Why Use PEM Studs for Steel Applications?

Leading Self-Clinching Fasteners Manufacturer and Supplier in China
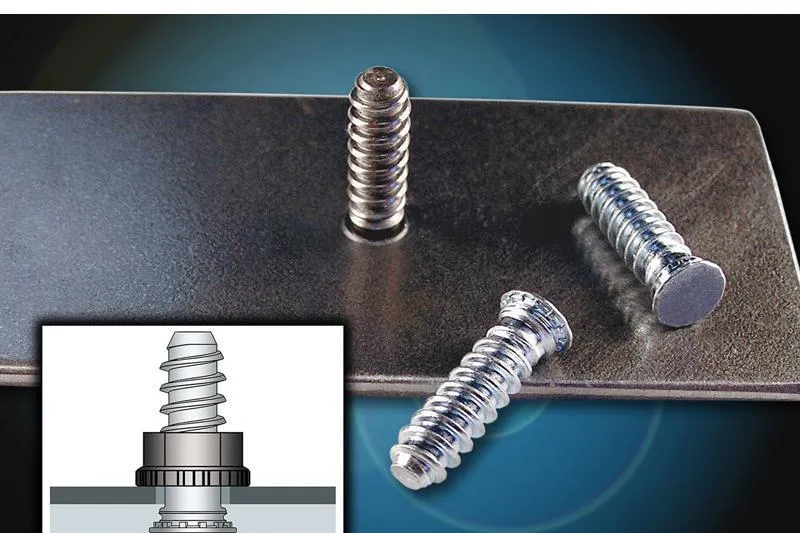

Whether designing precision automotive components or heavy-duty steel frameworks, traditional fastening methods often fall short. PEM studs for steel emerge as a technological leap, replacing welding/threading with cold-forming efficiency—preserving material properties while delivering 30kN+ tensile strength and 90% shorter assembly cycles. But how do they outperform conventional solutions in corrosion resistance and long-term reliability?
Table of Contents
Why Use PEM Studs for Steel?

