Rivet Nuts and Rivet Nut Tools: What Are They and How Are They Used

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China

Rivet nuts and rivet nut tools are essential fasteners for creating strong, reliable threads in thin materials. Whether used in automotive, aerospace, or furniture assembly, they provide secure fastening without welding. This guide explores what rivet nuts and rivet nut tools are, how they work, and their key applications.
Table of Contents
What is a Rivet Nut and How Do They Work?
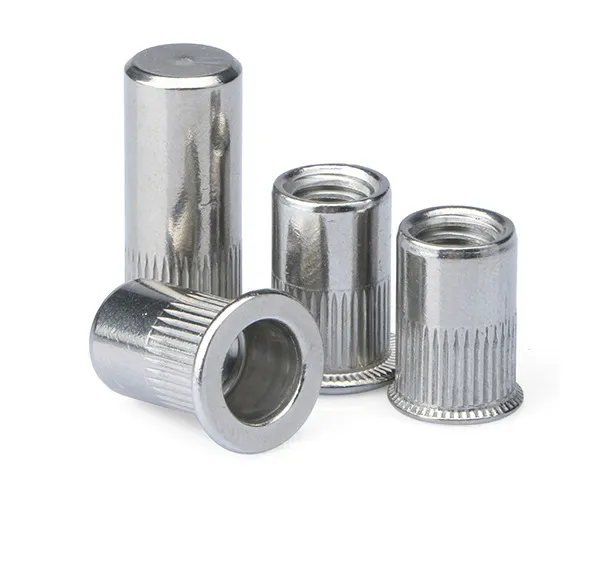

1. Definition of a Rivet Nut
A rivet nut is a fastener specifically designed for thin sheets or tubular materials that can form a reliable internal thread on materials without threads or materials that are unsuitable for direct tapping. It is installed using a rivet tool, and once fixed to the workpiece, it provides a strong threaded connection, making it easy to install bolts or screws.
Rivet nuts are also known as rivnuts or nut rivets, originally developed by the aerospace industry and are now widely used in automotive, rail transportation, machinery manufacturing, electronics, and building structures.
2. Structure of a Rivet Nut
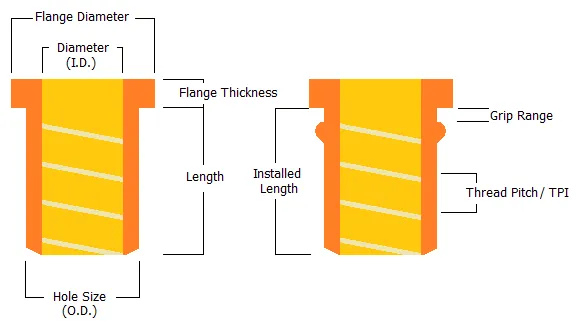
A rivet nut typically consists of the following components:
- Threaded Section: Provides the internal thread for bolt connections.
- Riveting Section: Deforms during installation to clamp onto the base material, forming a secure connection.
- Flange (Optional): Some rivet nuts feature a flange to enhance support and prevent loosening.
Common materials for rivet nuts include:
- Carbon Steel (high strength, suitable for general industrial applications)
- Stainless Steel (corrosion-resistant, suitable for damp or high-temperature environments)
- Aluminum Alloy (lightweight design, suitable for aerospace and automotive industries)
During installation, the pull rod of the tool passes through the threads inside the rivet nut and tightens the rivet nut. As pressure increases, the flange of the rivet nut expands on the material surface, generating clamping force and securely fixing it to the material. The deformed rivet nut forms a stable threaded connection that can withstand torque and tension, providing a reliable connection point for subsequent bolts or screws.
In simple terms, a rivet nut creates a mechanical lock inside the base material through plastic deformation, and its fixation principle is as follows:
- Radial Expansion: The bottom of the rivet nut expands, firmly clamping the base material.
- Friction Locking: The flange of the rivet nut provides additional support, increasing friction to prevent loosening.
- Self-Locking Effect: Once installed, the rivet nut is difficult to rotate, ensuring long-term stable connection.
What Are the Common Types of Rivet Nuts?
