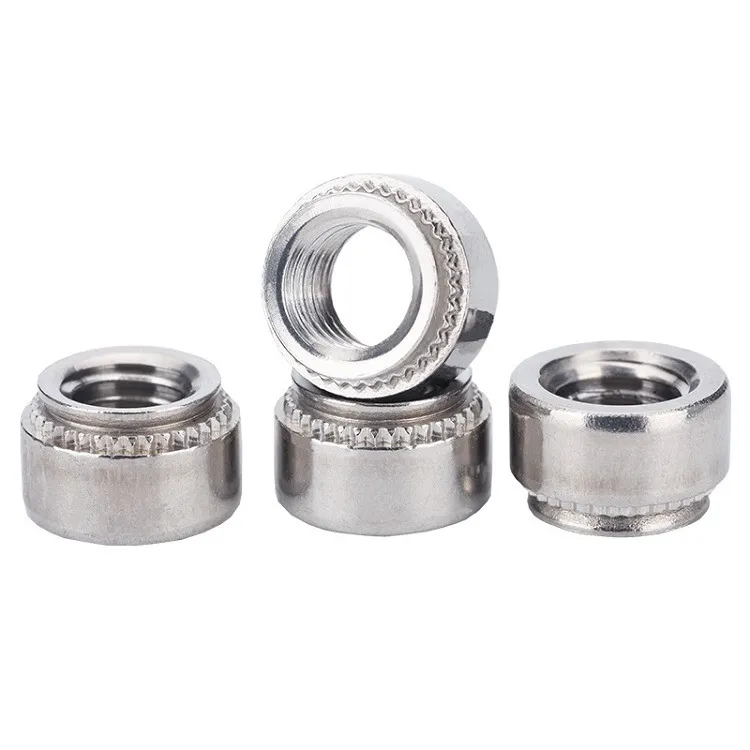
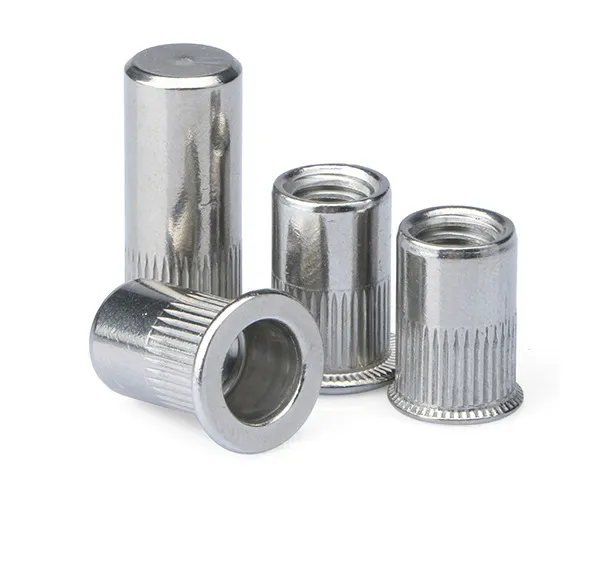
How to Choose Threaded Inserts for Steel?

Leading Threaded Inserts Manufacturer and Supplier in China

When working with heavy-duty materials like steel, achieving strong, reliable threads can be a challenge—especially when dealing with thin-walled sections or components that require frequent assembly and disassembly. That’s where threaded inserts for steel come in. These specialized fasteners provide enhanced thread strength, load-bearing capacity, and long-term durability in demanding applications. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key factors to consider when choosing the right threaded inserts for steel, including insert types, installation methods, and typical use cases across industries.
Table of Contents
Why Use Threaded Inserts in Steel?

1. Avoiding Repeated Assembly Leading to Wear and Tear of Parent Material Threads
Although steel is inherently strong, its internal threads can be damaged by stress concentration or fatigue in multiple screw disassembly or vibration environments.
- After repeated tightening of M5 threads in medium carbon steel for more than 30 times, the screwing-in torque can drop by 25-40% and there is a risk of loosening.
- With the use of wear-resistant inserts (e.g. stainless steel, self-locking type), >200 repetitions of assembly without thread damage can be realized.
2. Provide standardized threaded interfaces
In some complex or high-volume structures, direct tapping is costly and accuracy is difficult to control. Inserts provide:
- Pre-formed precision threads (to ISO, UNC, UNF standards);
- Avoidance of increased failure rates due to tapping deviations (especially suitable for difficult machining areas such as welded steel tubes, hot rolled steel plates, etc.).
