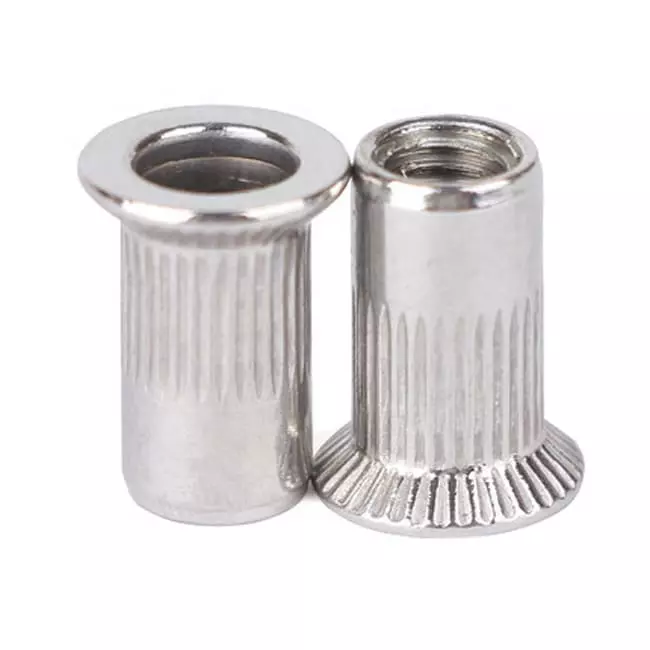
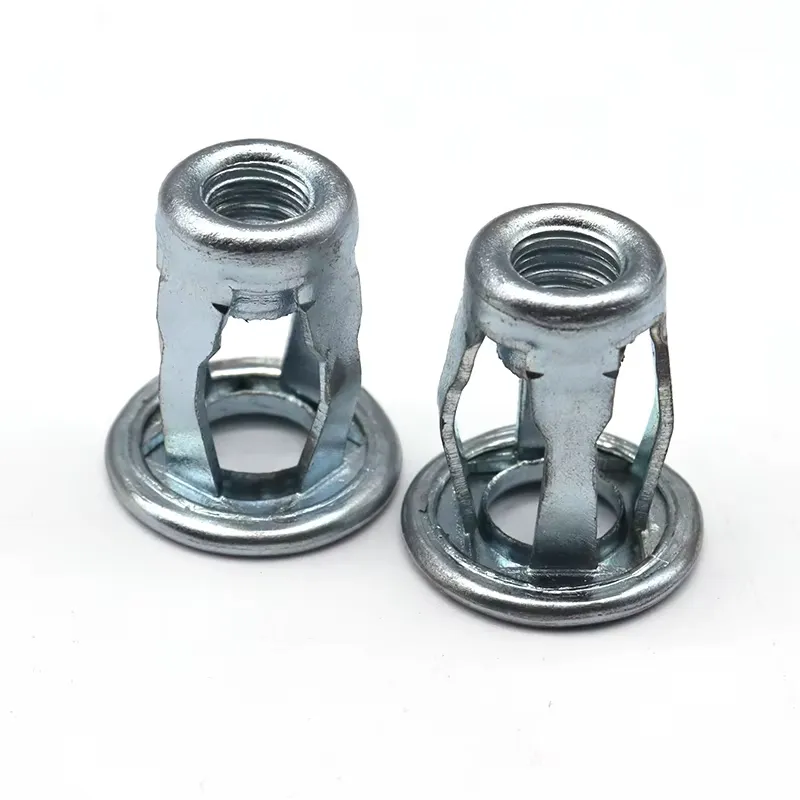
What Size Hole to Drill for 1/4-20 Rivet Nut

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China

When installing a 1/4-20 rivet nut, choosing the right hole size is crucial for ensuring a secure fit and optimal performance. In this blog, we’ll explore the recommended 1/4-20 rivet nut hole size, common mistakes to avoid, and how to achieve the perfect fit for a reliable and long-lasting installation.
Table of Contents
What Are the Uses and Features of 1/4-20 Rivet Nuts?