1. Closed End or Open End
Closed End Rivet Nut:
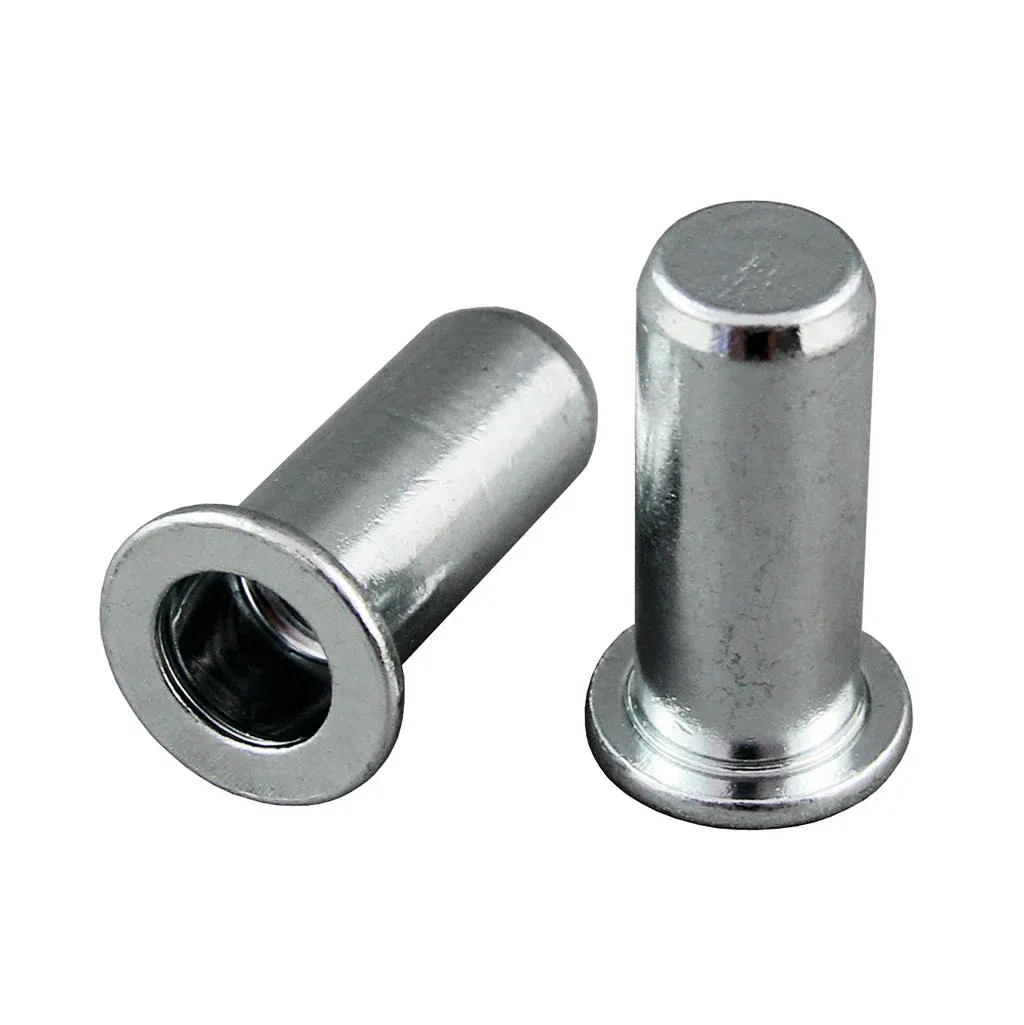

Also called Blind Rivet Nut. This type of rivet nut has a closed end, which prevents moisture, dust, or other contaminants from entering the internal threads, providing better sealing and corrosion resistance. Closed-end rivet nuts are commonly used in damp or corrosive environments, such as in ships, automobiles, and certain electronic devices.
Open End Rivet Nut:
Open-end rivet nuts have an open end, allowing better airflow around the threads. They are suitable for applications where waterproofing is not required. Open-end rivet nuts are typically used in light-load applications or environments where easier installation and lower costs are priorities.
2. Head Types
The countersunk head rivet nut has a tapered head design that, when installed, allows the nut to sit flush with the base material’s surface, avoiding any protrusions.
This type is ideal for applications where appearance is important, such as in electronic enclosures, automotive interior parts, and furniture. These rivet nuts prevent protruding parts from interfering with the installation of other components while providing a secure connection.
The flat head rivet nut has a flat head, which sits flush with the material surface once installed. This design is straightforward and does not require special space or complex installation procedures.
