Guide to Using PEM Fasteners for Plastic

Leading Self-Clinching Fasteners Manufacturer and Supplier in China

Choosing the right PEM fasteners for plastic is crucial for ensuring strong, reliable, and long-lasting connections. From material compatibility to installation techniques, understanding key factors can prevent failures like cracking or loosening. This guide explores the best practices, common challenges, and expert tips to help you select and use PEM fasteners for plastic effectively in various applications.
Table of Contents
What Are PEM Fasteners?
PEM fasteners (typically referring to products from Penn Engineering & Manufacturing Corp., but have become a general term for self-clinching fasteners in the industry) are a type of self-clinching fastener specifically designed for use with thin sheet metals.
These fasteners are inserted into the sheet material under pressure, using the material’s plastic deformation to achieve permanent fixation. No welding, nuts, or adhesives are required. After installation, a secure threaded connection forms on the opposite side of the sheet, making them widely used in electronics, enclosures, automotive, and industrial manufacturing.
Types of PEM Fasteners
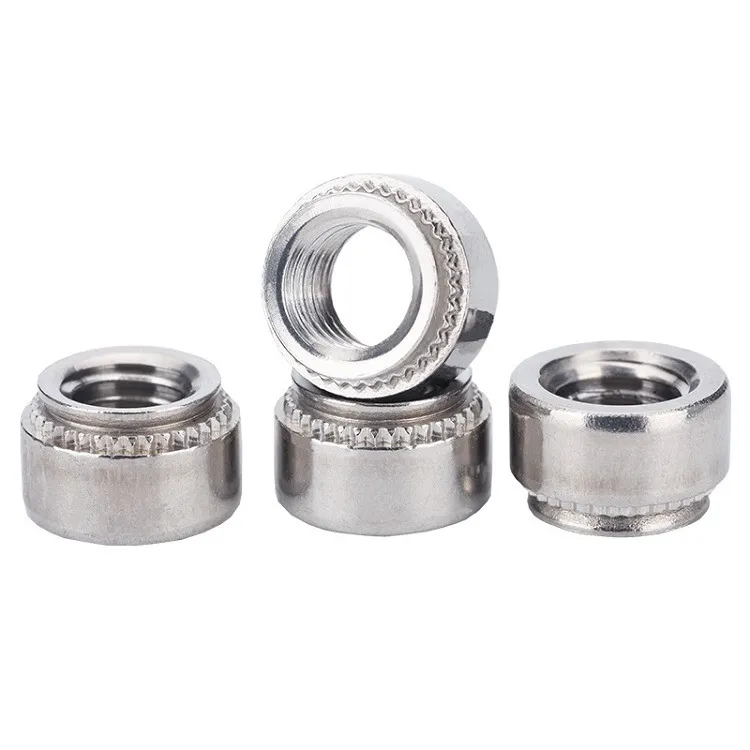
- Structure: A fastener with internal threads, which forms a reliable threaded hole on the backside of the sheet once inserted.
- Installation Method: Requires a pre-drilled hole in the metal sheet, which is then pressed in using a press machine. The sheet material deforms to lock the fastener in place.
- Applications: Panels, equipment enclosures, and brackets that require frequent disassembly, often used for bolted connections.
- Advantages: High tensile strength, supports repeated assembly, saves space.


- Structure: One end has external threads, while the other end is a fastening end that embeds into the sheet material. The external threads protrude from the surface once installed.
- Installation Method: Inserted after pre-drilling, fixed by the deformation of the sheet material.
- Applications: Components requiring external threaded connections, such as fixing sensors, panel accessories, or stacked components.
- Advantages: Provides stable external threads, avoids welding or additional nuts, ideal for automated installation.
- Structure: Hollow or threaded columns, with internal or external threads at both ends, used to maintain spacing between components.
- Installation Method: Pressed into the sheet to form a fixed support point.
- Applications: Used for circuit board support, device stacking, and heat sink mounting, where spacing is required.