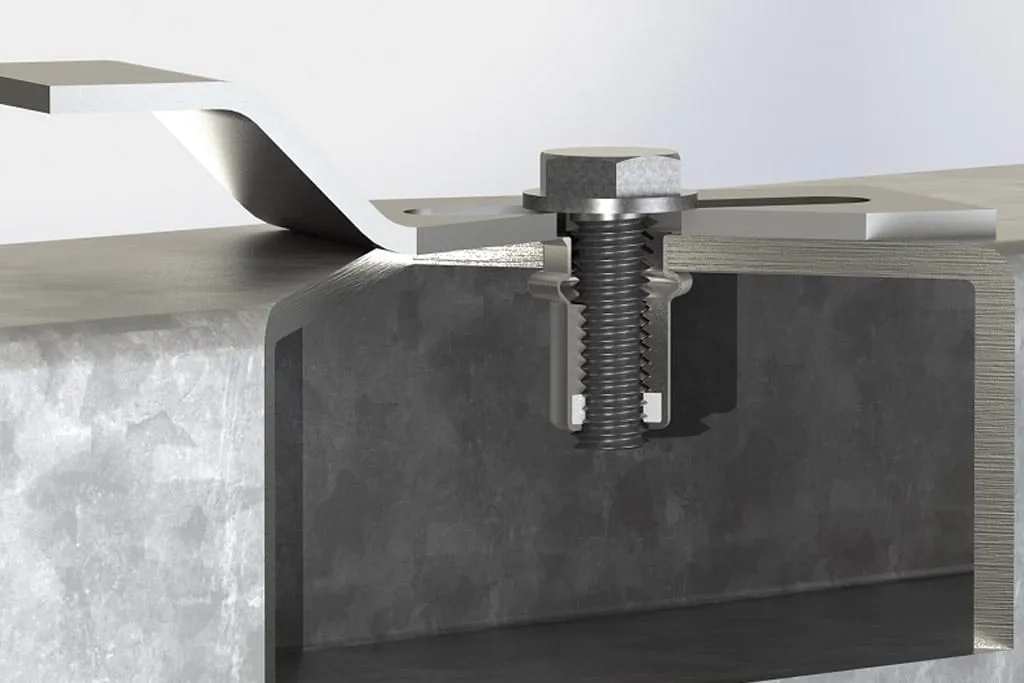
In mechanical assembly, sheet metal structures, and automotive manufacturing, the 1/4-20 rivet nut is a common and efficient internal thread fastener. Its primary function is to provide a reliable internal thread connection point for thin plates or hollow structures that cannot be accessed from the back. Due to its easy installation and strong load-bearing capacity, it is widely used in industrial and maintenance fields.
I. Main Uses
1/4-20 rivet nuts are commonly used in equipment enclosures, automotive sheet metal, industrial machinery, and electrical control boxes. They can achieve high-strength connections on thin plates with a thickness ranging from 0.5mm to 3mm without the need for welding or tapping. This structural advantage is particularly evident in environments with high vibration or frequent disassembly and assembly, effectively preventing loosening or damage to the hole positions.

II. Core Features
In terms of performance, the 1/4-20 rivet nut adheres to the UNC thread standard (with a diameter of approximately 6.35mm and a pitch of 1.27mm), making it fully compatible with American standard bolts. Its structural design can withstand a tensile force of 800–1200 N (depending on the material and wall thickness), and its anti-torque performance is further enhanced through flanging, knurling or a hexagonal anti-rotation structure.
How Important Is the Correct Hole Size for Installation Strength?
