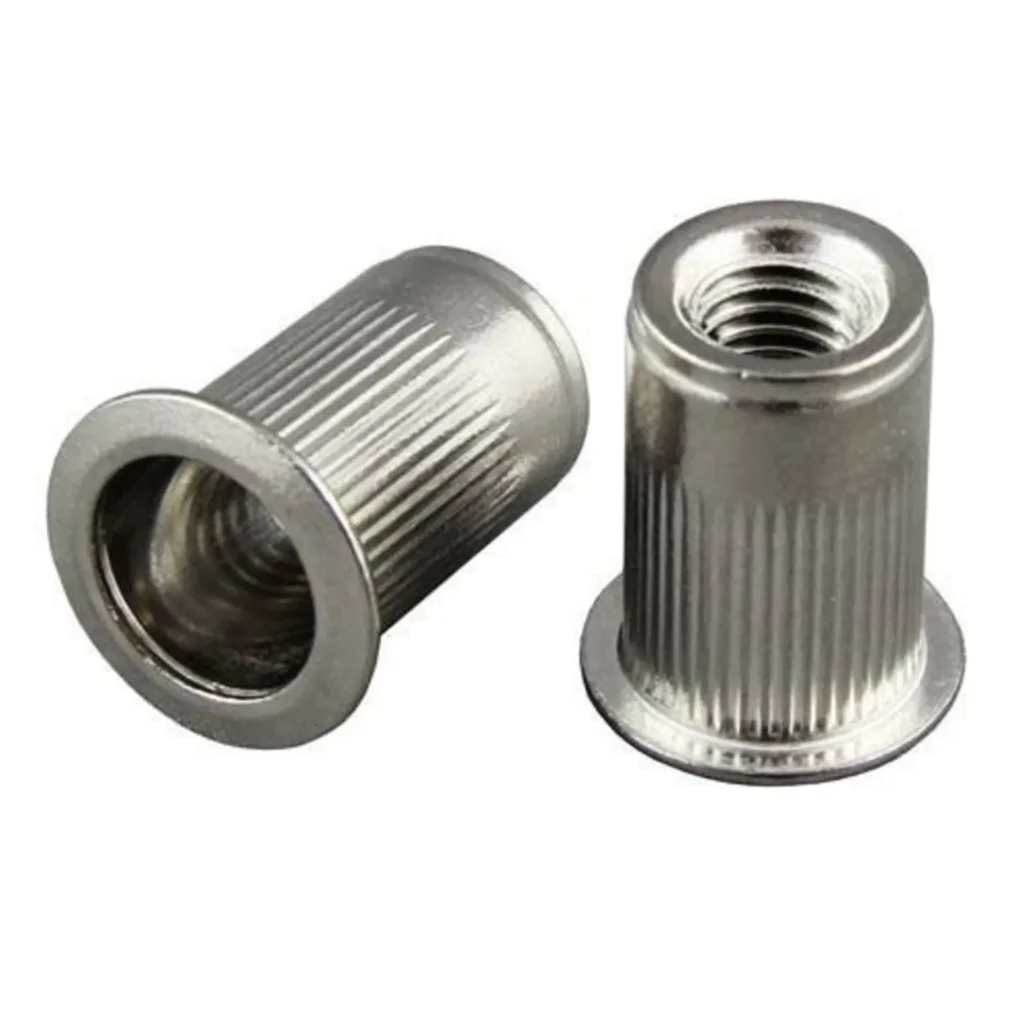
Rivnut Troubleshooting Guide

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China

Facing issues with rivnut installation? Our Rivnut Troubleshooting Guide is here to help you solve common problems like loose fittings, thread damage, and rotation. Learn how to address these challenges effectively and ensure a secure, reliable connection every time. Dive into the essential tips for rivnut troubleshooting today!
Table of Contents
Why Rivnut Problems Happen?

