The Ultimate Guide to Rivet Nut Sizes

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China

Rivet nut is an internal thread fastener that can be installed from one side. It can quickly create a load-bearing thread point in thin plates, profiles, and closed cavities. Compared to welded nuts, rivet nuts have less thermal impact, are friendly to surface coatings, and are convenient for later maintenance and replacement. The correct size selection determines the connection quality and lifespan. It is not just about choosing the thread size, but also the comprehensive matching of hole diameter, tolerance, gripping range, rivet body shape and head type. During the design stage, if appropriate rivet nut sizes are determined first, and the drilling and process parameters are planned simultaneously.
Table of Contents
Rivet Nut Size Basics
Before understanding the different sizes of rivet nuts, one must first grasp the key dimensions of the rivet nut. These parameters collectively determine the fit accuracy between the rivet nut and the workpiece, the locking strength, and the installation reliability. Any improper selection of any parameter will result in structural loosening or assembly failure.
①. Thread Size
The thread size is the most intuitive identification parameter. For example, M4, M5, M6 or ¼”-20. It represents the standard specification of the internal thread of the nut and directly affects the diameter and pitch of the compatible bolts.
In the design process, the appropriate thread size should be selected based on the load requirements of the product, the connection strength, and the grade of the matching bolts. Generally, the larger the thread, the higher the bearing capacity, but this also requires higher space and plate thickness requirements.
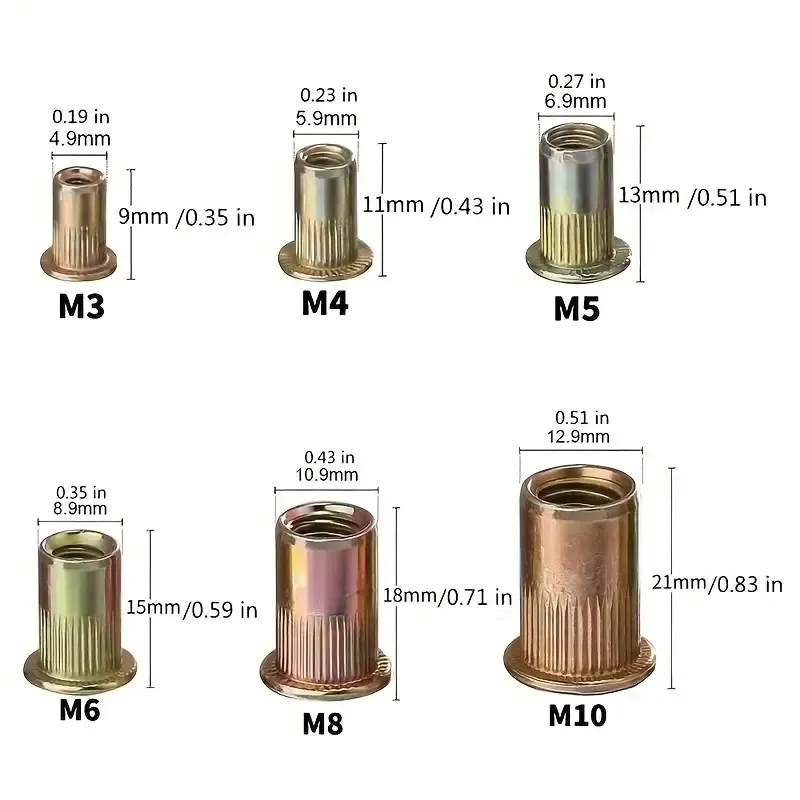

②. Body Diameter
The diameter of the rivet body is the size of the outer circle of the rivet nut, which is used to control the mating accuracy with the hole wall. It must be slightly smaller than the hole diameter to ensure smooth insertion and full expansion and locking during the riveting process.
Rivmate engineering standard recommendation: The hole diameter should be approximately 0.1–0.2mm larger than the rivet body diameter to achieve the best assembly effect and locking stability.
③. Hole Size

The hole size is a key parameter that affects the installation quality. If the diameter is too large, the rivet nut is prone to rotating or loosening; if it is too small, it is difficult to insert or may cause deformation of the workpiece. Depending on different materials, hardness and tolerance requirements, the recommended diameter may vary slightly. In the product specifications of each model, Rivmate will provide the corresponding recommended drill size (Drill Size). Users should process according to this value strictly to ensure the stability of the assembly.
