How Strong Are Rivet Nuts?

Leading Rivet Nut Manufacturer and Supplier in China

The strength of rivet nuts is determined by several key characteristics, and its performance is influenced by various factors. Learn how strong rivet nuts are to help advance your project.
Table of Contents
In engineering design, the strength of a Rivet Nut is not a fixed value but is a comprehensive indicator determined by multiple mechanical properties. Different force directions, material conditions, and installation methods all affect its overall load-bearing capacity.
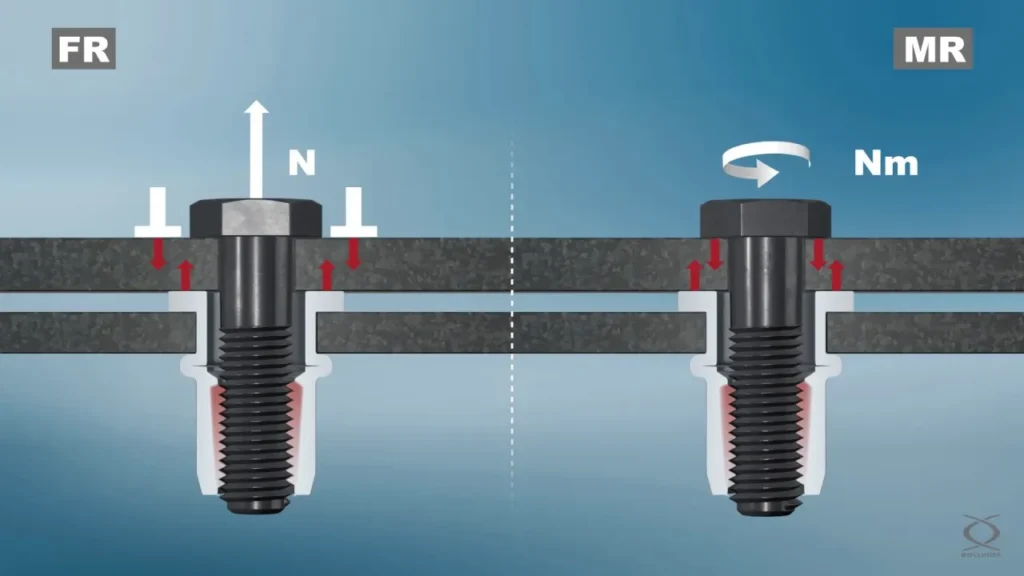
The pull-out strength refers to the maximum load at which the rivet nut is pulled out directly from the hole when subjected to force in the vertical direction. This property reflects the mechanical interlocking between the nut and the base material as well as the quality of the compression ring formation.
Generally speaking, the tensile pull force of steel Rivnuts is the highest, reaching 900–2000 lbs, while that of aluminum Rivnuts is approximately 60–70% of that. The influencing factors include: the thickness of the base material, the accuracy of the hole diameter, the riveting force and the anti-loosening structure. If the hole diameter is too large or the plate thickness is insufficient, the pull force will significantly decrease.
The shear strength refers to the ability of Rivnut to resist slipping or breaking when subjected to force in the plane direction. In most assembly scenarios (such as equipment brackets, vehicle body connections), shear loads are more common than pull-out loads.
Rivmate experimental data shows that in a standard steel plate (1.5mm thick), the shear strength of the M6 Rivnut is approximately 1,200 lbs, which is about 20–30% higher than the tensile strength. Reasonable installation hole accuracy and sufficient expansion of the rivet ring are the key to ensuring stable shear strength.
③ Torque Resistance
The torsional strength indicates the ability of Rivnut to resist rotational loosening, which is particularly crucial when tightening bolts or in vibrating environments. The torsional resistance of cylindrical Rivnut is relatively low, while ribbed or hexagonal anti-rotation structures can significantly increase the torque-bearing capacity.
Rivetfix Strength Test Data
The following table presents the test results of Rivetfix Engineering Laboratory for different material rivet nuts under standardized conditions, including their pull-out strength, shear strength and torque resistance.
All data were measured in accordance with the standards of ISO 14589 (Blind Rivet Nuts Mechanical Testing) and ASTM F606 (Fastener Strength Testing), ensuring repeatability and engineering reference value.