In actual production or assembly processes, the failure of Rivnut (rivet nut) is not caused by a single factor, but rather is the result of the combined effects of various mechanical, material, process and tool factors. Understanding these underlying causes is beneficial for preventing problems in the design and on-site installation stages and improving assembly consistency.
① Mechanical Issues
Aerodynamic drag or deformation of the base material causes the rivet nut to fail to form a complete fit on the hole wall. When the hole diameter is too large, the nut will rotate or loosen during tightening. Insufficient assembly force results in “false connection”, with unstable clamping.
Common manifestations: The nut rotates, the pulling force decreases, and the structure becomes loose.
② Material Factors
The sheet material is too thin or too soft, preventing the rivets from fully expanding. If the nut material is chosen incorrectly (such as using an aluminum nut on a steel structure), there is a risk of pull-through or thread breakage. In high-load or high-vibration environments, different material combinations may also lead to fatigue failure.
Common manifestations: Loose nuts, thread breakage, insufficient connection strength.
③ Process Errors
If the holes are not cleaned properly, there will be remaining paint, electrophoretic coatings, etc., which will prevent the rivet body from fully adhering to the base material. The burrs at the hole openings or the uneven surfaces will cause the retaining ring to deform unevenly. Without using deburring or degreasing processes, it will result in “false riveting” or an uneven appearance.
Common manifestations: False connection, incomplete installation, asymmetrical retaining ring.
④ Tool Setup & Calibration
Improper setting of the riveting stroke or tension is one of the most common problems encountered on site. If the tension is too high, the rivet body will break; if the stroke is insufficient, the rivet cannot fully expand. Wear of the tool’s gripper or misalignment of the pull rod can cause the nut to slip or rotate.
Common manifestations: Bursting of the nuts, poor deformation, and incomplete locking.
Rivnut Troubleshooting Chart
| Problem | Possible Cause | Rivetfix Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Rivnut spinning in hole | Hole too large; soft base material; low torque | Reduce hole by 0.1mm; use knurled or hex rivnut; increase pull setting |
| Rivnut not setting properly | Pull stroke too short; incorrect grip range | Adjust stroke length; verify panel thickness vs grip range |
| Rivnut cracked or over-expanded | Excessive pull force; thin material | Lower pull setting; use smaller stroke; add backing washer |
| Rivnut loose after installation | Incomplete expansion; debris in hole | Clean hole; ensure full stroke; use correct mandrel thread |
| Rivnut thread stripped | Over-tightened bolt; wrong tool | Verify torque spec; use hardened steel rivnut |
| Tool not pulling rivnut | Worn jaws or misaligned mandrel | Replace tool jaws; check mandrel threading |
📘 Data verified by Rivetfix Engineering Lab under ISO 14589 testing conditions.
Troubleshooting Guide
In the Rivnut installation process, problems usually have a clear cause-and-effect chain. By identifying the symptoms, locating the root cause, and taking targeted measures, the assembly quality can be quickly restored. The following is the typical problem path map summarized by the Rivetfix engineers, which helps you quickly identify and solve common Rivnut failures.
Diameter too large → Rivnut rotates → Replace with hexagonal hole type or serrated anti-rotation Rivnut
The large diameter of the hole results in insufficient friction between the nut and the hole wall, which makes it prone to slipping or spinning during tightening. It is recommended to reduce the diameter of the hole by approximately 0.1mm, or to use a model with anti-twisting structure (such as hexagonal or knurled body type).
Coating or paint inside the hole → Poor connection or improper tightening → Clean the hole wall and apply degreasing agent for treatment
The residual coating will prevent the rivets from fitting properly with the base material, resulting in a false connection. The hole openings need to be thoroughly cleaned to remove the electrophoretic or powder residue, and then the riveting can be carried out.
Insufficient travel → Not fully expanded → Increase the pull riveting travel by 0.2mm or adjust the force value setting
When the travel is insufficient, the expansion area of the rivet nut cannot fully extend, resulting in insufficient clamping force. Adjust the travel length of the riveting tool to ensure that the rivet ring is fully in contact with the base material.
Excessive riveting force → Breakage of the nut or deformation of the sheet → Reduce the set value and check the Grip Range compatibility
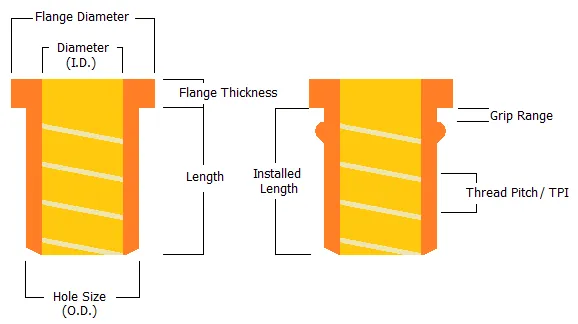
Excessive tension can cause the rivet body to break or the base material to bulge locally. The tension control system should be calibrated to ensure that the actual force value complies with the requirements of the nut material and the plate thickness.
The sheet is too thin → The rivet cannot fully expand → Add a backing washer or use a special type of Rivnut for thin sheets
The thin plate cannot provide sufficient supporting surface, causing the retaining ring to deform unevenly. It is recommended to install a metal gasket or choose the Rivnut model with a larger retaining ring design.
Thread stripping → Excessive tightening or thread contamination → Control the torque value and keep it clean
Excessive tightening torque can lead to loosening or failure. Use a torque wrench to keep the torque within the recommended range and clean the threaded area regularly.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Installation Best Practices
During the installation of Rivnut (rivet nuts), standardization and consistency are the key to ensuring the reliability of the connection. Control should be carried out from six aspects: hole diameter, positioning, stroke, clamping range, anti-twist matching, and data tracking.
Firstly, the diameter accuracy must be controlled within ±0.05mm. If the hole is too large, it will cause rotation or loosening; if it is too small, it may cause the sheet to deform. After drilling, use a chamfering tool to remove the burrs and ensure the hole is smooth. Before drilling, use centering punch positioning to prevent the drill bit from deviating and ensure the verticality of the hole, especially on high-hardness materials such as aluminum or stainless steel.
During the installation stage, the pull riveting stroke and pulling force value must be strictly defined. If the stroke is too short, the rivet ring will not fully expand; if it is too long, the nut is prone to cracking. It is recommended to conduct 3-5 trial rivets before each batch production to determine the optimal stroke parameters. At the same time, ensure that the thickness of the sheet material is within the Rivnut Grip Range, avoiding extreme values during installation to prevent false connections.
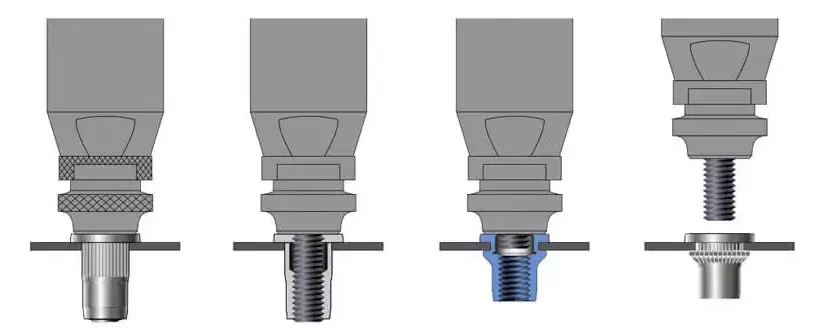
The selection of anti-torsion structures is also crucial. For round holes, a ribbed anti-torsion Rivnut should be used; for square or hexagonal holes, a hexagonal anti-torsion Rivnut should be employed to enhance the torsional resistance.

