What is a Self Clinching Stud/Pem Stud?

Leading Self-Clinching Fasteners Manufacturer and Supplier in China
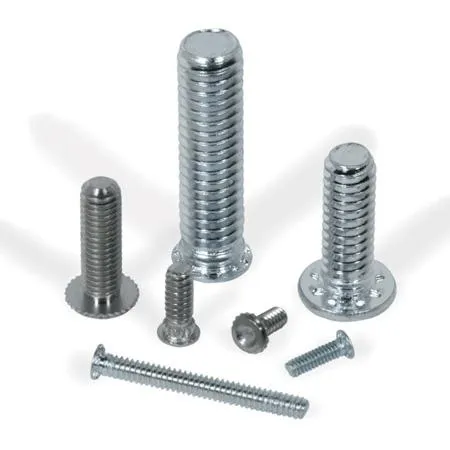

Learn “what is a Self-clinching Stud/Pem Stud” to help you quickly create reliable threaded interfaces for your sheet materials (e.g. metal, plastic).
This innovative fastener is embedded in the sheet through a cold-pressing process and uses a mechanical interlock between the serrated head and the material to form a high strength thread on one side. Withholds vibrations and loads without welding or tapping, making it a key player in sheet assembly for electronics, automotive and aerospace.
Table of Contents
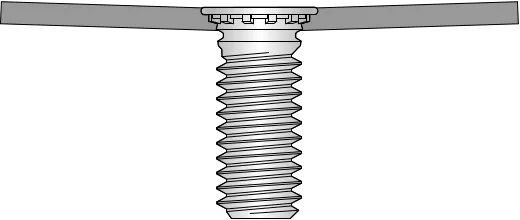
What are Self Clinching Studs/Pem Studs?
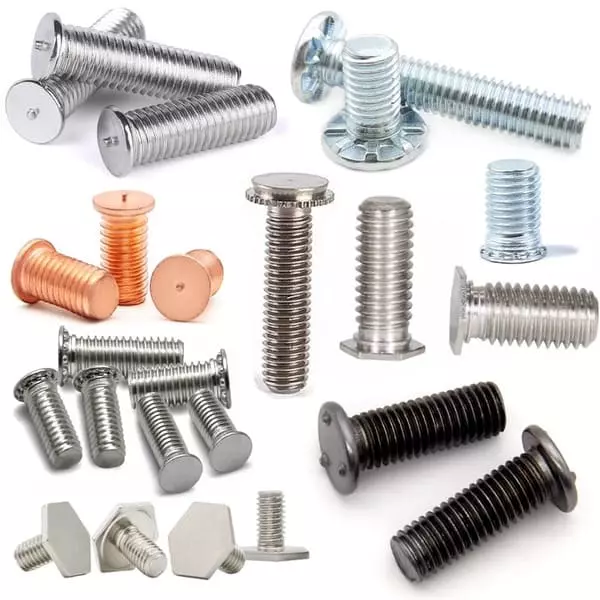

Self Clinching Studs (commonly referred to as Pem Studs, named after the industry-standard brand PEM®) are threaded fasteners designed to embed permanently into thin sheet materials (e.g., metal, plastic). They are installed using pressing tools or machinery, which deforms their pre-engineered features (like knurled collars or serrations) to lock into a pre-drilled hole, creating a durable threaded anchor without welding, adhesives, or secondary operations.
These studs are widely used in electronics, automotive panels, and industrial enclosures where lightweight materials require reliable, high-strength threads. Their installation preserves material integrity, resists rotation/torque, and simplifies assembly.
Structure:
- Head: Typically features serrations or knurling that interlock with the hole wall when pressed into the sheet material, preventing the stud from rotating or detaching.
- Threaded Shank: Standard metric or imperial threads (e.g., M3, M4) to allow attachment of bolts or nuts.
How to Install Self Clinching Studs?
a. Installation Steps
1. Prepare Tools and Materials
- Pressing Tools: Hydraulic presses, pneumatic presses, or specialized manual crimping tools (must match the stud specifications).
- Drilling Tools: Drill presses or punching machines for precise hole diameter control.
- Stud Selection: Ensure the stud matches the sheet material (metal/plastic), thickness, and thread requirements (e.g., M3/M4).