Flat head rivet nuts are usually used in light-load applications where appearance is less critical. They are commonly found in general machinery, electronic enclosures, and household appliances. While flat head rivet nuts have lower anti-rotation capabilities, they still provide a stable connection for most basic fastening needs.
The reduced head rivet nut has a smaller head diameter, making it ideal for installations in confined spaces. This type of rivet nut can be effectively installed in tight areas without affecting surrounding components.
Reduced head rivet nuts are widely used in compact structures, such as small devices and electronic equipment, especially where high-strength connections are required, such as in laptop casings, chassis components, or precision equipment.
3. Body Types
The hex rivet nut has a hexagonal shape, which allows it to fit into a hexagonal hole of the tool, preventing rotation during installation and enhancing torque resistance. The hex design provides better stability, making it suitable for environments that require higher loads and resistance to vibration.
Hex rivet nuts are commonly used in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, rail transportation, and heavy machinery. Due to their ability to withstand high stress and torque, they are the preferred choice for many high-strength connections.
The round rivet nut has a circular outer diameter, lacking the anti-rotation feature provided by the hexagonal design. However, it is versatile and can be used in applications where rotation resistance is not a major concern.
Round rivet nuts offer good general utility and are suitable for situations with lower installation accuracy and torque requirements, such as in furniture assembly, low-load industrial equipment, and some electronics. While their torque resistance is weaker, round rivet nuts perform well in a variety of materials and applications, meeting common fastening needs.
The knurled rivet nut has a unique knurled texture on its surface, which provides better friction during installation to prevent the rivet nut from rotating or loosening in the material. Knurled rivet nuts are widely used in applications requiring higher anti-rotation capability, especially in high-load or long-term vibration environments.
They are typically used in mechanical structures, heavy equipment, and applications that endure significant stress, such as industrial robots, conveyor systems, and construction machinery. The knurled design ensures stronger fixation and durability, ensuring the fastener connection does not loosen.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
How to Use Rivet Nut Tools for Installation?
Material Selection:
Rivet nuts are suitable for various base materials, including metals (such as aluminum, steel, stainless steel), plastics, and composite materials. The hardness and thickness of the base material will affect the installation outcome. Generally, the material thickness should match the rivet nut’s clamping range. Rivet nuts typically have a standard clamping range, and if the base material is too thin (e.g., less than the rivet nut’s minimum clamping range), it may result in insufficient holding power. If the material is too thick (e.g., exceeding the rivet nut’s maximum clamping range), the rivet nut may not fully compress, leading to an insecure connection.
- Common steel thickness: 1.5mm – 10mm
- Plastic material thickness: 0.8mm – 5mm
- The clamping range of rivet nuts is usually between 1mm to 12mm (depending on the model).
The hole diameter must precisely match the outer diameter of the rivet nut. A hole that is too small will prevent the rivet nut from being inserted smoothly, affecting the installation process and connection strength. On the other hand, a hole that is too large will prevent the rivet nut from securely clamping the base material, creating a risk of loosening.
For example, for an M5 rivet nut, the recommended hole diameter is 6mm; for an M6 rivet nut, the recommended hole diameter is 6.6mm, with an error margin controlled within ±0.1mm to ensure the best installation outcome.
Torque Control:
It is crucial to apply the appropriate torque during the rivet nut installation. Excessive torque may cause the rivet nut to crack or damage the base material; insufficient torque may result in the rivet nut failing to deform properly, affecting connection strength. To avoid these issues, tools with torque control are recommended, especially for batch production, ensuring consistent installation quality.
Generally, the installation torque for an M5 rivet nut is between 6Nm and 8Nm, and for an M6 rivet nut, the installation torque is between 8Nm and 12Nm. The actual torque used may vary depending on the material of the rivet nut (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum alloy).