3. Enhances structural strength or provides higher locking force
For applications such as welded structures, steel pipe supports, etc., threaded inserts can be designed in such ways as flange seating and knurled outer walls:
- Increased torque bearing surface;
- Enhance pullout strength and rotational resistance;
- Some reinforced steel inserts can withstand >15,000N pulling force and >20Nm screwing torque (M8 size).
4. Improved Assembly Consistency and Modularity
The use of inserts in automated assembly lines helps:
- Achieve a consistent action of quick insertion and bolt tightening;
- Control press-in force and torque to ensure consistent quality;
- Facilitate later replacement of modules and maintenance of equipment without the need to rethread or replace entire parts.
5. Mandatory solution for special surface/thin-walled steel structures
When steel parts have been coated, electrophoresed, heat-treated, direct tapping will destroy the protective layer and form a corrosion hazard. And inserts can be:
- be assembled and completed before pre-treatment, avoiding secondary processing;
- For <1.2mm steel plate, rivet nut becomes the only reliable thread bearing program.
5.1. Problem 1: Threading after surface treatment destroys the protective layer
In many steel parts, the following surface treatments are usually applied to enhance corrosion protection and aesthetics:
- Powder Coating / Spray Painting (e.g., steel cases for home appliances, electric control boxes);
- Electrophoretic painting / electroplating (e.g. automobile chassis parts, brackets);
- Heat treatment/carburizing/nitriding (e.g. structural steel parts, functional parts).
The thickness of the coating formed by the above treatments is usually 10-25μm, which will result in post-tapping:
- Destruction of the coating on the threaded part, resulting in the formation of an “exposed galvanic zone”;
- Accelerated localized corrosion, or even pitting within 240 hours of the salt spray test;
- In severe cases, screws loosening, coating skinning, mother material erosion through.
Advantage of inserts: threaded inserts can be pre-assembled before surface treatment, and then integrated with the base material for anti-corrosion treatment, to avoid the destruction of the coating after tapping threads.
5.2. Problem 2: Difficulty in forming effective threads directly on thin-walled steel plates
With a steel plate thickness of <1.2 mm, it is difficult to form a complete and effective tooth structure with a conventional tapping pitch, and the following problems are likely to occur:
- Screws “slipping” or “hollowing out”;
- Unstable tightening torque;
- Unstable tightening torque. Thread failure after repeated loading and unloading.
Solution: The following inserts are recommended:
- Rivet Nut (Rivnut): especially suitable for 0.5-1.5mm thin plates, single-sided assembly, stable clamping;
- Pressure rivet nut / stud: suitable for SPCC, SGCC, 5052 and other ductile steel plates, the inserts are self-locking to form a permanent threaded seat.
5.3. Additional Advantage: Sealing and Visual Consistency
Certain structures require dustproofing, waterproofing, or cosmetic consistency, which can be matched with the use of inserts:
- Sealing rubber ring (O-ring);
- Painted adhesive ring gasket;
- Buried low head construction to maintain a flat surface.
5.4. summarize recommendations:
| Structural Characteristics | Unrecommended Practices | Recommended Insert Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Spray then tap threads | Coating damage, threads prone to rusting | Pre-assembled pressurized rivets + sprayed in one piece |
| Steel Plate <1.2 mm | Tapping prone to slippage failure | Riveting Nuts / Miniature Pressurized Riveting Studs |
| High Humidity or Vibration Structures | High Risk of loosening of common threads | Combined Inserts with Anti Loosening Gear Rings + Stopper Adhesives |
What Are Common Types of Threaded Inserts for Steel Applications?
Structural features:
Utilizing the ductility of steel plate, the nut is pressed into the metal plate by stamping to form a permanent locking with anti-rotation and anti-pull-off structure (such as barbed ring or knurled profile).
Applicable steel materials:
Cold rolled plate (SPCC), stainless steel (SUS304) and other ductile materials, plate thickness is usually 0.8-3.0 mm.
- Application Scenarios:
Industrial control box, elevator structural parts, server chassis, power cabinet door panels, etc.
Structural features:
Through the special rivet gun will be inserted in the back of the sheet expansion locking, suitable for single-sided assembly, closed-type structure, both installation flexibility and strength.
Applicable steel:
All metal sheet, including carbon steel, stainless steel, galvanized plate, painted plate, etc., applicable plate thickness range 0.5-3.5 mm.
Advantages:
- Can be retrofitted after completion of the structure;
- Can be used with different types of bolts;
- Available in cylindrical, half-hexagonal, closed-end and other configurations.