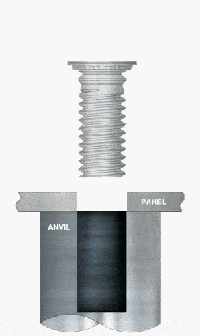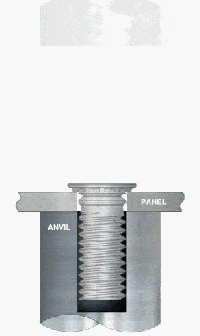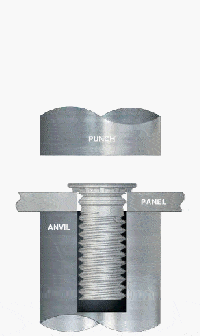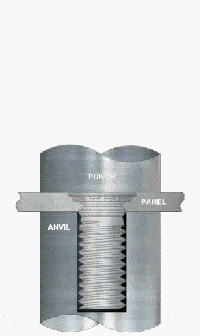
2. Create Pre-Drilled Holes
- Drill a hole of precise diameter in the sheet material based on the stud model (typically 0.05–0.1mm smaller than the stud’s shank diameter).
- Ensure the hole edges are burr-free and undamaged (to avoid compromising installation quality). Use deburring tools if necessary.
3. Position the Stud
- Align the stud’s head (serrated/knurled end) with the hole and press it flat against the sheet surface.
- Ensure Vertical Alignment: Avoid tilting, as misalignment may cause installation failure or reduced strength.
4. Apply Pressure for Installation
Use the pressing tool to apply steady, perpendicular pressure on the stud head.
Pressure Control: Adjust based on stud specifications and material (typical industrial press force: 0.5–5 tons).
When critical pressure is reached, the stud’s serrations/knurlings displace the material, causing plastic deformation to form a mechanical interlock within the stud’s grooves.
5. Inspect Installation Quality
- Visual Check: Confirm the stud head is fully embedded in the sheet surface with no tilting or protrusion.
- Torque Test: Use a torque wrench to verify thread strength (e.g., recommended torque for M3 studs: 2–3 N·m).
- Pull Test (Optional): For critical applications, use a tensile tester to validate pull-out resistance.
b. Notice
Hole Diameter Compatibility:
- Oversized holes cause loose fittings; undersized holes risk sheet cracking or installation failure.
- Ensuring Hole Accuracy:Consult technical manuals (e.g., PEM® specifications) for standard hole diameters (e.g., 3.2±0.05mm for M3 studs).General formula: Hole Diameter ≈ Stud Shank Diameter + (0.05–0.1mm), adjusted for material and design.
Sheet Thickness Limits:
Typically suits sheets 0.5–6mm thick; thicker materials require specialized stud designs.
Avoid Reinstallation:
Replace failed studs or relocation holes; never re-press a damaged stud.
Material Hardness Differences:
Harder sheets (e.g., stainless steel) may require higher installation pressure.
c. Possible Causes of Installation Failure
- Incorrect hole diameter or rough hole walls.
- Mismatched pressing tools and stud specifications (e.g., insufficient pressure).
- Material incompatibility (e.g., galvanic corrosion from pairing carbon steel studs with aluminum sheets).
Advantages of Self Clinching Studs

①. Simplified Installation
No Welding, Gluing, or Threading
Cold-Forming Pressure Process:
Self-clinching studs are embedded using controlled mechanical force (typically 0.5–5 tons) that plastically deforms the sheet material around the stud’s knurled head.
Eliminates Heat Risks:Unlike welding, no thermal energy is involved, preventing warping, microstructural changes, or surface damage in thin sheets (e.g., 0.5mm aluminum or 1mm stainless steel).
No Secondary Adhesives:Avoids curing time, off-gassing, or bond degradation in high-temperature environments (common in automotive engine bays).
Omits Tapping:Ideal for brittle or hard materials like fiberglass or 316 stainless steel, where traditional threading might crack the sheet.Applicability:
Fast Production Cycles: 2–3 seconds per stud with automated presses (vs. 30+ seconds for welding + cleaning).
Example: Automotive assembly lines install 200–300 studs/hour with robotic arms.
Single-Step Process
- Tool Standardization:Compatible with universal press tools (e.g., PEM®-style dies) or custom fixtures for niche applications.
- Operator Ease:Minimal training required—alignment and press activation are the primary actions.
- Cost Impact:Reduces labor costs by 40–60% compared to welding or threaded inserts, especially in high-volume sectors like consumer electronics.