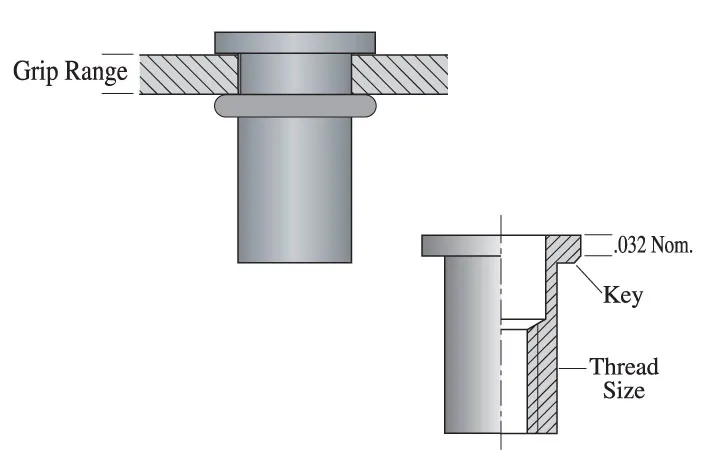
④. Grip Range
The grip range refers to the thickness range of the sheet material that the rivet nut can effectively rivet. For example, the Grip Range of an M6 nut might be 0.5–3.5mm. Exceeding this range will result in the formation of the retaining ring not being complete or excessive stretching, thereby reducing the connection strength.
When selecting the type, priority should be given to the matching relationship between the actual plate thickness and the clamping range. If necessary, sample testing should be conducted.
⑤. Head Type
The common head types of rivet nuts include flat head, countersunk head and reduced head.
- Flat head: Large bearing surface, suitable for general structural connections.
- Sunk head: Installed, it is flush with the surface, presenting a neat appearance.
- Small head: Used in narrow spaces or for areas with lower requirements for appearance.
The head shape determines the installation method and the structure of the hole opening, and it is a factor that must be clearly defined during the design stage.
Rivet Nut Size Chart
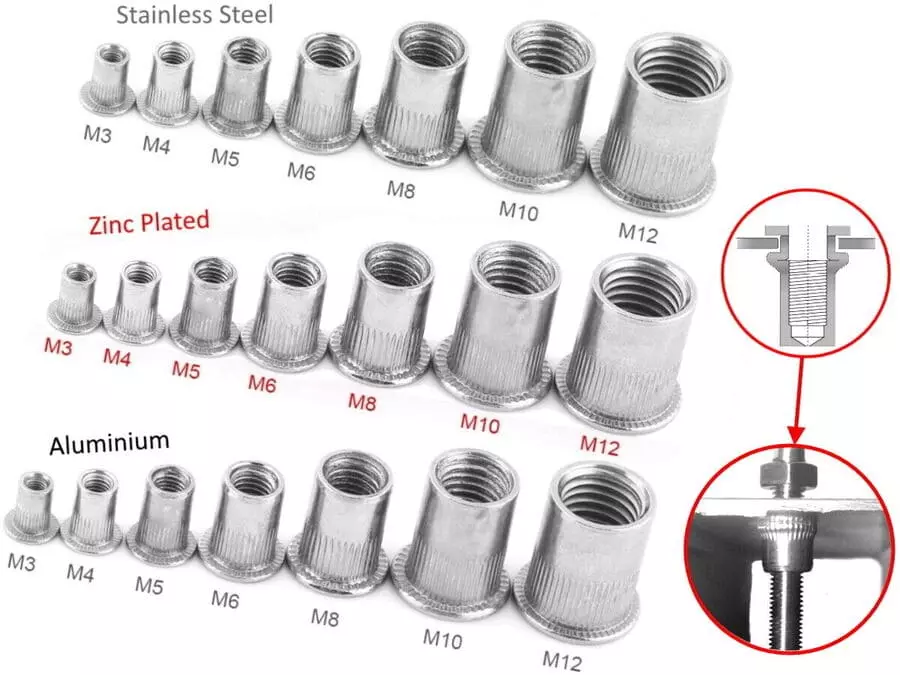

Metric Rivet Nut Sizes
Metric rivet nut sizes typically start with “M” followed by the thread diameter, such as M4, M5, M6, etc. The common metric rivet nut sizes are as follows:
| Size (M) | Thread Diameter (mm) | Common Grip Range (mm) | Total Length (mm) | Recommended Hole Diameter (mm) |
| M3 | 3.0 | 0.5 – 2.0 | 9-11 | 4.9-5.1 |
| M4 | 4.0 | 0.5 – 3.0 | 11-13 | 6.0-6.2 |
| M5 | 5.0 | 0.5 – 3.5 | 13-15 | 7.0-7.2 |
| M6 | 6.0 | 0.5 – 4.0 | 15-18 | 9.0-9.2 |
| M8 | 8.0 | 1.0 – 5.0 | 18-21 | 11.0-11.2 |
| M10 | 10.0 | 1.0 – 6.0 | 21-24 | 13.0-13.2 |
| M12 | 12.0 | 1.5 – 6.5 | 25-28 | 15.0-15.2 |
- Widely used internationally, common in global manufacturing industries.