In steel structures, the choice of fastening method directly affects the strength, reliability, and service life of the components. Compared to traditional welded studs, PEM studs use a cold press installation method that not only avoids issues related to heat-affected zones (HAZ) but also offers superior mechanical performance and installation efficiency.
1. Preserved Material Integrity
Avoiding Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
When welding studs onto steel, a heat-affected zone (HAZ) forms around the weld, causing local annealing and a reduction in hardness by approximately 20-30%, which can compromise the strength of the material.
In contrast, PEM studs use a cold-press installation process that does not alter the metallurgical structure of the steel, thereby preserving the original mechanical properties.
Minimized Stress Concentration
The flanged design of PEM studs helps to distribute the load, reducing the stress concentration around the hole in the steel, which minimizes the risk of crack formation. Compared to traditional riveting methods, using PEM studs can improve the component’s fatigue life by 50%, making them more suitable for long-term loading or vibration-prone steel structures.
2. Superior Mechanical Performance
Tensile Strength
PEM studs form a high-strength connection with steel, with their tensile strength often reaching 85-95% of the base material’s strength. For example, when installing an M10 PEM stud on 8mm thick Q345 steel, the tensile load capacity can exceed 30kN, meeting the demands of high-load applications.
Vibration Resistance and Anti-Loosening Capability
PEM® S-type studs feature annular locking teeth, which enhance the stud’s torque retention. In SAE J2530 vibration tests, PEM studs showed a 40% higher anti-loosening capability than traditional welded nuts, making them ideal for high-vibration environments (e.g., automotive chassis, rail transport).
Table1: Mechanical Performance Comparison
| Fastening Method | Tensile Strength (kN) | Installation Time (sec/piece) | Risk of Thermal Deformation |
| Welded Studs | 25–35 | 15–20 | High |
| PEM Studs | 28–32 | 3–5 | None |
As shown in the table, PEM studs not only provide comparable or higher strength but also offer faster installation times and avoid the thermal deformation issues associated with welding.
3. Adaptability to Complex Application Scenarios
Suitable for Ultra-Thin Steel Plates
PEM studs can be securely installed on steel plates as thin as 0.5mm, making them ideal for laser-cut or stamped steel structures, ensuring stable fastening performance.
Compatibility with Various Surface Treatments
For specialized surfaces such as pre-galvanized or color-coated steel, PEM studs’ cold-press installation method results in minimal damage to the coating. In comparison, traditional welding can cause 30% coating loss, while PEM studs cause less than 3% coating damage, effectively preserving the steel’s corrosion resistance.
Resistance to Extreme Environments
Some applications require fasteners to maintain stability in highly corrosive environments, such as marine engineering or outdoor equipment. PEM studs with Dacromet coating can withstand up to 1200 hours of salt spray testing (ISO 9227) without rusting, far outperforming traditional galvanized studs in corrosion resistance.
Table2:Surface Treatment and Extreme Environment Adaptation
| Steel Surface Treatment | PEM Stud Solution | Weather Resistance Data |
| Hot-Dip Galvanized (HDG) | Dacromet Coated Studs | Salt spray test >1200 hours without red rust |
| Electrophoretic Coating (ED) | Pre-allocation of 0.2mm height compensation | Coating coverage 100% |
| Organic Color Coating (PVDF) | Low-temperature compression (<50°C) | Film thickness damage <5μm |
4. Improved Installation Efficiency and Reduced Labor Costs
Installation Speed Comparison
Welded studs typically require preheating, welding, and cooling, taking about 15 seconds for each stud installation. In contrast, PEM studs use a cold-press installation method, completing the process in just 3 seconds, making the overall efficiency 5 times faster.
Labor Cost Comparison
For an automotive subframe production line with an annual output of 100,000 parts, welding requires 2 certified welders (hourly wage $40), resulting in an annual labor cost of $332,800. PEM compression only requires 1 unskilled worker to operate the automatic press (hourly wage $18), reducing the annual labor cost to $37,440, a savings of approximately 89%.
5. Reduced Secondary Processing and Increased Production Efficiency
Using welded studs or nuts requires several complex steps, such as:
Traditional Process (Welded Studs):
- Drilling
- Tapping
- Deburring
- Cleaning
- Welding
PEM Process (Cold-Pressed Studs):
- Punching
- Pressing
The overall processing time for welded studs is approximately 8 minutes per hole, while PEM studs only require 1 minute per hole, saving 75% of process time and avoiding issues like welding-induced deformation and oxidation, thus improving product quality and production efficiency.
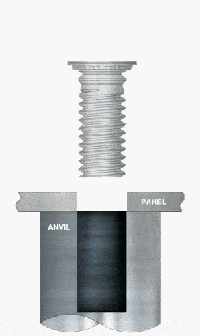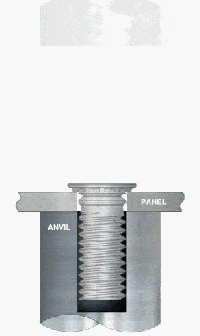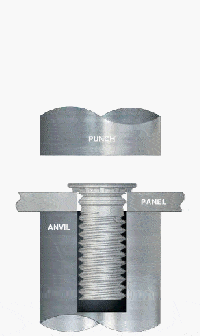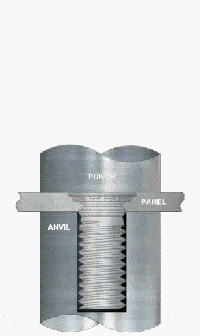
What Are the Applications of PEM Studs for Steel?

