How to Choose PEM Nuts/Self Clinching Nuts for Aluminum?

Leading Self-Clinching Fasteners Manufacturer and Supplier in China

Choosing the right PEM Nuts (Self Clinching Nuts) for aluminum is crucial for ensuring strong, reliable, and efficient fastenings in lightweight metal structures. Whether for electronics, automotive, or industrial applications, understanding material compatibility, load requirements, and installation techniques will help you optimize performance and prevent common issues.
Table of Contents
What is PEM Nut/Self Clinching Nut?
PEM Nuts (also known as Self-Clinching Nuts) are a type of embedded fastener designed specifically for sheet metal materials. Through a cold-pressing process, these nuts are permanently fixed into metal sheets without the need for welding, adhesives, or additional parts. Their core function is to provide high-strength internal threaded holes for thin-sheet structures (such as aluminum, stainless steel, etc.), simplifying assembly processes and enhancing structural stability.

Working Principle:
The structure of a PEM nut typically includes two key design elements—the head engaging slot and the internal threads.
During installation, the nut is precisely aligned within a pre-punched hole, and pressure is applied vertically through a hydraulic press or a specialized tool. Under pressure, the serrated or raised structures at the bottom of the nut deform the sheet metal, embedding the nut’s head into the sheet material and forming a 360° ring-shaped “lock”. This process forces the nut to securely bond with the sheet metal while maintaining the integrity of its internal threads (ranging from metric M3-M12 or imperial sizes), providing a solid base for subsequent bolt connections. Ideal for use with thin materials like aluminum or other soft metals as thin as 0.5mm.
Key Advantages:
- No welding required: Avoids high-temperature distortion and protects aluminum surface treatments (such as anodizing).
- Space-saving: The embedded design requires no space for back-end operations, making it ideal for compact structures.
- Lightweight: Significantly reduces weight compared to rivets or welded studs.
- High reliability: Mechanical interlocking between metals provides long-term stability, superior to adhesive or clinching processes.
Application Examples of PEM Nuts on Aluminum Materials

a. Consumer Electronics
In the design of consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, aluminum is widely used for its light weight and excellent heat dissipation. Using PEM Nuts can simplify the assembly process, ensuring that components like batteries, displays, and internal hardware are securely fixed. Self-clinching nuts effectively embed threaded connection points into thin aluminum sheets, avoiding the complexities of traditional bolts and welding.
b. New Energy Vehicle Battery Boxes
Aluminum alloys are becoming increasingly popular in new energy vehicle battery boxes due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making them an ideal material. PEM Nuts are used for securing battery modules, providing strong and stable connection points, and reducing reliance on traditional bolts and welding. Especially in high-frequency vibration environments, the use of self-clinching nuts greatly minimizes the risk of loosening and corrosion.
c. Industrial Enclosures
In various industrial equipment, such as computer servers, control panels, and sensor devices, aluminum alloy enclosures are commonly used. PEM Nuts provide a convenient installation solution, allowing for fast and efficient fastening of internal components while reducing the difficulty of equipment maintenance and disassembly. The combination of aluminum’s advantages with PEM Nuts’ benefits results in long-term stable connections.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
How to Choose PEM Nuts/Self-Clinching Nuts for Aluminum?