Rivetfix Rivet Nut Strength Chart
| Thread Size | Material | Pull-Out Strength (lbs) | Shear Strength (lbs) | Torque Resistance (in-lbs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M4 | Steel | 550 | 650 | 45 |
| M5 | Steel | 720 | 800 | 60 |
| M6 | Aluminum | 700 | 800 | 60 |
| M8 | Stainless Steel | 1,500 | 1,800 | 120 |
① Difference in Materials Determines the Strength Grade
The stainless steel Rivnut has the highest tensile and shear resistance, with an average strength approximately 25–30% higher than that of ordinary steel. Although aluminum Rivnut is lightweight, its ultimate pulling force is about 60–70% of that of steel, making it suitable for light-load and anti-corrosion scenarios. In high-load structures, Rivetfix recommends using carbon steel or stainless steel series to ensure long-term connection stability.
② Proportional Relationship Between Tensile Pullout Strength and Shear Strength
In most structural applications, the shear strength is typically 15–25% higher than the pull-out strength. This is because the shear force is distributed over a larger contact area, making the structure more evenly loaded. For instance, a M6 aluminum Rivnut can withstand approximately 800 lbs of shear force in a 2mm sheet, while the pull-out force is 700 lbs.
③ Torque performance affects the safety of installation and usage
The torsional strength represents the ability of Rivnut to resist rotational loosening.
Rivetfix test shows that Rivnuts with anti-twist teeth or hexagonal structures can increase torsional resistance by approximately 35–50%, effectively preventing loosening or rotation during tightening. For instance, the M8 stainless steel Rivnut with anti-twist structure can achieve a torque of 120 in-lbs under the anti-twist design, which is much higher than that of the ordinary cylindrical design.
Factors Affecting Rivet Nut Strength
The material of the rivet nut is the primary factor determining its strength. The strength difference among different materials can reach 2–3 times.
- Steel Rivnut: Balances strength and cost-effectiveness, suitable for most industrial applications.
- Stainless Steel Rivnut: Has slightly higher strength than carbon steel, offers better corrosion resistance, but requires greater installation tension.
- Aluminum Rivnut: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, but its tensile strength is approximately 60–70% of that of steel, making it more suitable for light-load structures.
b. Base Material Thickness
The thickness of the substrate is one of the key parameters that determine the strength performance of Rivet Nut (magnetscrew). It directly affects the quality of the crimping zone formed after riveting, the distribution of force, and the overall structural stability.
The thicker the sheet material is, the larger the force-bearing area of the rivet nut becomes, and the more fully the rivet ring is formed. Thus, the pull-out strength and shear strength are significantly enhanced.