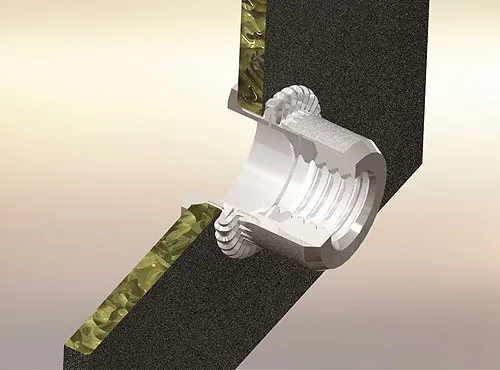
When installing 1/4-20 rivet nuts, the accuracy of the drilled hole size directly impacts the installation quality and fastening reliability. If the hole size is incorrect, the following issues may arise:
1. Hole Too Large: Rivet Nut Cannot Be Securely Fastened
- Rotation or Loosening: The rivet nut may not fit tightly against the hole wall, causing it to rotate during installation or use, affecting the stability of the threaded connection.
- Reduced Pull-Out Resistance: Insufficient expansion deformation results in weaker gripping force, reduced load-bearing capacity, and potential detachment under stress.
- Installation Failure: If the rivet nut cannot be properly fixed, it may require reworking the hole to a smaller size, increasing difficulty and costs.
2. Hole Too Small: Difficult Installation or Damage to Base Material
- Incorrect Installation: The rivet nut may not fit or may be subjected to excessive force during installation, leading to deformation or damage.
- Damage to Base Material: For materials like plastic or thin-walled metal, too small a hole may cause cracking, deformation, or even material breakage.
- Increased Installation Difficulty: Additional steps, such as reaming or filing, may be needed, which can impact production efficiency.
3. The Role of Recommended Hole Sizes
- Ensures Precise Fit of the Rivet Nut against the hole wall, providing sufficient friction to prevent rotation or detachment.
- Optimizes the Rivet Nut’s Deformation Effect, ensuring a secure grip on the base material after installation.
- Enhances Connection Strength, extending the service life and reducing repair or replacement costs due to loosening or failure.
What Size Hole to Drill for 1/4-20 Rivet Nut?

① Standard Hole Size Range
Generally, the recommended hole size for 1/4-20 rivet nuts falls within the range of 0.357″–0.362″ (approximately 9.07mm–9.19mm). The exact size may vary depending on the material, type, and installation method of the rivet nut.
| Rivet Nut Material | Recommended Hole Size (inches) | Recommended Hole Size (mm) |
| Aluminum | 0.357″ – 0.360″ | 9.07mm – 9.14mm |
| Carbon Steel | 0.360″ – 0.362″ | 9.14mm – 9.19mm |
| Stainless Steel | 0.360″ – 0.362″ | 9.14mm – 9.19mm |
- Aluminum Rivet Nuts: Aluminum is softer, so deformation occurs more easily during installation, allowing for a slightly smaller hole size to enhance the gripping force.
- Carbon Steel/Stainless Steel Rivet Nuts: Harder materials expand less during the installation process, so a slightly larger hole size is recommended to avoid installation difficulties.
② Influence of Different Types of 1/4-20 Rivet Nuts on Hole Size
- These are suited for standard hole sizes, where the hole diameter should closely match the outer diameter of the rivet nut.
- Recommended Hole Size: 0.357″ – 0.360″ (9.07mm – 9.14mm).
- The knurled design enhances friction, so a slightly larger hole size should be used to avoid damaging the knurling.
- Recommended Hole Size: 0.360″ – 0.362″ (9.14mm – 9.19mm).
- These require a hexagonal punch hole, rather than a round hole, to provide better anti-rotation capabilities.
- Standard hex hole size typically ranges between 0.370″ – 0.380″ (9.4mm – 9.65mm).

After determining the hole size, selecting the appropriate drill bit is crucial. Different drill bit numbers represent different diameters. Below are the recommended drill bits:
| Hole Size (inches) | Hole Size (mm) | Recommended Drill Bit Size |
| 0.357″ | 9.07mm | U Drill Bit (0.368″) |
| 0.360″ | 9.14mm | T Drill Bit (0.358″) |
| 0.362″ | 9.19mm | Q Drill Bit (0.332″) |
- Letter Drill Bits (U.S. Standard) correspond to slightly different sizes than metric drill bits. It is recommended to use the drill bit closest to the recommended hole size for testing.
