capable of withstanding high-vibration environments. Therefore, cross nuts are widely used in several industries, particularly in automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, and electronics.
1. Suitable for Thin Materials
- Due to the four-claw expansion feature, Plus Nuts can provide stable threaded connections on thin metal sheets, plastic sheets, composite materials, and other thin materials.
- Traditional Rivet Nut Disadvantages: Regular Rivet Nuts, with their direct compression at the bottom, may not offer enough grip on extremely thin materials, and could cause deformation or breakage of the material.
- Plus Nut Advantage: cross nuts distribute the force during expansion, preventing material deformation while enhancing the fastening effect. They are ideal for ≤1mm thin-wall materials.
Typical Applications:
- Automotive Interiors: Used for fastening door panels, dashboards, plastic trim, etc.
- Electronics Enclosures: Suitable for fastening metal or plastic housings, such as laptops and telecom equipment.
- Instrument Panel Fixing: Fastening thin outer shells, such as in medical devices or laboratory instruments.
2. Suitable for Softer Materials
- Traditional Rivet Nuts are suited for harder substrates like metals, but they tend to pull out or damage softer materials such as plastics, fiberglass, and wood.
- Plus Nut’s expanding claws provide a larger contact area, making it suitable for softer materials, effectively distributing the pull-out force and reducing the risk of material damage.
Typical Applications:
- Fiberglass (FRP) Structures: For fastening components like yacht and RV interiors.
- Wood Products: Used for connecting wood panels, such as in furniture or cabinetry.
- Plastic Assemblies: Ideal for removable connections in plastic housings, like electrical enclosures or LED lighting fixtures.
3. Suitable for Lightweight Designs
- Reducing weight is crucial in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
- Plus Nuts are typically made of aluminum alloys or stainless steel, which are lightweight and provide strong fastening capabilities, making them perfect for lightweight applications.
Typical Applications:
- Aerospace Industry: Used for fastening internal components, such as lightweight alloy panels.
- New Energy Vehicles (EVs): Used for battery pack fixation, electrical component brackets, and more.
- Drones: Used for assembling lightweight materials, such as connecting carbon fiber frames.
4. Suitable for Quick Assembly
- Plus Nuts only require operation from one side, making them ideal for installations where access to the back is not possible, thus improving assembly efficiency.
- They are well-suited for quick installation and mass production in industrial applications, such as on assembly lines.
Typical Applications:
- Automotive Assembly Lines: Fastening dashboards, door panels, windshield brackets, etc.
- Cabinet and Rack Installations: Fast assembly for server cabinets, telecom equipment.
- Rail Transit Equipment: Interior installations for high-speed trains and subways, reducing manual labor time.
5. Suitable for Limited Installation Space
- In narrow spaces, traditional nuts or welded nuts may be difficult to install, but cross nuts only require installation from one side, making them perfect for tight or enclosed spaces.
Typical Applications:
- Aircraft Seat Installations: Providing secure fixation in confined spaces.
- Automotive Engine Compartment Components: Suitable for engine mounts, air conditioning systems, and wiring harness fastenings.
- Appliance Internal Fixing: For fastening internal components in appliances like washing machines, air conditioners, and televisions.