1. Material Compatibility
Aluminum Characteristics:
- Soft Aluminum (e.g., 3003-H14): Offers good ductility but low strength, requiring PEM nuts with serrated or flanged designs to enhance resistance to rotation.
- Corrosion-Resistant Aluminum (e.g., 5052-H32): Commonly used in humid environments; it is recommended to pair with stainless steel nuts (e.g., 316 stainless steel) or anti-corrosion coatings.
- High-Strength Aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6, 7075-T6): High hardness and load-bearing capacity; standard PEM nuts or plated steel nuts (to avoid galvanic corrosion) are suitable.
PEM Nut Material Matching
- Stainless Steel (304/316): Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for outdoor and chemical exposure environments but more expensive. Pay attention to the aluminum’s electrochemical potential difference (ideally within 16μV) to prevent galvanic corrosion.
- Carbon Steel (Galvanized or Nickel-Plated): Cost-effective and strong but requires ensuring the coating integrity to prevent rust. Loss of coating can accelerate aluminum corrosion (insulating washers should be used).
- Titanium Alloy: Extremely light, high-strength, and biocompatible, ideal for medical or aerospace applications but costly.
Surface Treatment Considerations
Aluminum anodizing thickness should be controlled between 10-20μm. Excessively thick anodization may impact the nut’s clinching strength post-installation.
2. Load and Application Requirements
Static vs. Dynamic Loads:
- Static Loads (e.g., enclosures, brackets): Standard PEM nuts can meet requirements (e.g., PEM® FH series), focusing on thread strength (M3-M8 provides tensile strength of 500-3000N).
- Dynamic Loads (e.g., vehicle chassis, vibrating equipment): For vibration-prone environments, nuts with anti-loosening designs or additional thread-locking adhesives (e.g., Loctite 263) should be selected. The safety factor for dynamic loads should be ≥1.5.
Torque and Thread Matching:
- M3: Recommended torque is 0.5-1.5 N·m, suitable for PCB fastening.
- M6: Torque range is 8-12 N·m, appropriate for high-load scenarios such as battery enclosures.
3. Aluminum Sheet Thickness and Nut Size Compatibility
Critical Thickness Range:
- PEM nuts are typically suitable for aluminum sheet thicknesses between 0.5mm and 6mm. Check manufacturer’s “Clinch Range” specifications (e.g., PEM® FH4 nuts are for aluminum thicknesses of 1.0-3.2mm).
- Thin Aluminum Sheets (<0.5mm): Floating nuts or ultra-thin nuts (e.g., FT series) are recommended to avoid deformation.
- Thick Aluminum Sheets (>6mm): Rivet nuts or welded nuts should be selected instead.
Hole Diameter Precision Control:
The precision of the installation hole for PEM nuts is critical, typically requiring H11 tolerance (e.g., 4.3±0.05mm). Using carbide drill bits or precision punching tools is recommended to minimize burrs from aluminum chips that could affect nut engagement.
4. Environmental Factors and Special Requirements
Coastal/Chemical Environments:
It’s best to use 316 stainless steel nuts with hard anodized aluminum; alternatively, nylon washers can be added to isolate the electrolyte contact.
High-Temperature Environments (>150°C):
Avoid galvanized steel (as the zinc coating may melt) and instead use Inconel alloys (temperature resistance up to 800°C) or anodized aluminum paired with PEM Tinnerman nuts.
Consumer Electronics/Medical Devices:
Flat-head nuts (e.g., CLS series) should be used for smooth surface requirements or electropolished stainless steel nuts to meet sterilization standards.
Mass Production:
Ensure compatibility with automatic clinching equipment (e.g., pneumatic press-fit tools) with a pressure accuracy of ±5%.
How to Install PEM Nuts on Aluminum?
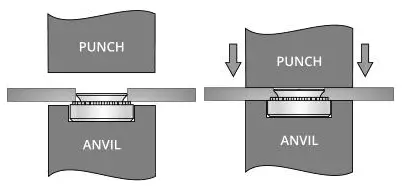
① Tool Preparation for Installation
- Hydraulic Press (Recommended tonnage range: 0.5-5 tons, adjusted according to nut size).
- Manual Press Tools (e.g., KJ Tools hand press, suitable for small batches or onsite maintenance).
- Avoid Using Hammering: Prevents aluminum deformation or misalignment of the nut.
② Installation Steps
1. Pre-Treatment of Aluminum Sheet
- Surface Cleaning: Use isopropyl alcohol to clean the aluminum surface, removing oil or oxidation layers (if not anodized).
- Marking the Position: Mark the center of the hole on the back of the aluminum sheet, ensuring the error is <0.1mm, according to the design specifications.
2. Precise Hole Drilling
- Key Parameters:
- Refer to the PEM nut specification chart for recommended hole diameter (e.g., PEM® FH4 nut corresponds to a hole diameter of Φ4.3mm).
- Tolerance Control: H11 grade (e.g., hole diameter Φ4.3±0.05mm).
- Drilling Process:
- Secure the aluminum sheet with a drill press or CNC machine and drill vertically downward.
- Recommended drilling speed: For soft aluminum (e.g., 3003), use 3000 RPM; for hard aluminum (e.g., 6061), use 2000 RPM.
- After drilling, deburr the hole using a conical deburring tool.
3. Nut Alignment and Clinching
- Alignment Techniques:
- Place the nut in a positioning fixture or guide sleeve, ensuring it is perpendicular to the hole.
- For soft aluminum (e.g., 3003), pre-apply a small amount of lubricant to the hole edge (to reduce plastic deformation resistance).
- Clinching Parameters:
- Pressure Range: 0.5-5 tons (e.g., M4 nuts require 1.2 tons, refer to the manufacturer’s technical manual).
- Clinching Speed: Low pressure and slow speed (<10 mm/s) to prevent aluminum cracking.
- Clinching Process:
- Start the press and slowly apply vertical force until the nut is fully embedded in the aluminum sheet.
- Observe the backside of the aluminum sheet for a uniform raised ring (height 0.1-0.3mm) to ensure proper engagement.
4. Quality Inspection
- Visual Inspection: The front of the nut should be flush with the aluminum surface (tolerance ±0.1mm).
- Thread Inspection: Manually screw in a standard bolt (e.g., M4-0.7); it should rotate smoothly without binding.
- Tensile Testing: Conduct random sampling using a digital torque meter to measure the pull-out force (tensile strength should be ≥ 90% of the nominal value).
③ Common Issues & Solutions
| Problem Phenomenon | Cause Analysis | Solution |
| Uneven Raised Area on the Backside of Aluminum Sheet | Misalignment or insufficient pressure during clinching | Use guide fixtures and increase pressure to the standard value |
| Stripped or Sticking Threads | Burrs not removed from the drilled hole | Re-deburr the hole and use high-precision drill bits |
| Nut Becomes Loose After Installation | Hole diameter too large or aluminum material too soft | Switch to serrated nuts (e.g., SO series) or change to stronger aluminum (e.g., 5052 instead of 3003) |
| Cracking Around Hole in Aluminum Sheet | Clinching speed too fast or pressure too high | Reduce pressure to 80% of the nominal value and use a step-by-step pressure application method |
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Choose PEM Nuts/Self Clinching Nuts for Aluminum - FAQs