PEM studs (press-fit studs) play an important role in fastening steel in various industries due to their high strength, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. Compared to traditional welded studs, PEM studs avoid the issues associated with heat-affected zones (HAZ) caused by welding, while also improving assembly efficiency and reducing labor costs.
1. Automotive Manufacturing
Application Areas:
- Body panels (doors, hoods, underbody shields)
- Chassis structure (subframes, reinforcement beams)
- Onboard battery trays
Advantages of PEM Studs:
High-Strength Connections: PEM studs are suitable for high-strength steels (HSS) such as Q&P steel and dual-phase steel (DP980), maintaining a stable connection even under impact or vibration conditions.
Lightweight Design: Unlike welded studs, PEM studs do not require thickened steel plates, reducing the vehicle’s weight and contributing to better fuel efficiency.
No Heat-Affected Zone: The cold-press riveting method prevents material hardening issues caused by welding, reduces stress concentration, and improves fatigue life.
2. Steel Building Structures
Application Areas:
- Steel curtain wall connections
- Beam-to-bracket connections
- Roof steel structure reinforcement
Advantages of PEM Studs:
Wind and Seismic Resistance: PEM studs are suitable for high-rise buildings and infrastructure, able to withstand high-load conditions under extreme weather.
Strong Corrosion Resistance: Dacromet-coated or galvanized PEM studs can maintain rust resistance for extended periods in outdoor environments.
Easy Installation: On-site construction does not require welding equipment, avoiding the risks of high-altitude welding, and improving installation efficiency.
3. Industrial Equipment
Application Areas:
- Machine tool structural fasteners
- Conveyor equipment steel frames
- Electrical equipment cabinets
Advantages of PEM Studs:
Impact and Vibration Resistance: PEM studs are ideal for high-dynamic load environments such as large machine tools and stamping equipment, preventing loosening.
Reduced Welding Stress: For precision equipment, PEM studs avoid installation accuracy issues caused by welding-induced thermal deformation.
Compatible with Surface Treatments: Suitable for sprayed, electrophoretic, or galvanized steel plates, ensuring long-term stability.
4. Rail Transit
Application Areas:
- Internal supports of train carriages (seat fixtures, hanging brackets)
- High-speed rail/subway shield door systems
- Track signaling device enclosures
Advantages of PEM Studs:
Anti-Loosening Design: Featuring annular locking teeth, PEM studs can withstand high-frequency vibrations and meet the EN 61373 vibration standard for rail vehicles.
Lightweight and High Strength: PEM studs are suitable for stainless steel and carbon steel structures, enhancing the safety and durability of train components.
Adaptability to Harsh Environments: Resistant to high temperatures, humidity, and corrosion, making them suitable for the long-term usage requirements of rail transit equipment.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
PEM Studs vs Other Fastener Solutions
In the fastening applications for steel and other metal sheets, PEM studs have become the preferred choice in many industries due to their no heat-affected zone, high strength, and ease of installation. However, there are several other common fastening solutions on the market, such as weld studs, rivet nuts, and regular bolts + nuts. Below is a comparison of these solutions based on strength, installation efficiency, material adaptability, and cost, highlighting the advantages of PEM studs.
1. PEM Stud (Self-clinching Stud)

Characteristics:
- Fixed directly onto metal sheets through cold-press riveting, without damaging the base material structure.
- Suitable for thin steel plates (0.5mm and above) and adaptable to galvanized, painted, and other surface-treated materials.
- High tensile and torsional strength, and resistant to loosening under dynamic loads.
- Fast installation, requiring no welding or additional threading, improving production efficiency.
Application Areas: Automotive manufacturing, rail transit, electronics enclosures, industrial equipment, and other industries requiring high reliability and assembly efficiency.
2. Weld Stud (Welded Stud)

Characteristics:
- Requires high-temperature welding, which may damage the metallurgical structure of the base material and cause softening in the heat-affected zone (HAZ).
- Suitable for thicker steel plates (usually ≥2mm), with thin plates being prone to thermal deformation and perforation during welding.
- Requires professional welding equipment, and the welding process produces spatter and smoke, increasing safety hazards.
- Post-installation, welded areas require additional anti-corrosion treatment (such as painting or galvanizing) to prevent rust.
Application Areas: Suitable for thick steel plates and large structural components, such as bridges, ships, and building steel structures.
3. Rivet Nut
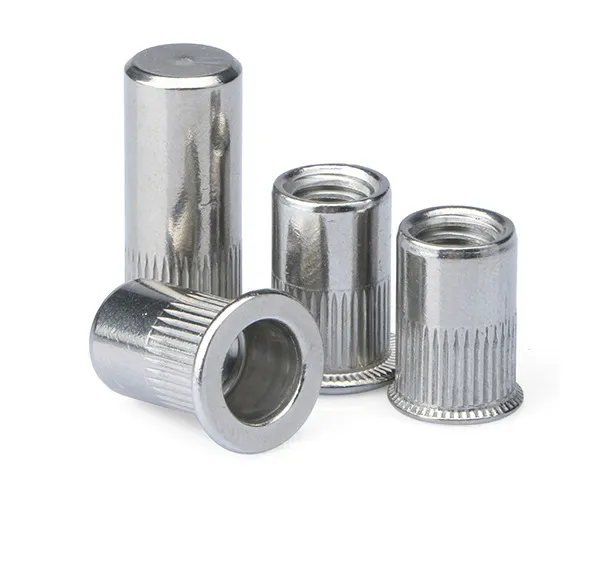