Rivetfix Experimental Data (Base Thickness vs Pull-Out Strength)
Test conditions: M6 Steel Rivnut, installed in different thicknesses of low-carbon steel plates. The tensile test was conducted in accordance with the ISO 14589:2020 standard.
| Base Material Thickness (mm) | Pull-Out Strength (lbs) | Shear Strength (lbs) | Strength Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 830 | 1,000 | — |
| 1.5 | 950 | 1,150 | +14% |
| 2.0 | 1,080 | 1,280 | +30% |
| 3.0 | 1,260 | 1,450 | +52% |
- When the plate thickness increases from 1.0mm to 2.0mm, the tensile pull strength of M6 steel Rivnuts increases by approximately 30%. This indicates that thicker sheets can provide a more stable plastic expansion space, allowing the rivets to be more evenly distributed on the hole wall.
- Beyond 3.0mm, the increase in strength becomes relatively flat, indicating that the expansion zone of the rivet body has fully expanded. Further thickening the base material offers limited additional benefit.
- For lightweight materials (such as aluminum sheets), due to the lower strength of the base material, the contribution of thickness increase to the overall load-bearing capacity is slightly smaller, but it still improves the riveting stability.
c. Installation Accuracy
Installation accuracy is a crucial aspect for maintaining Rivnut strength. If the hole diameter is too large, the installation angle is not perpendicular, or the pull riveting force is improperly set, it will result in incomplete pressure rings, rotation of the rivet body, or insufficient clamping.
Rivetfix test results show that when the hole diameter deviation is ±0.1mm or the tensile force deviation is 20%, the overall strength will decrease by 25–30%. It is recommended to use a hydraulic or pneumatic riveting tool with force control function, maintaining a constant riveting stroke and force to ensure consistent force on each rivet nut.
d. Head Style
The head shapes of riv nuts vary, and so do their force distribution and appearance performance. Under the same conditions, the tensile pull force of the flat-head Rivnut is approximately 12–18% higher than that of the countersunk head type.
- Flat Head: Has a large contact area and the strongest anti-pulling ability, suitable for fixing structural components.
- Countersunk Head: Has a smooth and aesthetically pleasing appearance, but has slightly lower anti-pulling performance.
- Reduced Head: Used in situations with limited space or for light loads.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
1️⃣ Automotive
In the automotive industry, Rivet Nut is widely used in body panels, chassis accessories, bumper brackets and interior installation. The M6 to M8 series Rivet Nut is the most commonly used specification, capable of forming a high-strength connection in body steel plates as thin as 1.0–1.5mm.
Compared with traditional welding nuts, Rivnut not only reduces the heat-affected zone but also enables assembly after electrophoretic coating, significantly reducing production complexity. In automotive structures, anti-tightening serrations or hexagonal anti-tightening designs are preferred to resist continuous vibration and fatigue stress.
2️⃣ Aerospace
The aerospace industry has extremely strict requirements for fasteners, with a particular focus on fatigue life, weight control and anti-corrosion performance. Rivetfix’s stainless steel and aluminum Rivnuts are widely used in airframe skins, electronic compartments, instrument panels and composite material connections.
Test data shows that the M6 stainless steel Rivnut can withstand a tensile force of 1,000 lbs on a 2.0mm aluminum alloy skin, and maintains 90% of its locking strength after being subjected to fatigue loading for more than 1,000,000 cycles.
Furthermore, Rivetfix’s Dacromet or nickel-zinc coating offers more than 1000 hours of salt spray resistance, meeting the standards for aviation and marine protection.
3️⃣ Industrial Equipment
In industrial equipment and mechanical assembly, the advantages of Rivet Nut lie in quick installation, strong maintainability, and adaptability to multiple material connections.
The M5 steel rivnut from Rivetfix can stably support a 600–700 lbs of shear load in a 2mm thick steel plate. It is widely used in the assembly of control boxes, electrical cabinets, conveying equipment and mechanical enclosures. Its one-sided assembly feature significantly reduces the time for traditional processes such as welding and tapping, increasing the assembly efficiency by approximately 40% or more. For structures that require periodic maintenance, the Rivet Nut can also achieve disassemblable connections, ensuring convenient maintenance and cost control in the future.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
FAQs
Q1: How strong are rivet nuts in steel vs aluminum?
The difference in material has a significant impact on the strength of the rivet nuts.
- Steel Rivnut: The tensile strength is approximately 900–1,500 lbs, and the shear strength is about 1,000–1,800 lbs.
- Aluminum Rivnut: The strength is approximately 60–70% of that of the steel one, making it suitable for light loads and anti-corrosion scenarios.
If aluminium nuts are used on steel substrates, it is recommended to maintain a tight fit clearance of 0.1–0.2mm to prevent slippage failure.
Q2: Can a rivet nut hold as much as a weld nut?
In most applications, the tensile and shear strength of Rivet Nut can reach 80-90% of that of welded nuts. Its advantages lie in the flexibility of installation, minimal heat influence, and its applicability to coated parts and thin-walled structures.
For instance, the M8 steel Rivnut can withstand approximately 1,500 lbs of pulling force on a 1.5mm steel plate, performing similarly to a similar-sized welded nut, but without the need for welding heat treatment.
Q3: How do I test rivet nut strength?
The standard test consists of three methods:
- Pull-Out Test: Apply load in a vertical direction to determine the ultimate pull-out force.
- Shear Test: Apply force in a planar direction to verify the structural load-bearing capacity.
- Torque Test: Test the anti-rotation performance and the stability of the threaded locking.
Rivetfix engineering laboratory uses ISO 14589 / ASTM F606 standard equipment for the measurement, and the accuracy is controlled within ±2% through an automatic loading system.
Q4: Do rivet nuts loosen over time?
Under normal operating conditions, Rivnut exhibits long-term stable locking performance. However, in environments with high vibration or frequent thermal cycling, there may be slight displacement at the threaded connection, resulting in a decrease in preload. After 1,000,000 vibration cycles, the strength retention rate of standard steel Rivnut remains above 90%.
Q5: What safety factor should I use for rivet nuts?
The safety factor depends on the type of load and the working conditions:
- Static load structures (such as equipment enclosures and panels) → It is recommended to set the safety factor at 1.5× – 2×.
- Dynamic loads or vibration environments (such as vehicles and mechanical connections) → It is recommended to set at 2.5× – 3×.
- Critical structural components (such as aviation or structural supports) → The safety factor can reach 3.5× and above.

Rivetfix choose top-ranking domestic suppliers as partners, from material selecting, manufacturing, till shipment are all strictly monitored and recorded according to ISO/TS16949 management system.
As a leading fastener manufacturer in China with more than 15 years in the industry, we are committed to providing first-class quality fasteners and responsive services to the world. We can select the most suitable fasteners according to your project needs, and provide product customization services.
Contact us for project advice and the latest rivet nut quote!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.