Best Applications for Rivet Nuts
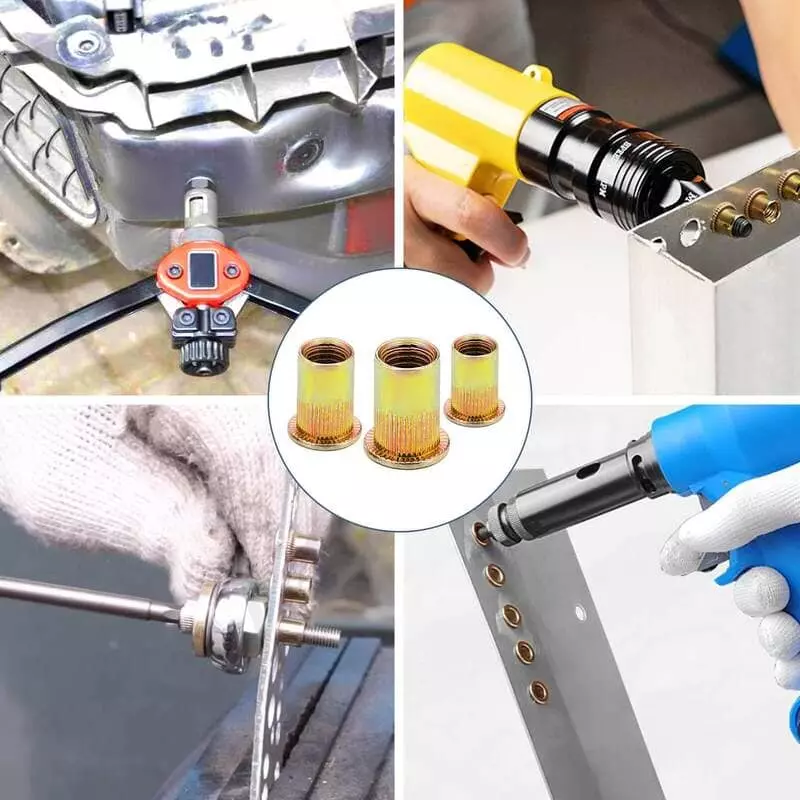

Rivet Nuts, with their high strength, vibration resistance, and suitability for high-load structures, are widely used in industries requiring reliable threaded connections. Compared to Plus Nuts, Rivet Nuts are ideal for harder materials (such as metals and composite materials) and provide stable fastening performance in high-strength and high-vibration environments. As a result, they are especially important in industries like automotive manufacturing, construction engineering, heavy machinery, and aerospace.
1. Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications
- Rivet Nuts made from high-strength materials such as carbon steel or stainless steel can withstand higher pull-out and torque forces, making them ideal for high-load structures.
- They provide reliable threaded connections in materials like thin metal sheets and composite materials, which cannot be directly tapped, ensuring long-term load-bearing capability.
Typical Applications:
- Automotive Chassis and Body Structures: Used for fastening suspension systems, engine mounts, door hinges, and other high-strength components.
- Industrial Equipment and Heavy Machinery: Used for structural fastening in construction machinery, agricultural equipment, and mining equipment.
- Building and Bridge Engineering: Fastening in load-bearing structures such as metal beams and steel frame constructions.
2. Suitable for Vibration-Resistant Environments
- Rivet Nuts, using the rivet mechanism, offer stronger anti-loosening capabilities, providing more stability in vibration and shock environments than screws.
- In environments that require resistance to vibrations and loosening, such as in vehicles and engine components, Rivet Nuts are the ideal fasteners.
Typical Applications:
- Rail Transportation (High-Speed Rail, Subways, Trains): Used for connecting seats, ceilings, body shells, and other components, ensuring long-term stability without loosening.
- Aerospace: Used for fastening aircraft fuselages, engine covers, and internal structural components, ensuring high-strength connections.
- Wind Power Equipment: Used for fastening high-vibration components like blades, towers, and nacelles.
3. Suitable for Metal or Composite Materials
- As Rivet Nuts are made from metal, they are ideal for providing strong threaded connections on steel plates, aluminum alloys, carbon fiber, fiberglass, and other hard materials.
- In some applications, Rivet Nuts can replace traditional welded nuts, reducing welding costs and providing an alternative for environments that require corrosion resistance.
Typical Applications:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used for assembling metal sheet structures, such as car doors, hoods, and fenders.
- Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering: Suitable for fastening aluminum or stainless steel structures like hulls and decks.
- Composite Material Manufacturing: Used for fastening threaded connections in carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP), fiberglass reinforced plastic (GFRP), and other composite materials, such as in race car components or spacecraft structures.
4. Suitable for Blind Installations
- Rivet Nuts require installation from one side only, making them ideal for applications where access to the back is not possible, such as in enclosed pipes, aircraft cabins, or equipment housings.