- For high-strength rivet nuts (such as stainless steel), it is recommended to use carbide or cobalt alloy drill bits to improve drilling efficiency and reduce wear.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
What Are the Factors Affecting Hole Size for Rivet Nuts?
1. Material Type
The hardness, thickness, and deformation characteristics of the base material affect the choice of hole size:
Metals (e.g., Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloys)
- Harder materials deform less during installation, so a relatively larger hole diameter is needed to ensure smooth insertion of the rivet nut.
- Recommendation: For high-strength metals, deburring after drilling is advised to reduce installation resistance.

- Softer materials tend to deform under stress, so the hole size should be slightly smaller than the standard to provide a tighter fit, preventing nut rotation or loosening.
- Recommendation: Opt for knurled or textured rivet nuts to enhance gripping strength.
- These materials can be brittle and prone to cracking during drilling or installation.
- Recommendation: Use low-speed drilling with deburring and consider epoxy resin reinforcement at the hole edges to reduce stress concentration.
Different types of rivet nuts have distinct designs, resulting in varying hole size requirements:
- These rely primarily on friction with the hole walls for fixation, so the hole diameter should closely match the outer diameter of the rivet nut. Standard hole sizes are typically sufficient.
- Applications: General metal or plastic materials.
- The knurled outer surface enhances anti-rotation capability, so a slightly larger hole size is needed to avoid damaging the knurling.
- Applications: Soft metals, plastics, and situations requiring extra gripping force.
- These require a hexagonal hole or punching to provide better anti-rotation, preventing the rivet nut from rotating under high torque fastening.
- Applications: High-strength structures such as automotive chassis and mechanical equipment.
- Used in soft materials or hollow structures, these rivet nuts expand during installation to grip the material. Typically, a larger hole size is required compared to standard rivet nuts.
- Applications: Thin-walled plastics, composites, or hollow structures.
3. Installation Method
Different installation tools can influence the choice of hole size and the outcome of the riveting process:
Manual Installation
- Suitable for small batch applications, relying on hand-operated rivet nut guns for force application. A slightly smaller hole is recommended to enhance the nut’s fixation.
- Note: Manual tools provide less pulling force, and if the hole diameter is too large, the rivet nut may not be securely fixed.
Pneumatic/Electric Rivet Nut Guns
- Suitable for high-volume production, these tools offer fast installation with high consistency. Standard hole sizes usually suffice without the need for further adjustments.
- Note: Ensure proper torque adjustment before use to avoid excessive pressure that could damage the material or cause rivet nut deformation.
Hydraulic Installation
- Used for high-strength fastening applications (e.g., heavy machinery, aerospace), requiring precise hole size with a tolerance controlled within ±0.05mm.
- Note: Ensure the base material is sufficiently strong to avoid damage around the hole due to excessive hydraulic force.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
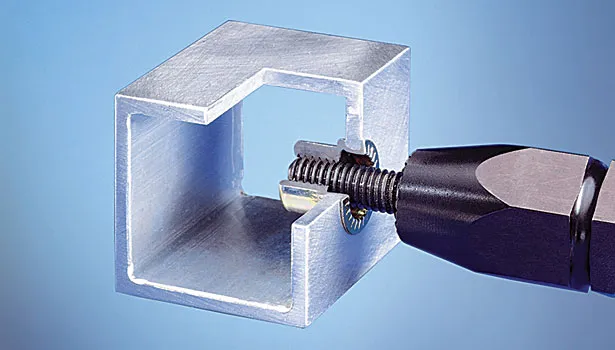
1. Hole Size Too Large
Common Mistake:
A hole that is too large is one of the most common mistakes. This leads to insufficient contact area for the rivet nut, preventing it from being securely fixed. This can cause the rivet nut to rotate, loosen, or even fall off during use.
How to Avoid:
- Follow Standard Hole Size Recommendations: For a 1/4-20 rivet nut, the recommended hole size is 0.357″–0.362″ (9.07mm–9.19mm). A larger hole will affect the rivet nut’s expansion, preventing it from securely holding.