1. Main Types of Rivnut Installation Tools
Features:
- Simple structure, easy to operate, no power or air source required.
- Suitable for small batch installations or maintenance work.
- Lower cost, ideal for users with a limited budget.
- Requires significant manual force, not suitable for high-strength or large-sized nuts (M8 and above).
Applications:
- DIY projects, small assembly tasks, small-scale factory production.
Recommended Specifications:
- Suitable for M3-M6 small-sized rivnuts.
Features:
- Motor-driven, fast installation speed, suitable for mass production.
- Adjustable torque, more precise installation, reduces the risk of nut damage.
- Suitable for medium to large-sized rivnuts, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
- Requires power supply, not suitable for outdoor or off-grid environments.
Applications:
- Large-scale factory assembly lines, automotive assembly, machinery manufacturing, etc.
Recommended Specifications:
- Suitable for M4-M12 rivnuts.
Features:
- Air-powered, fast installation speed, extremely high efficiency.
- Suitable for mass production, can work continuously at high intensity.
- Requires an air compressor, ideal for industrial assembly lines.
Applications:
- Large-scale industrial production, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, shipbuilding, etc.
Recommended Specifications:
- Suitable for M6-M16 rivnuts.
(4) Hydraulic Rivet Nut Tool
Features:
- Hydraulic-driven, suitable for extra-large, high-strength rivnuts.
- Stable torque output, can be used on thick metal materials.
- High equipment cost, suitable for specialized industrial applications.
Applications:
- Shipbuilding, bridge construction, large steel structure installation, etc.
Recommended Specifications:
- Suitable for M8-M20 and above rivnuts.
2. How to Choose the Right Rivnut Tool?
| Selection Factor | Recommended Option |
| Rivnut Specifications | Small-sized (M3-M6): Hand or lever tools; Large-sized (M8 and above): Electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic tools. |
| Workload | Small installations: Hand tools; Medium batch: Electric tools; Large batch production: Pneumatic or hydraulic tools. |
| Material Thickness | Soft materials (aluminum, plastic): Hand or electric tools; Thick steel plates: Pneumatic or hydraulic tools. |
| Ease of Operation | High portability: Hand tools; Fast installation speed: Electric or pneumatic tools. |
| Cost Budget | Low cost: Hand tools; Medium cost: Electric tools; High cost: Pneumatic or hydraulic tools. |
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Buy Rivet Nuts from Rivetfix

As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, Rivetfix are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world.
Rivetfix offers a wide range of rivet nuts and rivet nut tools designed to meet the unique demands of your projects. Rivetfix ensures you have the right solution for every application. Choose Rivetfix for versatile, cost-effective, and durable fastening solutions tailored to your specific needs. In addition, we can also provide customized rivet nuts service according to your requirements.
Contact us for project advice and the latest rivet nuts and rivet nut tools quote!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.