- Advantages: Combines both connection and support functions, resistant to vibration, reduces component wear from contact.

Key Advantages and Considerations
Advantages:
- Saves space, simplifies assembly processes, and reduces costs.
- Suitable for thin sheets (0.5-3mm thickness) with materials that have certain ductility (such as aluminum or low-carbon steel).
- High tensile and torsional strength, supports heavy-duty applications.
Considerations:
- Installation requires precise pre-drilled holes; incorrect hole size or pressure may lead to failure of fixation.
- Once installed incorrectly, removal without damage is difficult.
- Material and thread types (such as metric/imperial) need to be chosen based on the application requirements (e.g., stainless steel for corrosion resistance).
Why Use PEM Fasteners on Plastic?
1. Why Choose Plastic?
With the continuous development of industrial design, plastic materials have become widely used in various industries due to their lightweight, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
- Lightweight: The density of plastic is much lower than that of metals, making it the preferred material in industries such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and consumer electronics for reducing product weight and improving energy efficiency.
- Corrosion Resistance: Compared to metals, plastic does not rust and can resist chemical corrosion, making it suitable for medical devices, food processing equipment, and outdoor products.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The production cost of plastic is relatively low, and it can be mass-produced through methods like injection molding, which reduces manufacturing costs.
- Design Flexibility: Plastic can be molded into complex shapes, making it ideal for products that require precise structures or special functions.
2. Challenges of Using Fasteners on Plastic
Despite the numerous advantages of plastic, its material properties necessitate special consideration when using fasteners, particularly with respect to brittleness, heat resistance, and creep. If these factors are not accounted for, they may impact the long-term performance and safety of the fasteners.
Brittleness of Plastic
- Some plastics (such as ABS, PS, etc.) are prone to cracking or breaking under external forces, especially during the installation of fasteners. If excessive pressure or torque is applied, the plastic may crack or the threads may fail.
- When designing fastening solutions, it is essential to choose the appropriate type of PEM fastener and ensure that the installation pressure does not exceed the plastic’s tolerance.
Low Heat Resistance
- Many plastics have heat resistance that is far lower than that of metals. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to material softening, deformation, or even failure.
- For example, nylon (PA) can absorb moisture and change size at high temperatures, while polycarbonate (PC) may become brittle in elevated heat.
- Therefore, when choosing PEM fasteners, it is important to avoid fasteners that require high-temperature press fitting or welding methods and consider the impact of temperature on the connection strength.
Creep Phenomenon
- Plastic materials may experience creep, a slow deformation under sustained pressure (such as the ongoing pressure from a fastener), which can lead to loosening or failure of the connection.
- To reduce the effects of creep, PEM fasteners with larger bearing surfaces can be selected, such as self-locking nuts with flanges or fasteners specifically designed for plastic applications.
Which PEM Fasteners Are Suitable for Plastic?
1. Material Compatibility Analysis
When selecting PEM fasteners, it is essential to consider the compatibility between the fastener material and the plastic substrate. Mismatched material properties may lead to connection failure or corrosion issues.

ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene)
- Characteristics: Moderate strength, good toughness, easy to process
- Suitable PEM Materials: Stainless steel, aluminum
- Caution: Avoid using high-strength fasteners, as excessive pressure may cause the plastic to crack.
Nylon (PA)
- Characteristics: Wear-resistant, impact-resistant, highly hygroscopic
- Suitable PEM Materials: Stainless steel, galvanized steel
- Caution: Since nylon is highly hygroscopic, long-term exposure to high humidity may lead to dimensional changes. Choose an appropriate fastening method.
Polycarbonate (PC)
- Characteristics: High transparency, high strength, excellent impact resistance
- Suitable PEM Materials: Aluminum, stainless steel
- Caution: Avoid high-pressure installation. It is recommended to use low-pressure embedded fasteners.
2. Avoid Electrolytic Corrosion Combinations
Electrolytic Corrosion (Galvanic Corrosion) Principle: When two different metals are in contact in an electrolyte (such as water or salt spray), the potential difference drives the anode metal (e.g., aluminum) to accelerate oxidation and corrosion.