Typical applications:
Automobile subframe, door frame reinforcement, communication chassis, battery tray, etc.
c. Weld Nuts / Weld Studs
Structural Features:
Inserts are securely fused to the steel member by resistance spot welding or arc welding and are suitable for high pulling and torsion loads.
Applicable Steel Materials:
Carbon steel, thick stainless steel structural parts (≥1.5 mm), especially suitable for high strength connections.
Precautions:
- Welding surface needs to be cleaned and plating removed;
- The heat-affected zone needs to be treated twice to prevent corrosion;
- Recommended with welding anti-spatter protection adhesive.
Application Scenarios:
Vehicle frames, construction machinery, pipe fittings flange plate, power tools shell, etc..
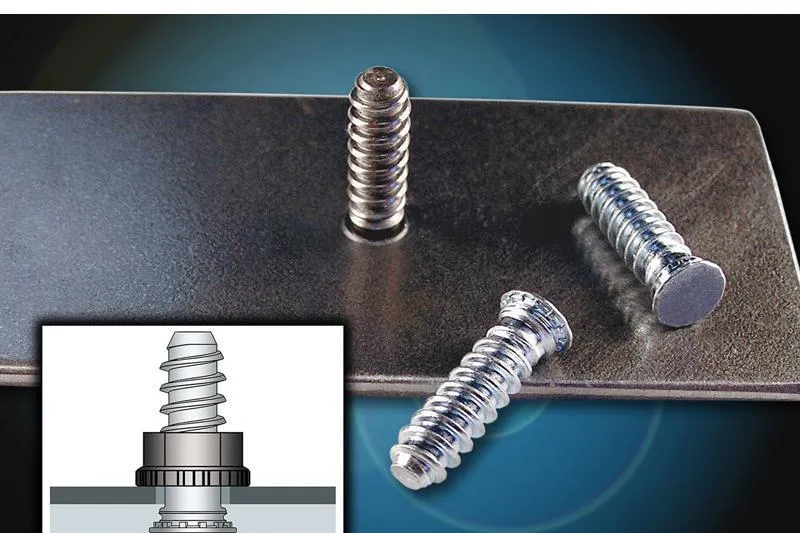
Constructive Features:
Same principle as pressure rivet nuts, but provides exposed threaded studs for pendant, bracket or cable snap fixing, widely used in structures where extended support points are required.
Recommended steel thickness:
≥1.0 mm, material must have a certain degree of plasticity.
Application areas:
Cabinet frames, in-chassis supports, rail mounting slots, rail transit port plates, etc.
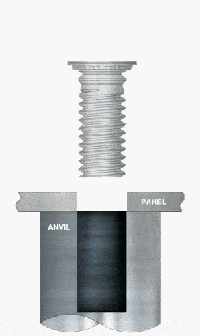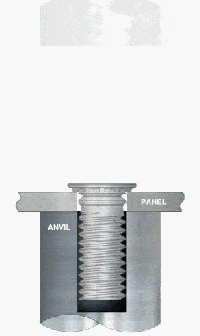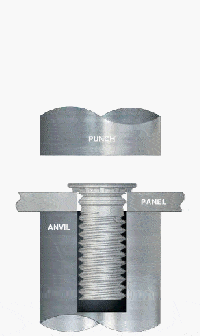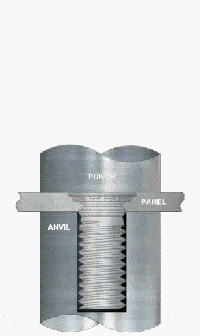
e. Self-Tapping Inserts / Press-in Steel Bushings
Structural Features:
Suitable for thick steel plate or cast steel structures where the threaded interface is constructed by screwing or mechanical press-in, usually with anti-loosening structures (e.g. interference teeth, locking grooves).
Typical Uses:
Mold construction, repair hole reinforcement, heavy duty racks, etc.
Advantages:
- Repairable thread failure areas;
- Suitable for special working conditions (e.g. frequent vibrations, impact conditions);
Forms: Common Types of Threaded Inserts for Steel
| Insert Type | Mounting Method | Applicable Plate Thickness | Application Key Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rivet Nuts | Pressure Rivet Stamping | 0.8-3mm | Automation for high efficiency and anti-rotation |
| Pull Rivet Nuts | Pull Rivet Molding | 0.5-3mm | Single Sided Assembly, Multi-Size Options |
| Welded Nuts/Studs | Welded Nuts/Studs | Resistance/Arc Welding | ≥1.5mm |
| Press Riveted Studs | Stamping Press-Fit | ≥1.0mm | Exposed Pendant Support Points |
| Self-Tapping/Press-Fit Sleeves | Thread Cutting/Press-Fit | ≥2.0mm | For Repairing or Heavy Duty Situations |
How to Match Insert Type with Steel Grade and Thickness?