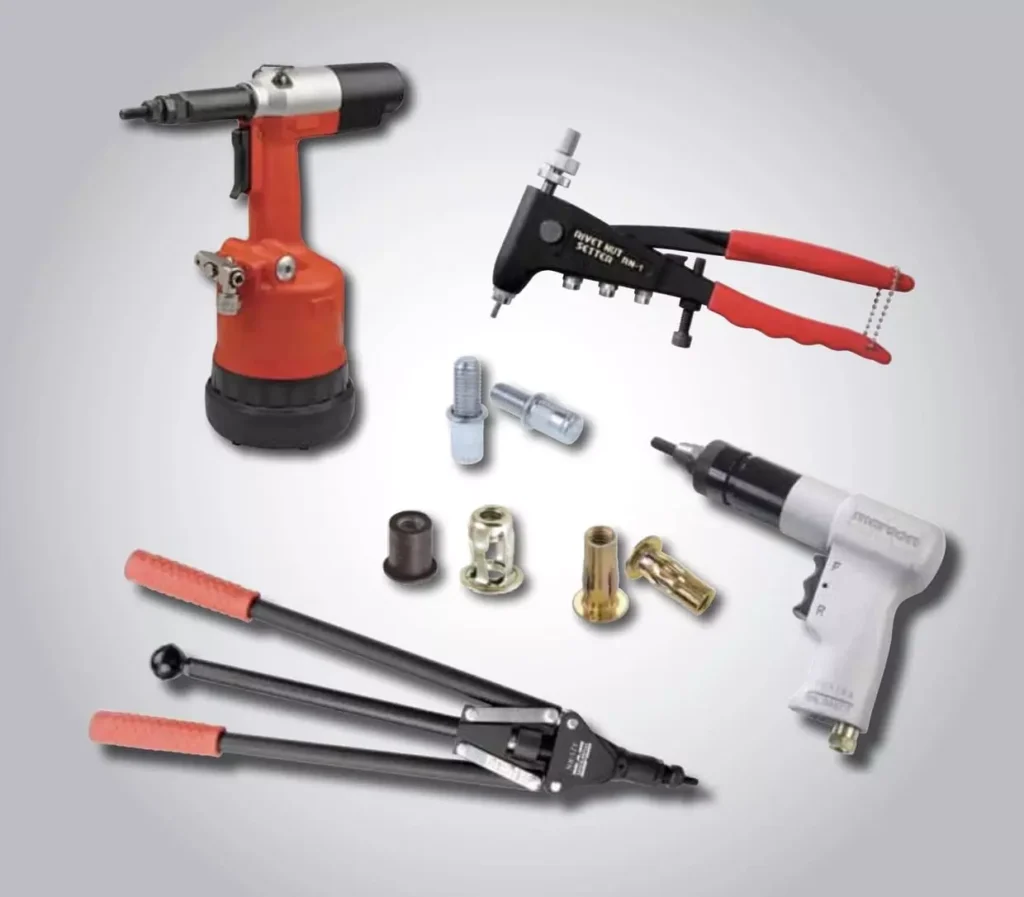

Rivet nut tools (riveter guns) are key equipment for installing rivet nuts. Choosing the right tool can improve work efficiency, ensure riveting quality, and reduce long-term maintenance costs. Below, we analyze factors like tool type, applicable nut specifications, pulling force, work efficiency, cost, and application scenarios.
I. Main Types of Rivet Nut Tools
- Suitable for M3-M8 small-size rivet nuts
- Low cost, ideal for low-frequency use or small batch repairs
- Requires considerable hand strength, low efficiency
- Suitable for M3-M12 rivet nuts
- Requires an air compressor, ideal for assembly line production
- High pulling speed, up to 30-60 times per minute
- Suitable for M3-M12 rivet nuts
- Rechargeable version suitable for on-site work, no air source required
- Higher cost, but portable
Hydraulic Rivet Nut Gun
- Suitable for M5-M20 large-size rivet nuts
- Strong pulling force (25-50kN), ideal for heavy industrial manufacturing
- High equipment cost, high maintenance requirements
II. Key Factors in Choosing a Rivet Nut Tool
1. Applicable Nut Specifications
- M3-M6 → Manual or electric rivet nut guns
- M6-M12 → Pneumatic or electric rivet nut guns
- M12-M20 → Hydraulic rivet nut guns
2. Pulling Force and Work Efficiency
- Manual tools: 10-15 times per minute
- Pneumatic tools: 30-60 times per minute
- Electric tools: 20-50 times per minute
- Hydraulic tools: 10-30 times per minute
- Riveting > 200 pieces per day: Recommended pneumatic or electric tools
- Riveting > 1000 pieces per day: Recommended hydraulic tools
3. Cost and Budget
- Manual rivet nut guns: 100-500 RMB, suitable for <100 units/day
- Pneumatic rivet nut guns: 800-3000 RMB, suitable for 200-1000 units/day
- Electric rivet nut guns: 2000-8000 RMB, suitable for 200-800 units/day
- Hydraulic rivet nut guns: 5000-20000 RMB, suitable for >500 units/day
4. Environment and Portability
- Assembly line production → Pneumatic or hydraulic rivet nut guns
- On-site construction → Electric rivet nut guns (rechargeable)
- Small batch repairs → Manual rivet nut guns
- High-intensity continuous operation → Hydraulic rivet nut guns