- Suitable for various material thicknesses, typically selected based on the grip range.
- Compatible with ISO and DIN standards, ensuring consistent quality and specifications.
Imperial Rivet Nut Sizes
Imperial rivet nut sizes are typically expressed in a number + threads per inch (TPI), such as 6-32, 8-32, 10-24, 1/4-20, etc. The common imperial sizes are as follows:
| Size | Thread Diameter (inch) | Threads Per Inch (TPI) | Grip Range (inch) | Total Length (inch) | Recommended Hole Diameter (inch) |
| 6-32 | 0.138 | 32 | 0.020 – 0.060 | 0.375 – 0.450 | 0.190 – 0.192 |
| 8-32 | 0.164 | 32 | 0.020 – 0.070 | 0.420 – 0.480 | 0.250 – 0.252 |
| 10-24 | 0.190 | 24 | 0.025 – 0.090 | 0.500 – 0.560 | 0.312 – 0.314 |
| 1/4-20 | 0.250 | 20 | 0.030 – 0.125 | 0.600 – 0.700 | 0.375 – 0.377 |
| 5/16-18 | 0.313 | 18 | 0.040 – 0.187 | 0.750 – 0.850 | 0.437 – 0.439 |
| 3/8-16 | 0.375 | 16 | 0.050 – 0.250 | 0.850 – 0.950 | 0.500 – 0.502 |
- Mainly used in North American markets, suitable for American-made equipment.
- Typically compatible with ANSI (American National Standards) due to the use of inch-based units.
- Suitable for imperial screw-based products like those in aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Major Standard Systems
Different countries and industries adopt different standards to define rivet nut sizes, thread specifications, and tolerances. Below are several common standard systems:
| Standard | Description | Applicable Regions |
| ISO (International Organization for Standardization) | Uses the metric system, defining tolerances and thread standards for rivet nuts | Global, general industry |
| ANSI (American National Standards Institute) | Uses the imperial system, mainly for the North American market | USA, Canada |
| DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) | Mainly used in European manufacturing, compatible with ISO | European manufacturing |
- If the product is intended for the international market, it is recommended to choose ISO/DIN standards to ensure compatibility.
- For products primarily sold in North America, it is advisable to select imperial rivet nuts following ANSI standards.
- DIN standards are widely used in European industrial manufacturing and can usually be interchangeable with ISO standards.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Factors to Consider When Choosing Rivet Nut Sizes
When determining the appropriate rivet nut sizes, engineers not only need to consider the thread specifications, but also should comprehensively evaluate the material properties, structural loading conditions, and assembly environment. The following factors are crucial for ensuring the accuracy of the selection and the reliability of the connection.
Thin Materials (0.5 – 2mm) → Recommended M3 – M5 or 6-32 – 10-24 rivet nuts, avoiding excessive length that could lead to instability during installation.
Medium Thickness Materials (2 – 4mm) → Suitable for M6 – M8 or 1/4-20 – 5/16-18, offering stronger tensile and torque load-bearing capacity.