I. Suggestions for selection by steel grade
① Mild steel (e.g. SPCC, Q235, DC01)
Low carbon steel due to low carbon content (≤ 0.25%), with good plasticity and toughness, ductility usually reach 28-36%, can withstand large deformation processing without cracking. Commonly used in cold roll forming and stamping process, widely used in structural components shell, support plate, reinforcing frame, etc..
Recommended Insert Structure:
- Self-Clinching Nuts/Studs
- The inverted tooth structure around the insert is made to bite the metal fiber inside the steel plate by stamping pressure;
- Permanent anti-rotation and anti-pull-off structure after installation;
- Suitable for automated press-fit equipment, high installation accuracy and good batch consistency;

2. Pull rivet nuts (Rivnuts)
- Suitable for areas where the structure has been molded or where double-sided contact is inconvenient;
- Provide blind hole assembly capability, easy to later overhaul bits, reinforcement parts thread expansion;
- Recommended for half-hex anti-rotation type or closed-end structure to enhance torque locking force and sealing.
Recommended Plate Thicknesses and Pre-Hole Parameters:
- For SPCC materials:
- Recommended plate thickness for riveted inserts ≥0.8 mm, pre-hole accuracy H10;
- For SPCC materials: rivet inserts are recommended to be ≥0.8 mm thick with H10 pre-hole accuracy; rivet nuts are recommended to have a hole diameter tolerance within ±0.05 mm to ensure reliable locking after riveting.
② Medium Carbon / Alloy Steels (e.g. Q345, S355, SCM440)
The yield strength of medium carbon steel and alloy steel is usually between 350-800 MPa (Q345 ≈ 345 MPa, SCM440 can reach 800+ MPa after tempering), with excellent bearing capacity and impact resistance, commonly used in the structure of the main frame, suspension components, powertrain bracket and other parts.
However, its cold working performance is relatively poor, and cracks, stress white edges and other defects are likely to occur during riveting or stamping.
Recommended Insert Structures
Welded Nut / Welded Stud
- Suitable for high stress areas, such as: connecting lugs, base flanges, heavy duty suspension connections;
- Firmly fused to the base material, mostly by means of resistance or arc welding;
- Weldable inserts with positioning bumps/welding bosses are recommended for stable welding and uniform load transfer;
- Conventional M8-M12 weld studs are available with axial pull-out forces** of 10,000-20,000 N**.
Process Considerations
- Oxidation and residual stresses exist in the heat affected zone (HAZ) after welding. The following measures should be taken to prevent corrosion:
- Immediately spray zinc-aluminum paint or antirust paint;
- Electrophoretic coating (E-coating) or pickling passivation** is recommended for critical structures;
- Control the welding current and energizing time to avoid over-burning or local deformation of the base material.
③ Stainless Steel (SUS304, SUS430, SUS316)

Stainless steel is widely used in structural parts with high strength and corrosion resistance requirements, among others:
- SUS304 (A2 grade): the most common austenitic type stainless steel, good ductility, strong corrosion resistance;
- SUS430: ferritic stainless steel, low cost, worse than 304 acid resistance, strong magnetism;
- SUS316 (A4 grade): added molybdenum, stronger resistance to chloride corrosion, commonly used in outdoor or marine environment.
This type of material has higher hardness (Brinell hardness HB ≈ 160-210), but is prone to microcracks, stress white edges and narrower molding window under impact loads or over-pressure loading.
Recommended Insert Structures
A2/A4 grade riveting studs/nuts
- The material should be matched with the base material (A2 corresponds to SUS304, A4 corresponds to SUS316) to avoid the formation of galvanic corrosion potential difference;
- For riveting inserts, it is recommended to use reinforcement structure (e.g. 4 barbed teeth ring) to improve the anti-rotational torque (M6 size up to 8-12 Nm);
- Suitable for 1.0-3.0 mm thickness range, especially suitable for precision sheet metal parts such as medical equipment shells, communication cabinets, power switchgear, etc..