Form 1:Key Risk Combinations and Solutions
| Risk Combination | Corrosion Mechanism | Solution |
| Aluminum + Stainless Steel | Aluminum acts as the anode and undergoes oxidation in a wet environment | – Use anodized aluminum (to add a surface insulating layer)- Isolate the two metals (e.g., with plastic seals) |
| Aluminum + Copper Alloys | Copper acts as the cathode, accelerating aluminum corrosion (especially in marine environments) | Avoid direct contact; replace copper components with passivated stainless steel |
| Low Carbon Steel + Nylon | Steel oxidizes and rusts in moist nylon | Replace with 316 stainless steel or galvanized steel, or add a rust-resistant coating |
Note: For high-humidity or salt-spray environments (e.g., automotive undercarriages, marine equipment), it is best to choose fasteners made from the same material or use insulating coatings (e.g., anodized aluminum, passivated stainless steel).
3. Optimized PEM Fastener Design for Plastics
Structural Enhancements:
- Ring-shaped Barbs/Knurled Designs: Increase mechanical engagement between the plastic and PEM (ideal for brittle plastics like PC).
- Flanged Design for Larger Contact Surface: Distribute stress and reduce creep risk (e.g., PEM® FH series).
- Hollow Weight Reduction Structure: Aluminum PEM reduces weight (ideal for fiberglass-reinforced nylon frames).
Surface Treatments:
- Aluminum PEM: Anodizing (for corrosion resistance), PTFE coating (to reduce frictional heat).
- Stainless Steel PEM: Passivation, nickel plating (for chemical resistance).
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
How to Install PEM Fasteners on Plastic?

1. Pre-Installation Preparation
Hole Design
- Hole Diameter: The hole diameter should be 0.05-0.15mm larger than the outer diameter of the PEM fastener (adjusted based on the plastic’s toughness):
- Brittle Plastics (e.g., PC): Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations strictly (e.g., SP-5 nut hole should be 5.20±0.05mm).
- Tough Plastics (e.g., Nylon): The hole diameter can be slightly smaller to improve the engagement force (e.g., leave 0.05mm expansion space).
- Hole Depth: Ensure the PEM fastener is fully embedded with at least 0.3mm clearance at the bottom to prevent compression cracking.
- Chamfering: Process a 0.1-0.3mm chamfer on the hole edge to avoid stress concentration and cracking during installation (as shown in the diagram below).
Surface Treatment
- Cleaning: Wipe the installation area with isopropyl alcohol to remove mold release agents or grease.
- Deburring: Use a deburring tool or fine sandpaper (#800 grit) to polish the hole walls for smoothness.
2. Installation Methods
Heat Pressing:
- Heat pressing is suitable for applications requiring higher holding strength. By heating the plastic to its softening point, it becomes more responsive to physical or chemical interactions with the PEM fastener.
- Temperature control is crucial; excessive heating can lead to plastic over-softening or deformation. Set the appropriate heating temperature based on the material properties of the plastic.
- After heating, apply pressure to press the PEM fastener into the plastic substrate.
Ultrasonic Welding:
- Ultrasonic installation is ideal for high-volume production, using ultrasonic vibrations to embed the PEM fastener into the plastic.
- This method is efficient and suitable for precise control, commonly used in electronics or automotive industry plastic components.
- When using ultrasonic welding, calibrate the amplitude and time parameters to ensure correct embedding and prevent damage to the plastic surface.
Cold Pressing:
- Cold pressing uses simple tools to press the PEM fastener directly into a pre-designed hole. This method doesn’t require heating equipment and is easy to operate.
- However, special attention must be paid to pressure control, as excessive pressure may lead to deformation or cracking of the plastic. Cold pressing is generally used for thin-walled plastic or small components.