Thick Materials (4mm and above) → Choose M10 – M12 or 3/8-16 to ensure the rivet nut can fully expand and secure the material.
b. Material Hardness (For harder materials: a larger hole size)
The requirements for hole size tolerance vary depending on the material. For hard materials such as stainless steel and carbon steel, the installation resistance is high. Therefore, the drilling size should be slightly enlarged (usually by +0.05 to 0.1mm) to prevent the rivet nut from getting stuck or experiencing uneven force distribution.
Soft materials such as aluminum and plastic should maintain the accuracy of the hole diameter to avoid deformation of the hole walls or excessive loosening. Engineering tests by Rivmate show that a hole diameter deviation within ±0.1mm can ensure an installation qualification rate of over 90%.
c. Load and Vibration Environment (Selection of Strength Grade)
Different working conditions require different strength grades. If the connection part is subjected to high tension or continuous vibration, high-strength steel or stainless steel rivet nuts should be selected, and anti-tightening design should also be considered.
In high-frequency vibration environments (such as vehicle chassis and mechanical equipment), it is recommended to use hexagonal anti-loosening rivet nuts or combine them with locking rubber rings to prevent loosening and failure due to vibration.
d. Hole Precision and Surface Treatment (Anti-loosening and Anti-rotation Requirements)
The roundness and surface condition of the hole will affect the adhesion force of the rivet nut. Rough hole walls or excessive coating thickness will both reduce the anti-rotation performance.
If the workpiece has undergone surface treatments such as electroplating or spraying, the hole diameter needs to be corrected in advance. Generally, for every 10 μm increase in the coating thickness, the hole diameter should be enlarged by 0.02 mm.
Rivmate offers anti-rotation patterns and serrated edge designs, which can maintain stable gripping force on the coated surface.
Rivet Nut Applications by Size
| Application Scenario | Recommended Thread Size | Common Materials | Recommended Rivet Nut Type |
| Automotive Manufacturing (Body connections, chassis fixation) | M6 – M12 | Steel, Stainless Steel | Large flange rivet nuts, high-strength |
| Furniture Manufacturing (Metal frames, panel connections) | M4 – M8 | Aluminum, Thin Steel Sheets | Flat-head rivet nuts, hexagonal anti-rotation |
| Electronics (Enclosures, device casings) | M3 – M5 | Aluminum, Plastic | Small flange rivet nuts, short-body design |
| Industrial Equipment (Sheet metal, bracket fixation) | M6 – M10 | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | Cylindrical rivet nuts, high tensile strength |
| Construction Engineering (Steel structure connections) | M8 – M12 | Steel, Aluminum | Long-body rivet nuts, improved stability |
Installation Considerations for Different Sizes of Rivet Nuts

1. How to Choose the Right Installation Tool Based on Size
Choosing the correct installation tool based on the rivet nut size is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the fixation. Below are tool selection recommendations for different sizes of rivet nuts:
Small Size Rivet Nuts (M3 - M6):
- Tool Selection: Manual rivet nut tools or small pneumatic/electric tools are suitable.
- Reason: These smaller rivet nuts have lower tensile strength requirements, so lightweight tools are sufficient for installation.
- Considerations: Ensure that the tool head matches the rivet nut specifications to avoid uneven expansion of the rivet nut due to excessive pulling force.
Medium Size Rivet Nuts (M8 - M10):
- Tool Selection: Electric rivet nut tools or medium-sized pneumatic tools are more appropriate, providing higher tensile strength to ensure a secure fixation.
- Reason: Medium-size rivet nuts require greater pressure and uniform pulling force to ensure they expand fully during installation.
- Considerations: When using electric tools, ensure that the pulling force is set appropriately to avoid over-expansion, which can damage the nut.
Large Size Rivet Nuts (M12 and above):
- Tool Selection: Hydraulic rivet nut tools or large pneumatic tools are preferred, as they provide enough tensile force to handle larger rivet nuts.
- Reason: Installing large rivet nuts requires high pressure, typically used for thick materials and heavy industrial applications.
- Considerations: Before installation, check the tool’s oil or air pressure settings to ensure the pulling force does not exceed the rivet nut and base material’s load capacity.