III. Summary – Choose the Best Rivet Nut Tool
| Application Scenario | Recommended Tool | Not Recommended Tool |
| Home/Small Repairs | Manual rivet nut gun | Hydraulic rivet nut gun (high cost) |
| Medium-Small Factories (200-1000 units/day) | Pneumatic rivet nut gun | Manual rivet nut gun (low efficiency) |
| On-site Construction/Field Work | Electric rivet nut gun | Pneumatic rivet nut gun (requires air source) |
| Large-Scale Production (>1000 units/day) | Hydraulic rivet nut gun | Manual/Pneumatic rivet nut gun (insufficient pulling force) |
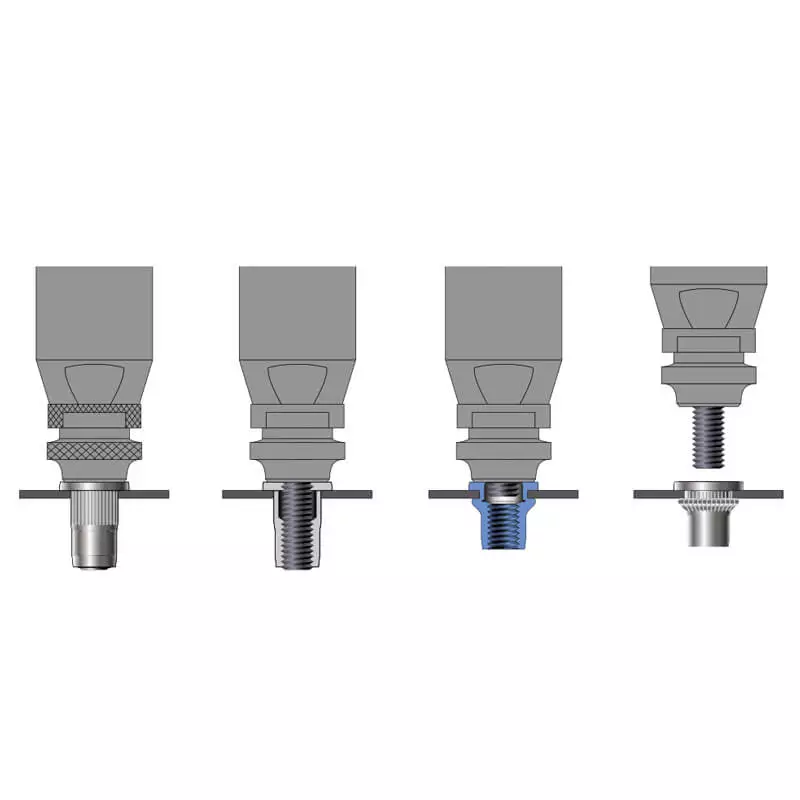

1. Preparation (Prepare the Materials and Tools):
- Confirm the rivet nut specifications, hole size, and tools. Prepare the correct drill bit to ensure the hole diameter matches the rivet nut size.
- Select the appropriate rivet nut tool and adjust it based on the rivet nut type and size.
2. Drill the Hole:
- Use the appropriate drill bit and drill press to drill a hole of the correct size in the base material. Ensure the hole diameter matches the rivet nut’s outer diameter and the hole depth meets the installation requirements.
- Clean the burrs and debris inside the hole to ensure a smooth surface, avoiding any adverse effects on the rivet nut installation.
3. Insert the Rivet Nut:
- Insert the rivet nut into the pre-drilled hole, ensuring the flange part of the rivet nut is flush with the base material’s surface. Check the alignment and ensure the installation position is correct.
4. Set the Rivet Nut with the Tool:
- Connect the installation tool to the rivet nut and operate according to the tool type (manual, pneumatic, electric). Typically, insert the bolt or tool’s plug into the internal threads of the rivet nut.
- Activate the tool, compress the rivet nut, and deform it using the tool’s force to secure it into the base material. This process ensures a firm connection between the rivet nut and base material.
5. Check the Installation Quality:
- After installation, gently rotate the rivet nut to check if it is secure. If the rivet nut is not loose and can be smoothly threaded onto the bolt, the installation is successful.