Form 2: Summary of Installation Methods
| Method | Applicable Scenarios | Key Parameters | Precautions |
| Heat Pressing | Thermoplastic plastics (e.g., ABS, PC, PA) | – Heating temperature: 10-15°C below softening point (e.g., heat ABS to 85-90°C, Nylon to 200-220°C)- Pressure: 0.5-3MPa, hold for 3-5 seconds | ① Heating time ≤ 10 seconds, avoid plastic charring② Evenly preheat the hole area using a heat gun |
| Ultrasonic Welding | High-volume production (e.g., POM, PET) | – Amplitude: 20-40kHz- Time: 0.5-2 seconds- Pressure: 1-2MPa (with ultrasonic generator) | ① Too high amplitude may melt the plastic② Frequency calibration needed for matching plastic density |
| Cold Pressing | High-rigidity plastics (e.g., glass-filled PBT, PEEK) | – Pressure: 2-5MPa (based on plastic compression strength)- Speed: Slow pressing (0.5-1mm/s) to reduce impact force | ① Only for short-glass fiber reinforced plastics② Hole diameter must match tolerance ±0.03mm |
3. Tool List
- Heat Pressing Tools: Heat plates, temperature control systems, heating molds.
- Ultrasonic Installation Equipment: Ultrasonic welding machine, amplitude adjuster.
- Cold Pressing Tools: Press machines, riveting tools, molds.
- Auxiliary Tools: Hole diameter measurement tools, deburring tools, cleaning agents.
4. Common Issues and Solutions
- Cracked Hole Walls: Check if the hole diameter is too small or if the insertion speed is too fast (switch to step-by-step pressure application).
- PEM Fastener Loosening: Replace with PEM fasteners featuring barbed designs (e.g., PEM® SJ Series) or increase the contact area (expand flange width).
- Thread Damage: Apply a small amount of lubricant (e.g., PTFE-based lubricant) before installation to prevent direct friction between the metal and plastic.
What Are the Application Cases of PEM Fasteners in Plastics?

1. Automotive Industry
Case: Instrument Panel Bracket Fastening
Due to frequent vibrations and impacts within the car interior, self-clinching nuts (Self-Clinching Nuts) are used to provide stable connections, ensuring the secure installation of components. Additionally, these fasteners are easy to maintain and replace, contributing to improved vehicle maintenance efficiency.
2. Medical Equipment
Case: Portable Ultrasound Machine Housing
These fasteners can withstand high-temperature sterilization processes and ensure the long-term reliability of fasteners in strict environments, offering efficient and secure connections. In medical devices, PEM fasteners ensure durability and performance, even under stringent conditions, ensuring patient safety.
3. Consumer Electronics
Case: Ultra-Thin Laptop Metal Bracket Fastening
Press-fit nuts (PEM Press-Fit Nuts) are used to connect structural components to the housing, balancing strength and weight. In electronic devices where lightweight designs are essential, PEM fasteners provide the necessary fastening force and stability without adding excess weight, enhancing the overall performance and portability of the device.
4. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Devices
Case: Outdoor Sensor Housing
IIoT devices often operate in harsh environments, requiring fasteners that offer high strength, corrosion resistance, and long-term stability.
PEM fasteners, such as self-clinching nuts and press-fit nuts, provide strong connection forces. These fasteners ensure the devices remain reliable in environments with continuous vibrations, high temperatures, or humidity fluctuations. The application of these fasteners not only enhances the device’s performance but also simplifies the installation and maintenance processes.
5. Emerging Fields: Drones and Robots
Case: Collaborative Robot Joint Cover Plates
Drones and robots often require compact and lightweight designs, and PEM fasteners offer a sturdy yet lightweight connection solution that meets the dual demands of weight and strength.
In the robotics field, PEM fasteners are used to secure robot joints and drive system components, providing long-term stable connections. These fasteners support high-frequency operations and high-load usage, significantly improving the operational efficiency and safety of robots and drones.