2. Common Mistakes During Installation of Different Size Rivet Nuts and How to Avoid Them
1: Mismatch Between Tool and Rivet Nut Size
- Issue: If the selected tool is not suitable for the rivet nut size, the rivet nut may not expand fully, resulting in a loose fixation or even damage to the rivet nut or base material.
- How to Avoid: Before installation, ensure that the tool selected fully matches the rivet nut’s specifications and size. Check the tool head’s specifications and choose the appropriate tool type based on the rivet nut size.
2: Using Excessive Pulling Force
- Issue: Excessive pulling force may cause the rivet nut to over-expand, damaging the threads or cracking the base material.
- How to Avoid: Adjust the tool’s pulling force according to the rivet nut size and material thickness. Use the correct setting to avoid applying too much pressure.
3: Incorrect Installation Angle
- Issue: If the rivet nut tool is not perpendicular or is tilted during installation, it may cause the rivet nut to be installed incorrectly, resulting in misalignment or loosening.
- How to Avoid: Ensure that the tool is perpendicular to the base material during installation to avoid any angular deviation. Adjust the tool position as needed to maintain a vertical installation.
4: Inaccurate Drilling Hole Size
- Issue: If the hole size is too small or too large, the rivet nut may not be installed correctly, affecting the fixation effectiveness.
- How to Avoid: Ensure that the drilling hole size matches the rivet nut specifications, especially for larger rivet nuts. The hole diameter should be precise to ensure the correct gripping range.
FAQs - The Ultimate Guide to Rivet Nut Sizes

Q1: What is the standard hole size for M6 rivet nut?
The standard drilling size for M6 rivet nuts is typically 9.0mm. There may be slight variations depending on the brand or structural type (such as flat head, countersunk head, or anti-loosening type), and the recommended tolerance range is +0.1 / 0mm.
Rivetfix suggests conducting sample installation before the batch installation to ensure that the hole diameter, plate thickness and expansion amount of the rivet body are all compatible. The correct hole diameter can guarantee that the rivet nut forms a complete compression ring after riveting, avoiding rotation or loosening problems.
Q2: How do I know which rivet nut size to use?
To select the appropriate rivet nut size, one needs to consider a combination of factors such as the thread specification, plate thickness (Grip Range), hole diameter, tolerance, and load requirements. The general steps are as follows:
- Select the corresponding thread based on the design bolt (such as M5, M6, ¼”-20);
- Confirm the total thickness of the workpiece and match the appropriate Grip Range;
- Adjust the drilling size according to the hardness of the material;
- Confirm the head shape and the installation space.
Rivetfix offers online selection tables and technical consultation services, which can quickly recommend suitable models based on the user’s materials and application scenarios.
It is not recommended to use them interchangeably.
Metric and Imperial rivet nuts have completely different standards for thread pitch and hole diameter. Although they look similar, they are prone to poor fit or thread damage after installation.
For example: The M6 size is similar to the ¼”-20 size, but the pitch difference is 1.0mm versus 1.27mm, which makes complete compatibility impossible.
It is suggested that the specification system be unified during the design stage to ensure consistency in subsequent production and maintenance.
Grip Range refers to the thickness range of the sheet material that the rivet nut can effectively grip during assembly.
For example: The Grip Range of a certain model is 0.5–3.5mm, indicating that this nut is suitable for structures with a total thickness within this range.
During measurement, only the total thickness (including coating) of the multi-layer board or component needs to be taken into account. If the board thickness exceeds the range, the clamping ring cannot form adequately; if it is too thin, it is prone to tearing or loosening. Rivmate suggests leaving a 0.2mm margin when selecting the type to accommodate tolerances and process variations.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Rivetfix - Leading Fastener Supplier in China

As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, Rivetfix are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world.
Rivetfix offers a wide range of rivet nuts designed to meet the unique demands of your projects. With options like countersunk, flat, and hex heads, as well as knurled and round body types, Rivetfix ensures you have the right solution for every application. Choose Rivetfix for versatile, cost-effective, and durable fastening solutions tailored to your specific needs. In addition, we can also provide customized rivet nuts service according to your requirements.
Contact us for project advice and the latest rivet nut quote!
Reference
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.