- Difference from Plus Nuts: Compared to the four-claw expansion of multi-grip nut, Rivet Nuts are better suited for rigid materials, as they do not affect material integrity due to expansion.
Typical Applications:
- Automotive Assembly: Used for fastening vehicle frames and seats, particularly in closed spaces such as car doors and A/B/C pillars.
- Appliance Manufacturing: Used for threaded connections in washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioning housings, improving assembly efficiency.
- Industrial Cabinets: Used for fastening metal frames in electrical cabinets and data racks.
5. Suitable for Mass Production & High-Efficiency Assembly
- Rivet Nuts require a rivet nut tool for installation. While the initial equipment cost is higher, it can significantly speed up assembly and is well-suited for mass production lines.
- Ideal for industries requiring high efficiency and standardized production, such as automotive, home appliances, and rail transportation.
Typical Applications:
- Automotive Assembly Lines: Used for the mass assembly of engine compartments, exhaust systems, and dashboard brackets.
- Construction: Suitable for fast installation of curtain wall structures and steel frame projects on-site.
- Medical Equipment Manufacturing: Used for high-efficiency fastening in surgical tables, hospital beds, and medical device enclosures.
Conclusion:Plus Nut vs Rivet Nut

When choosing between Plus Nuts and Rivet Nuts, a comprehensive evaluation should be made based on factors such as material characteristics, strength requirements, installation efficiency, and budget.
1. Key Differences
| Comparison Factor | Plus Nut | Rivet Nut |
| Suitable Materials | Suitable for soft materials, thin sheets, and easily deformed materials | Suitable for metal, composite materials, and hard plastics |
| Clamping Force | Provides greater clamping force through expansion fixation | Fixed by riveting deformation, offering lower clamping force |
| Load Capacity | Better for light load applications, good vibration resistance | Suitable for high load and better impact resistance |
| Installation Tools | Requires specialized stretching tools, higher initial investment | Can use standard rivet nut guns, lower tool costs |
| Installation Efficiency | Suitable for small batch assembly, more complex installation process | Suitable for mass production, faster installation speed |
| Maintenance and Durability | May deform with expansion, affecting reuse | More durable, lower long-term maintenance costs |
| Cost | Higher unit price, higher installation tool costs | Lower production costs, more tool options, overall more economical |
2. Suitable Applications
Choose Plus Nut if your project requires:
- Installing threaded connections on soft materials (such as thin metal, composite boards, or plastic).
- Additional clamping force to prevent nuts from rotating or loosening on thin materials.
- High-strength fixation in confined spaces without needing rear support.
- Vibration resistance, such as in aerospace, rail transportation, or electronic device mounting.
Choose Rivet Nut if your project requires:
- Creating threaded connections on metal or hard materials.
- Withstanding high loads, suitable for heavy machinery, automotive manufacturing, and construction fastening.
- Efficient, mass production to reduce labor costs and increase installation speed.
- Long-term stability, requiring reliable pull-out and shear fixation, such as in industrial equipment, automotive chassis, or structural assembly.
3. Final Recommendation: How to Choose the Right Fastener?
- If you need stronger clamping force and are working with soft or thin materials, Plus Nut is the better choice. While the installation tool costs are higher, it offers a more secure fixation.
- If you are looking for an economical, efficient solution suitable for mass production and installation on metal or composite materials, Rivet Nut provides better cost performance and is ideal for most standard industrial applications.
Ultimately, although we talked about Plus Nut vs Rivet Nut, the decision should be based on your application needs, load capacity requirements, installation environment, and budget.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Rivetfix - Leading Rivet Nuts Supplier in China

As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, Rivetfix are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world.
Rivetfix offers a wide range of rivet nuts and plus nuts designed to meet the unique demands of your projects. With options like countersunk, flat, and hex heads, as well as knurled and round body types, Rivetfix ensures you have the right solution for every application. Choose Rivetfix for versatile, cost-effective, and durable fastening solutions tailored to your specific needs. In addition, we can also provide customized rivet nuts service according to your requirements.
Contact us for project advice and the latest rivet nut quote!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.