Key Notes & Tips
Material Compatibility
Ensure the chosen PEM fastener is compatible with the plastic or other base materials. Different types of plastics (such as ABS, Nylon, Polycarbonate, etc.) and PEM materials (like stainless steel, aluminum) have distinct chemical and physical properties. It’s advised to avoid material combinations that might cause electrochemical corrosion, especially in wet or chemically exposed environments. Thoroughly understand the expansion, contraction, and other characteristics of plastics to ensure the long-term stability of the PEM fasteners.
Environmental Adaptability
Choosing the appropriate PEM fastener for the specific application environment is critical. For high temperatures, high humidity, or chemically corrosive environments, choose PEM fasteners made of materials like stainless steel that have superior corrosion resistance. For environments with significant mechanical vibration, select PEM fasteners with higher fatigue resistance. Understanding the specific environmental requirements will ensure the durability and reliability of the connection.
Tips to Avoid Failure
- Avoid Excessive Installation Pressure: Too much pressure during installation may cause plastic cracking or PEM fastener failure. Ensure the installation pressure stays within the recommended range and adjust it based on the type of plastic used.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Especially in environments with vibration, impact, or high loads, regularly check the fastening effectiveness and connection strength of PEM fasteners to avoid loosening or fatigue failure.
- Avoid Prolonged Exposure to High Temperatures or Chemical Environments: Even heat-resistant PEM fasteners should not be exposed to extreme conditions for extended periods. Ensure the materials and coatings used are suitable for the specific environmental conditions before installation.
Question: Is it suitable to use PEM fasteners in plastic?
- Is the long-term load > 50N?
- No → Consider molded threads.
- Yes → Proceed to step 2.
- Does the base material contain fiberglass/carbon fiber reinforcement?
- No → Assess creep characteristics.
- Yes → Proceed to step 3.
- Is frequent disassembly required?
- No → Use adhesives for securing.
- Yes → PEM fasteners are preferred.
Final Check: If both temperature fluctuations < 80°C and material toughness > are met, PEM is applicable. Otherwise, use thermoplastic inserts.
FAQs - Using PEM Fasteners for Plastic

Q1: What to Do if Radial Cracks Appear After Press-Fitting in Plastic Holes?
Plastic hole cracking is typically caused by the following factors, with corresponding solutions:
1. Hole Diameter Too Small or Tight Tolerances:
- Calculation Standard: The hole diameter should be 0.5%-1% larger than the PEM fastener’s outer diameter (e.g., for a 4mm PEM, the hole should be 4.02-4.04mm). For brittle plastics (like PC), an additional 0.05mm expansion tolerance is required.
- Case Example: An ABS medical device housing had cracking due to a hole diameter that was too small (tolerance ±0.01mm). The solution was to increase the hole diameter by +0.08mm and add a 0.2mm chamfer, reducing the cracking rate from 15% to 0%.
2. Mismatch Between Installation Pressure and Speed:
- Pressure Gradient Optimization: Use staged pressure application (e.g., 30% pre-pressure → 60% main pressure → 10% hold pressure) to avoid sudden impacts.
- Device Parameters: For Nylon (PA66), a press-in speed ≤2mm/s with impact energy <5J is recommended.
3. Material Toughness Insufficient:
Alternative Solution: Use glass fiber-reinforced plastics (e.g., PA6-GF30) which increase crack resistance by 50%, or switch to PEM fasteners with stress-relief grooves (e.g., PEM® SF series).
Q2: How to Choose Plastic and PEM Combinations for High-Temperature Environments?
Form3:Material Compatibility
| Plastic Type | HDT (1.8MPa) | Recommended PEM Material | Maximum Applicable Temperature | CTE Matching Solution |
| PPS | 260°C | 316 Stainless Steel | 200°C | Reserve 0.1mm gap to compensate for CTE differences (PPS: 54×10⁻⁶/°C vs 316: 17×10⁻⁶/°C) |
| PEI | 210°C | Titanium Alloy (Grade5) | 180°C | Thermal conductive adhesive for interface (e.g., Dow Corning® 1-4173) |
| LCP | 310°C | Nickel-based Alloy (Inconel 718) | 280°C | Wavy flange design to absorb expansion stress |
Enhanced Measures:
- Thermal Isolation Design: Design air circulation channels around the PEM to reduce heat transfer (temperature difference reduction of 30-50°C).