Characteristics:
- Suitable for applications where welding or clinching is not possible, and can be used in enclosed structures (e.g., the interior of square tubes).
- Requires pre-drilling and installation via a riveting tool, making it suitable for thinner metal sheets (0.5-4mm).
- Moderate torsional strength, and may lead to slipping if the hole diameter tolerance is too large.
- Lower strength, especially under high loads, with a higher risk of pull-out.
Application Areas: Thin-walled components such as aluminum enclosures, home appliance casings, and lightweight frame structures.
4. Regular Bolt & Nut

Characteristics:
- Requires drilling holes and installing nuts on both sides, making it suitable for thicker plates.
- Due to the potential for nuts to loosen, vibration resistance is poor, requiring additional locking washers.
- Installation and removal are relatively time-consuming, making it unsuitable for mass production or automated assembly.
- Connection strength depends on the tightening force of the nuts, and long-term use may result in loosening or stress concentration leading to breakage.
Application Areas: Suitable for low-cost, low-strength applications such as simple brackets or repair scenarios.
Table3:PEM Stud vs Other Fastener Solutions Comparison Table
| Comparison Factor | PEM Stud | Weld Stud | Rivet Nut | Bolt & Nut |
| Installation Method | Cold-press riveting | Arc welding | Rivet tool installation | Manual tightening |
| Suitable Plate Thickness | ≥0.5mm | ≥2mm | 0.5-4mm | ≥2mm |
| Strength | High (tensile strength up to 30kN) | High (weld point strength, but HAZ softening) | Low (limited pull-out strength) | Moderate (nuts prone to loosening) |
| Vibration Resistance | High (flange clinching + locking teeth) | Moderate (weld points stable, but crack risk) | Low (possible rotation/slippage) | Low (needs anti-loosening washers) |
| Installation Speed | Fast (3 seconds/piece) | Slow (15-20 seconds/piece) | Moderate (5-8 seconds/piece) | Slow (manual tightening required) |
| Effect on Base Material | No heat impact, does not damage structure | Affects metallurgical structure (HAZ hardness decrease) | Requires drilling, impacts strength | Requires drilling, may cause stress concentration |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective | High (welding equipment + anti-corrosion costs) | Moderate (cheap rivet, but tool installation needed) | Low (cheap materials, but high labor cost) |
How to Properly Use PEM Studs on Steel?