II. Selection Recommendations Based on Sheet Metal Thickness
| Thickness Range | Recommended Insert Types | Installation Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| <0.8 mm | Mini Rivet Nuts, Closed-End Rivet Inserts | Use special models with low clamping force and minimal expansion |
| 0.8–1.5 mm | Clinching Nuts, Rivet Nuts | Most commonly used in standard structures; highly adaptable |
| 1.5–2.5 mm | Clinching Studs, Weld Nuts | Suitable for medium loads; supports spot welding or reinforced pressing |
| ≥2.5 mm | Welded Studs, Threaded Steel Inserts | Suitable for high loads, repeated disassembly, or repair scenarios |
Form:Match Threaded Insert Type with Steel Grade and Thickness
| Steel Grade | Thickness Range | Recommended Insert Types | Installation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPCC | 0.8–2.5 mm | Clinching Nuts, Studs | Press-fitting |
| Q235 | ≥2.0 mm | Weld Nuts, Rivet Nuts | Welding / Riveting |
| SUS304 | 1.0–3.0 mm | Stainless Steel Clinching Inserts | Specialized clinching tools |
| Q345 / S355 | ≥2.5 mm | Reinforced Steel Inserts, Welded Studs | Welding / Self-tapping |
What Should You Consider When Selecting Inserts for Steel?
① Type of structural load and strength requirements
- Static load occasions (e.g. fixed bracket, panel threaded connection):
- Conventional compression rivet nuts or pull rivet nuts can be used;
- The pulling force needs to meet the structural safety factor (recommended ≥ 3 times the maximum working load);
- M6 rivet nuts have a conventional pull-out strength of approximately 6,000-8,000 N in mild steel.
- High load/dynamic structures (e.g. vehicle frames, machine mounts, engine bays):
- The use of welded nuts/studs or reinforced threaded steel sleeves is recommended;
- Shear strength, fatigue life in stress concentration areas need to be accounted for.
② Matchability of mounting method to production process
- Can be operated on both sides of the structure:
- High efficiency of press riveting type inserts, suitable for automated production lines;
- Need to cooperate with special molds to control the press-in force and press-fitting flatness.
- Single-sided closed structure or rear mounting requirements:
- Recommended to use ** rivet nuts **, suitable for a variety of steel thickness (0.5-3.5mm);
- Use anti-rotation type (hexagonal shank, half-round shank) for vibration structure to enhance locking performance.
- High-strength steel structure or welded frame:
- Prioritize the use of ** resistance spot welding nuts ** to meet the high strength torque and tension;
- Pay attention to the heat impact of the welding area and anti-corrosion treatment.
③Environmental adaptability: corrosion, humidity, heat and galvanic risks
- High humidity / salt spray environments (e.g. seaside, outdoor equipment):
- Recommended Stainless steel A2/A4 inserts;
- When mating with aluminum or galvanized plate, an isolation washer or anti-corrosion grease should be added to prevent galvanic coupling corrosion.
- High temperature / areas of significant thermal expansion and contraction:
- Combinations of dissimilar materials with large differential coefficients of thermal expansion should be avoided;
- Give preference to insert materials that are similar to the parent material (e.g. carbon steel to carbon steel, 304 to 304).
- Electronic Equipment / EMC Requirements:
- Avoid using galvanized carbon steel mixed with stainless steel to prevent grounding failure or stray current interference.
How Can Galvanic Corrosion Be Prevented in Steel Structures?
I. Basic Principles of Galvanic Corrosion
Galvanic Corrosion (Galvanic Corrosion) is a phenomenon that occurs when two metals with different electrochemical properties come into contact with each other in an electrolyte (water or humid environment), forming a proto-cell reaction that results in accelerated corrosion of the more reactive metal (anode). It is common in steel structures in the following situations:

- Connection of different metals (e.g. carbon steel with stainless steel, aluminum, copper, etc.);
- Exposed fasteners, bolts, flanges, etc. in humid or salt spray environments;
- Uneven, damaged or perforated surface coatings resulting in direct metal-to-metal contact.
II. Common risk areas for galvanic coupling corrosion in steel structures
Fasteners connection
If stainless steel bolts are used to connect carbon steel components, stainless steel is the cathode and carbon steel is the anode, carbon steel accelerates corrosion.
Welding or reinforcement part
The use of welding wire or patch plate made of different metals, the contact surface is prone to form galvanic corrosion.
Roofing/curtain wall and bracket connection
Aluminum alloy, galvanized steel and carbon steel component connections are prone to corrosion in rainfall or condensation environments.
Bridges, marine platforms, harbor facilities
High humidity, high salt environment is very easy to induce and aggravate galvanic corrosion.