- Perform necessary quality checks to ensure the rivet nut threads are intact and can withstand the expected load and torque.
How to Remove and Maintain Rivet Nuts?
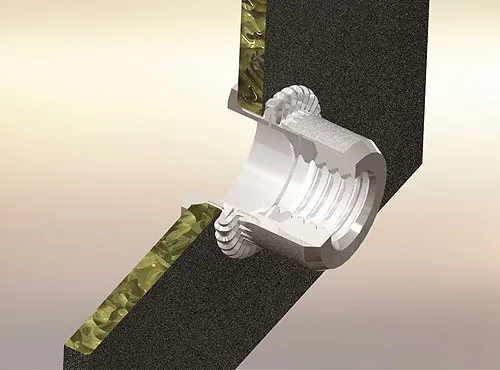
1. How to Remove Rivet Nuts?
Since rivet nuts are expanded and fixed in the base material after installation, their removal is not as simple as that of regular nuts. Common removal methods include mechanical destruction and non-destructive removal, as detailed below:
Mechanical Destruction Method (For Irreusable Rivet Nuts)
(1) Using a Drill to Remove the Rivet Nut (Most Common Method)
Steps:
- Select an appropriate drill bit: Typically, choose a drill bit slightly larger than the inner thread of the rivet nut (e.g., for an M6 rivet nut, use a 7mm-8mm drill bit).
- Drill at the center of the rivet nut: Use an electric drill or bench drill at a low speed to drill through the threaded portion of the rivet nut.
- Remove the remaining part: Once the drill bit penetrates, the rivet nut will loosen. You can use a punch or flat-head screwdriver to knock out the remaining part.
(2) Using a Cutting Tool (Angle Grinder/Metal Saw Blade)
Steps:
- Use an angle grinder or metal saw blade to cut along the edge of the rivet nut, weakening its strength.
- Use a punch or screwdriver to pry and gradually remove the rivet nut.
- If the rivet nut is still difficult to remove, use a hammer and punch to strike and detach it from the base material.
Non-Destructive Removal Method (For Reusable Rivet Nuts)
If the rivet nut needs to be reused, destructive removal should be avoided. The following methods are suitable for non-destructive removal in certain cases:
(1) Reverse Pulling Method (For Certain Rivet Nuts)
Steps:
- Use a rivet nut tool that matches the rivet nut and select the reverse pulling mode (for recyclable rivet nuts).
- Apply reverse force to attempt to pull the rivet nut out.
(2) High-Strength Bolt Removal Method (For Slightly Damaged Rivet Nuts)
Steps:
- Select a bolt slightly larger than the inner thread of the rivet nut and screw it into the rivet nut.
- Continue tightening the bolt to create internal pressure, causing the rivet nut to loosen and eventually exit.
2. Rivet Nut Maintenance Tips
To extend the service life of rivet nuts and ensure the stability of the fasteners, the following maintenance steps should be performed:
1. Regularly Check the Tightening State
- Periodically check whether the rivet nuts have loosened, especially when used in high-vibration environments (e.g., automotive or machinery applications).
- Use a torque wrench to test the tightening degree of the rivet nuts to ensure they are within the allowed range.
2.Corrosion Protection
- When used in humid, salt spray, or highly corrosive environments (e.g., offshore equipment, outdoor machinery), choose stainless steel or galvanized rivet nuts.
- For installed carbon steel rivet nuts, apply rust-proof oil or use anti-rust spray for protection.
3. Avoid Overloading
- Different rivet nut specifications have their own tensile strength and torque limits. Choose the appropriate model based on the design requirements.
- Avoid applying excessive pulling force during installation to prevent the rivet nut from deforming or getting damaged.
4. Choose the Right Installation Tools
- Use reliable pneumatic or electric rivet nut tools to ensure uniform installation force.
- Avoid using poor-quality or heavily worn tools to reduce errors during the installation process.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Where to Buy Rivet Nuts?

As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, Rivetfix are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world.
Rivetfix offers a wide range of rivet nuts and rivet nut tools designed to meet the unique demands of your projects. Rivetfix ensures you have the right solution for every application. Choose Rivetfix for versatile, cost-effective, and durable fastening solutions tailored to your specific needs. In addition, we can also provide customized rivet nuts service according to your requirements.
Contact us for project advice and the latest rivet nuts and rivet nut tools quote!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.