1. Material Matching — Prevent Galvanic Corrosion and Improve Durability
When different metals come into contact, they can create galvanic corrosion, which affects the longevity of fasteners. Therefore, the material of PEM studs should match the base steel to prevent corrosion issues. For example:
- Carbon steel base (Q235, Q345, etc.) → Galvanized carbon steel or stainless steel PEM studs (Recommended galvanized layer ≥8μm).
- Stainless steel base (SUS304, SUS316) → SUS304 or SUS316 PEM studs, avoid carbon steel studs which could cause rust.
- Galvanized steel (SGCC, DX51D+Z) → Nickel-plated PEM studs, to reduce coating damage and contact corrosion.
Note: Using incompatible materials (e.g., carbon steel studs in stainless steel plates) may cause localized electrochemical reactions, leading to stud corrosion or even fracture.
2. Hole Accuracy — Control Hole Tolerances to Prevent Loosening or Installation Issues
PEM studs are installed through clinching, so hole size precision is crucial. Oversized holes can cause the stud to loosen, while undersized holes may result in failed clinching or damage to the steel plate.
Recommended Hole Tolerances:
- Hole Tolerance: It is recommended to control within ±0.05mm to ensure a tight fit.
- Manufacturing Methods:
- Laser Cutting (Recommended, precision ±0.02mm);
- Precision Punching (For mass production, precision ±0.05mm);
- CNC Drilling (For small batches or high-precision machining, precision ±0.03mm).
Table 4: Common Problems of Hole Size
| Issue | Phenomenon | Solution |
| Oversized Hole | Stud loosens and may pull out under load | Strictly adhere to standard hole dimensions, use laser cutting or precision punching |
| Undersized Hole | Difficult clinching, plate deformation | Use appropriate punching molds or laser cutting, avoid burrs |
Note: After punching, remove burrs from the hole edges to prevent the stud from being improperly seated or affecting the contact surface quality during installation.
3. Clinching Force Calculation — Ensure Fastening Strength and Prevent Failure
When installing PEM studs on steel, the clinching force must be correctly set to ensure a firm connection between the stud and the base material, while preventing damage to the plate or stud deformation.
Clinching Force Calculation Method:
Based on steel yield strength:
- Example: Q235 steel (yield strength 235MPa), recommended clinching force 3.5kN;
- Q345 steel (yield strength 345MPa), recommended clinching force 4.5kN;
- SUS304 stainless steel (yield strength 210MPa), recommended clinching force 3.0kN.
Table 5:Recommended Clinching Force for Different PEM Stud Sizes
| Stud Size | Clinching Force (kN) | Suitable Plate Thickness (mm) |
| M3 | 2.5–3.0 | ≥0.8mm |
| M4 | 3.0–3.5 | ≥1.0mm |
| M6 | 4.0–4.5 | ≥1.5mm |
| M8 | 5.5–6.0 | ≥2.0mm |
Note:
- Too high a clinching force may cause surface indentation or stud deformation, affecting subsequent fastening.
- Too low a clinching force may result in the stud not being fully fixed, leading to rotation or loosening.
4. Coating Compensation — Account for Coating Thickness to Ensure Installation Accuracy
In many applications, the steel surface may be treated with coatings (such as painting, electrophoresis, or Dacromet), which increases the thickness and affects stud installation height and thread fit.
Table 6: Common Coating Thickness References
| Coating Type | Average Thickness (mm) | Impact |
| Electrophoresis | 0.015–0.025 | Minimal risk of thread blockage |
| Powder Coating | 0.08–0.12 | May cause threads to become obstructed |
| Hot-Dip Galvanizing | 0.1–0.3 | Requires height adjustment for stud installation |
How to Address This:
- Reserve Installation Height Before Coating:
- For example, if the steel plate has a coating thickness of 0.2mm, choose PEM studs with an appropriate 0.2mm increased installation height to avoid coating blocking the threads.
- Clean Threads After Coating:
- Use coating removal thread gauges or re-tapping to ensure the threads are clear.
- Use Coatings That Do Not Block Threads:
- For example, choose Dacromet treatment, which provides excellent corrosion resistance without blocking threads.
Note: Before coating or electrophoresis, it is advisable to cover the stud threads with thread protectors to avoid additional procedures later.
Table 7: Summary - Key Points for Proper PEM Stud Installation
| Key Factor | Specific Requirements | Impact |
| Material Matching | Stud material must match the steel to avoid galvanic corrosion | Improves durability and prevents stud rusting |
| Hole Accuracy | Control tolerance to ±0.05mm, remove burrs | Ensures stable clinching, prevents loosening |
| Clinching Force Calculation | Set based on the steel yield strength | Ensures fastening strength and prevents damage |
| Coating Compensation | Reserve 0.1–0.3mm height or protect threads | Ensures installation accuracy and prevents thread blockage |
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem

With over 15 years of expertise in fastener manufacturing, Rivetfix has become a trusted global PEM fasteners supplier. Our team of 200+ skilled workers and 40+ sales professionals ensures reliable service and consistent supply.
Partnering with Rivetfix means access to top-quality fasteners, cost-saving solutions, and custom designs. We focus on boosting your efficiency, enhancing product durability, and providing on-time delivery. Count on our expert support and continuous innovation for your fastening needs. Choose Rivetfix for premium PEM fasteners and more!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.