III. Preventive measures for galvanic corrosion
1. Optimization of material selection
- Avoid direct contact with combinations of metals with different potentials;
- If combinations are necessary, try to select materials with close potentials (e.g. carbon steel and zinc is safer than carbon steel and copper);
- Select fasteners with the same or higher corrosion protection level (e.g. hot-dip galvanized bolts with hot-dip galvanized members).
2. Insulation Separation
- Use insulating shims, nylon washers, coated or corrosion-resistant tapes where dissimilar metals come in contact;
- Add plastic sleeves or epoxy insulation to bolted joints to prevent electrical contact.
3. Surface Preparation and Anti-corrosive Coating
- Apply hot dip galvanizing, zinc rich primer, epoxy, and other anti-corrosion treatments to all steel;
- Regularly maintain the integrity of the coating to avoid paint breakage to bare metal;
- Avoid exposure of cathodic metals (e.g., stainless steel) to the external environment by coating breakage.
4. Consideration of drainage and ventilation at the design stage
- Ensure that structural nodes are not waterlogged or wet;
- Ventilation design accelerates drying and reduces electrolyte presence time;
- For exposed members, design to avoid water accumulation in crevices and dead ends.
5. Cathodic Protection (for large/critical structures)

- For high-value components such as bridges and wharves, cathodic protection can be provided by means of sacrificial anodes (e.g. zinc blocks) or applied current.
Where Are Threaded Inserts for Steel Commonly Used?

Automotive Manufacturing
Threaded inserts are widely used in automotive manufacturing for body sheet metal, chassis supports and engine mounts. As automobiles are subjected to a large amount of vibration and impact during driving, threaded inserts are fixed by high-strength riveting or welding to ensure that the connecting parts do not loosen under high loads and dynamic environments, which improves the durability and safety performance of the overall structure. At the same time, the inserts allow multiple disassembling and assembling, which is convenient for maintenance and parts replacement.
Structural frames
Threaded inserts provide a reliable bolted connection solution in steel buildings, industrial plants and equipment support frames. Compared to welded connections, the use of inserts reduces the difficulty of on-site construction, improves assembly efficiency, and facilitates future maintenance and retrofitting. Through standardized insert design, modular and fast assembly can be realized, improving construction quality and speed.
Construction Machinery
Heavy machinery such as excavators and cranes require high strength and stability of connectors. Threaded inserts can not only withstand tensile and shear forces of up to thousands of Newtons, but also maintain structural integrity under complex working conditions. Their corrosion-resistant materials and processes ensure the durability and safety of machinery in long-term use, reducing maintenance downtime due to connection failure.
Industrial equipment
Threaded inserts are used to secure critical structures and wearable parts in a variety of machinery manufacturing equipment, conveyor systems, and heavy-duty production lines. Through high-precision assembly of inserts, a balance between structural robustness and ease of disassembly is achieved, supporting regular maintenance and upgrading of equipment, extending equipment life and improving productivity.
Rail Transportation
Rail transit vehicles and rail infrastructure have extremely stringent requirements for safety and vibration durability. Threaded inserts ensure structural safety by remaining tight during the intense vibration and shock of high-speed operation. Inserts made from corrosion-resistant materials are also able to adapt to changing climatic conditions, ensuring the long-term stable operation of rail systems.
Summary: Choosing the Right Threaded Insert For Steel
Choosing the right threaded inserts for steel construction is a matter of considering the thickness of the plate, the load requirements, the installation process and the environment in which it will be used. By matching the type of insert to the properties of the steel, you not only increase the strength and durability of the connection, but also ensure assembly efficiency and ease of maintenance. Whether it is automotive, heavy machinery or precision industrial equipment, choosing the right inserts is the foundation of structural safety and performance.
With the experience and diversity of products from specialized suppliers such as Rivetfix, you can complete your selection with confidence and ensure that your project moves forward smoothly and reliably.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Why Choose Rivetfix for Threaded Inserts For Your Steel Applications

When you choose Rivetfix for different threaded inserts, you not only get a high-quality, durable and high-performance product, but also a professional and customized service. We understand the diversity of insert sizes, materials and mounting methods required for different projects, and have the advanced production facilities and technical experience to create the most suitable solution for you.
Whether it’s a standard model or a special specification, Rivetfix can respond quickly to ensure that the product is perfectly matched to your sheet metal structure, improving the strength and life of the connection.
Choose Rivetfix to make your structural steel connections stronger and more reliable, and to help your projects succeed!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.