- Use the Correct Drill Bit: For aluminum or stainless steel rivet nuts, select the appropriate drill bit to ensure the hole size is within the required specifications.
- Consider Material Type: For soft plastics like PP or PVC, the hole tolerance may need to be reduced to enhance the fastening strength and prevent loosening.
2. Hole Size Too Small
Common Mistake:
A hole that is too small will prevent the rivet nut from fully expanding, generating excessive pressure during installation. This can result in the cracking or deformation of plastic or metal base materials.
How to Avoid:
- Choose the Correct Hole Size: For 1/4-20 rivet nuts, too small of a hole will cause installation difficulty and prevent the rivet nut from properly expanding and fixing. A small hole may also damage the installation surface, especially with harder metals or plastics.
- Recommended Hole Size Range: For metal materials, the hole size should be within 0.357″ (9.07mm) ± 0.002″ (±0.05mm) to ensure proper expansion of the rivet nut.
- Use Test Holes: Before mass production, drill test holes and perform installation tests to ensure the hole size is appropriate and avoid material damage during installation.
3. Ignoring Material Characteristics
Common Mistake:
Overlooking the material hardness and characteristics can affect the hole size, leading to suboptimal installation results, especially with soft materials like plastics. Both over- and under-sized holes can negatively impact the rivet nut’s fastening performance.
How to Avoid:
- For Soft Materials (e.g., plastic): A tighter fit is required to reduce pressure during installation. Adjust the hole size tolerance to ±0.1mm around the outer diameter of the rivet nut.
- For Hard Materials (e.g., steel, aluminum): Choose a hole size close to the standard rivet nut size to avoid generating excessive pressure during installation.
- Hole Size Variations: For materials like ABS or PC, use hole sizes closer to the rivet nut’s outer diameter, whereas for softer materials like PE or PVC, opt for a slightly smaller hole for better gripping force.
4. Choosing the Wrong Rivet Nut Type
Common Mistake:
Choosing the incorrect type of rivet nut can result in mismatched hole sizes, affecting the fixing performance. For example, knurled rivet nuts, hex rivet nuts, and Jack Nuts each have different hole size requirements.
How to Avoid:
- Confirm Rivet Nut Type: For hex rivet nuts, the hole diameter may need to be slightly larger due to their design, which requires a broader contact surface to ensure proper fixation.
- Hole Size Requirements for Different Rivet Nut Types:
- Hex Rivet Nuts: These require a hole diameter slightly larger than standard rivet nuts. For 1/4-20 hex rivet nuts, the recommended hole size range is 0.372″–0.377″ (9.45mm–9.57mm).
- Knurled Rivet Nuts: The knurled surface provides extra friction, so the hole diameter should be more precise and tighter to improve gripping strength.
- Jack Nuts: These rivet nuts typically require a closer fit to avoid damaging softer materials during expansion.
5. Applying Excessive Pressure During Installation
Common Mistake:
Applying too much pressure during installation can cause the base material to crack or the rivet nut to over-expand, leading to poor fixation.
How to Avoid:
- Use Adjustable Torque Tools: To prevent excessive pressure on the base material, use torque-adjustable tools (such as pneumatic or electric tools). Set the correct torque value to ensure the rivet nut expands completely without damaging the material.
- Avoid Excessive Pressure: Especially when working with soft plastics, excessive pressure can cause cracking or deformation. The recommended torque is typically 30-40 N·m, depending on the material and rivet nut type.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Why Choose Rivetfix

As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, Rivetfix are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world.
Rivetfix offers a wide range of rivet nuts designed to meet the unique demands of your projects. With options like countersunk, flat, and hex heads, as well as knurled and round body types, Rivetfix ensures you have the right solution for every application. Choose Rivetfix for versatile, cost-effective, and durable fastening solutions tailored to your specific needs. In addition, we can also provide customized rivet nuts service according to your requirements.
Contact us for project advice and the latest rivet nut quote!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.