- Case Example: An electric vehicle battery cover using LCP + Inconel 718 PEM performed 2,000 hours at 140°C without loosening during cyclic testing.
Q3: How Many Times Can PEM Fasteners Be Disassembled? How to Maintain Them?
The number of disassemblies depends on the type of PEM fastener, plastic substrate, and thread design:
- Self-clinching PEM fasteners can typically be disassembled 2-3 times, but it’s recommended to check the threads for damage after each disassembly.
- Press-fit PEM fasteners are usually single-use because they form a tight connection with the base material, making them unsuitable for frequent disassembly.
Q4: How to Quickly Verify the Reliability of PEM Installation?
A simple four-step verification method:
- Visual Inspection: Check for visible cracks or deformation (using a 10x magnifying glass).
- Torque Testing: Apply the nominal torque (e.g., for an M3 nut, 1.5Nm) and maintain for 30 seconds without stripping or rotation.
- Pull-Out Force Sampling:
- Standard: Axial pull-out force should be ≥5 times the expected working load (e.g., for a 50N load, test should be ≥250N).
- Tool: Digital force gauge (e.g., IMADA ZTA-500N).
- Thermal Cycling Test:
- Conditions: -40°C (30min) → 85°C (30min), cycle 50 times.
- Acceptance: Displacement <0.1mm, torque decay <10%.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
What Are the Recommended PEM Fasteners Suppliers?

1. Rivetfix
Rivetfix is a leading supplier of Rivet Nuts and Self-Clinching Fasteners in China, specializing in providing a wide variety of high-quality PEM fasteners. It is particularly skilled in improving the strength and performance of rivet nuts.
Rivetfix offers custom services to ensure that products meet the demands of various industries, including electronics, automotive, and construction.
PEM is a globally renowned fastener brand that offers a wide range of PEM nuts, rivets, screws, and other products.
PEM’s products are widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, defense, medical, and industrial sectors. Their PEM fasteners are known for their excellent durability and high load-bearing capacity, especially suitable for connecting thin-walled metals and plastics. PEM’s fastening technology has been developed through years of innovation and is favored by many well-known companies worldwide.
Hilti is an internationally known supplier ·of construction and industrial equipment, providing a wide range of PEM fasteners and connection solutions, mainly for the construction, facility management, and mechanical assembly industries.
The PEM fasteners provided by Hilti have high tensile strength and seismic resistance, making them particularly suitable for applications that require high strength and long-term durability. In addition to PEM nuts, Hilti also provides related tools and equipment to help customers achieve more efficient installations.
Böllhoff is a Germany-based company that specializes in high-quality PEM fasteners and connection technology. Their PEM products are widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and mechanical industries.
Böllhoff offers a full range of connection solutions, including rivets, nuts, and clinch elements. The company is committed to providing high-performance fasteners that maintain stability and durability in demanding environments. Böllhoff also offers customized services to meet clients’ individual needs.
Stanley Engineered Fastening offers a wide range of PEM fasteners and engineering solutions, widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, home appliances, and aerospace.
The company is known for its efficient and innovative fastening solutions, and its PEM series products are renowned for their high reliability, corrosion resistance, and strength. Stanley provides comprehensive customer support, from the design phase to technical assistance, ensuring efficient connections in various complex environments.

With over 15 years of expertise in fastener manufacturing, Rivetfix has become a trusted global supplier. Our team of 200+ skilled workers and 40+ sales professionals ensures reliable service and consistent supply.
Partnering with Rivetfix means access to top-quality fasteners, cost-saving solutions, and custom designs. We focus on boosting your efficiency, enhancing product durability, and providing on-time delivery. Count on our expert support and continuous innovation for your fastening needs. Choose Rivetfix for premium PEM fasteners and more!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.