Q1: What to do if PEM Nuts become loose after clinching?
- Possible Causes:
- Hole diameter is too large (exceeds H11 tolerance upper limit).
- Insufficient clinching pressure (below 80% of the recommended value).
- Aluminum material is too soft (e.g., 1100 aluminum, with low resistance to deformation).
- Solutions:
- Hole Repair: If the deviation is <0.1mm, use serrated/flanged nuts (e.g., PEM® SO series) to increase the contact surface and enhance locking strength.
- Upgrade Aluminum: Replace with higher hardness aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6 with tensile strength ≥310 MPa, better than 3003 with 145 MPa).
- Secondary Reinforcement: Apply anaerobic adhesive (e.g., Loctite 638) on the contact surface between the nut and aluminum, increasing pull-out strength by 20-30% after curing.
Q2: How to repair stripped threads after installation?
Root Cause:
Low hardness of the aluminum (Brinell hardness HB<60) or repeated disassembly causing thread wear.
Repair Solutions:
- Thread Insert (Helicoil®):
- Drill the hole to the insert’s outer diameter (e.g., for M4 stripped threads, enlarge the hole to Φ4.5mm).
- Install a stainless steel insert and apply thread adhesive for curing, restoring thread strength to 90% of the original.
- Epoxy Fill: For non-critical load-bearing holes, use JB Weld aluminum repair compound to fill the hole, cure, then redrill and clinch.
- Thread Insert (Helicoil®):
Q3: How to prevent galvanic corrosion between aluminum and the nut?
Corrosion Mechanism:
Aluminum (electrode potential -0.91V) and steel/stainless steel (electrode potential -0.50V to +0.30V) form a potential difference in electrolytic environments, accelerating aluminum corrosion.
Protection Measures:
- Material Matching: Use stainless steel (316L, potential -0.50V) or titanium alloy nuts to minimize potential difference.
- Insulation:
- Add nylon/PTFE washers (0.5-1mm thick) to isolate metal contact.
- Spray an epoxy resin coating on the nut surface (50-100μm thick, ASTM B117 salt spray test ≥500 hours).
- Active Protection: Anodize the aluminum sheet (film thickness ≥20μm) and apply a sealing agent (e.g., chromic acid).
Q4: Can PEM Nuts be reused?
Not Reusable: The clinching process causes plastic deformation of the aluminum sheet, and removing the nut will damage the mechanical interlock of the engagement grooves. If forcibly removed:
- Aluminum hole edge cracks (stress concentration areas).
- Nut head deformation, leading to loss of thread accuracy.
Repair Solution:
Redesign a new hole (with the center offset ≥ 2 times the hole diameter) and re-clinch. Seal the old hole with aluminum tape or perform welding repairs.
Q5: How to calculate the number and layout of PEM Nuts on aluminum plates?
- Core Parameters:
- Single Nut Load Capacity: Refer to the manufacturer’s “Pull-Out Strength”.
- Total Load Requirement: Estimate the structure’s static load + safety factor (usually 2-3 times).
- Distribution Guidelines:
- Dense Areas (e.g., corners of brackets): Spacing 5-8 cm.
- Uniform Areas (flat sheet structures): Spacing 10-15 cm.

With over 15 years of expertise in fastener manufacturing, Rivetfix has become a trusted global supplier. Our team of 200+ skilled workers and 40+ sales professionals ensures reliable service and consistent supply.
Partnering with Rivetfix means access to top-quality fasteners, cost-saving solutions, and custom designs. We focus on boosting your efficiency, enhancing product durability, and providing on-time delivery. Count on our expert support and continuous innovation for your fastening needs. Choose Rivetfix for premium PEM fasteners and more!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.