②. Material Integrity Preservation
Cold Work Process
Heat-Free Bonding:
- Coating Protection: Critical for pre-anodized aluminum or zinc-nickel plated steel used in outdoor enclosures.
- No Annealing Zone: Maintains material hardness (e.g., 6061-T6 aluminum retains its temper).
Delicate Material Compatibility:
- Thermoplastics: Nylon or ABS sheets won’t melt or deform during installation.
- Thin-Gauge Metals: Works on foil-thin copper (0.25mm) without tearing.
No Backside Access Required
Flush Mounting: Leaves no protrusions on the reverse side, enabling:
- Aerodynamic surfaces in UAV components.
- Sanitary finishes in food processing equipment.
Space-Constrained Applications:
- Embedded in PCB mounting plates without interfering with circuitry.
- Used in wearable tech for slim-profile housings.
③. High-Strength, Durable Fastening
Mechanical Interlock
Engineering Design: Stud head serrations (depth: 0.1–0.3mm) force material to flow into grooves, creating a bond stronger than the base sheet.
Tested Performance:
- Vibration Resistance: >10,000 cycles at 50Hz (meets MIL-STD-810G).
- Torque Capacity: M4 studs in 2mm steel withstand 15–25 N·m (vs. 5–10 N·m for tapped threads).
- Pull-Out Strength: M6 studs in 3mm aluminum hold >3,000 N axial load.
Consistent Load Distribution
Stress Analysis:Finite Element Analysis (FEA) shows stress spread over 5–10x the stud diameter, reducing fatigue failure risks.
Real-World Use:
- Aerospace: Engine bay panels handle thermal cycling without fastener loosening.
- Renewable Energy: Solar racking systems endure wind loads of 150 km/h.
④. Versatility
Broad Material Compatibility
- Aluminum: Grades 5052, 6061 (common in automotive body panels).
- Steel: Mild, galvanized (HVAC ducting), and high-strength alloys (AR400 for mining equipment).
- Stainless Steel: 304/316 (marine environments).
- Plastics: Engineering Grades: PEEK (medical devices), Ultem (aerospace).
- Composites: CFRP (carbon fiber) used in drones and racing components.
Range of Sizes and Configurations
- Metric Threads: M2 (for microelectronics) to M12 (structural frames).
- Imperial Threads: #4-40 (optics mounts) to ½”-13 (industrial machinery).
- Specialized Designs:
Blind Studs: Seal fluid pathways in hydraulic systems.
Floating Studs: Accommodate ±0.5mm misalignment in assemblies.
Disadvantages of Self Clinching Studs
1. Limited to Thin Sheet Materials
- Thickness Constraints:
Designed for sheets between 0.5–6mm thick. Thicker materials (>6mm) may require specialized studs or alternative fastening methods (e.g., welding), increasing cost and complexity. - Hardness Limitations:
Extremely hard materials (e.g., hardened steel) may resist deformation during installation, leading to incomplete interlocks or tool wear.
2. Strict Hole Tolerance Requirements
- Precision Drilling Necessary:
Holes must match stud specifications within ±0.05mm. Deviations cause poor engagement (loose studs) or sheet damage during pressing. - Cost of Quality Control:
Requires precise drilling tools (e.g., CNC machines) and rigorous inspection (go/no-go gauges), adding upfront costs for small-scale users.
3. Permanent Installation (Non-Reusable)
- Irreversible Process:
Once installed, removing a self-clinching stud typically damages the hole or sheet, forcing replacement of the entire component in critical assemblies. - No Field Adjustments:
Misaligned studs often necessitate scrapping the part, especially in high-value applications like aerospace or medical devices.
4. Material Compatibility Risks
- Galvanic Corrosion:
Pairing dissimilar metals (e.g., stainless steel studs in aluminum sheets) without protective coatings can accelerate corrosion in humid or saline environments. - Plastic Deformation Limits:
Brittle plastics (e.g., acrylic) may crack during installation due to cold-forming pressure.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
What is the Difference Between Weld Studs and Clinch Studs?
| Feature | Weld Studs | Clinch (Self-Clinching) Studs |
| Installation | Welding (heat-based). | Cold-forming pressure. |
| Heat Generation | Yes (risk of warping). | No (ideal for sensitive materials). |
| Material Thickness | Best for thick metals (>3mm). | Designed for thin sheets (0.5–6mm). |
| Material Types | Metals only (conductive). | Metals, plastics, composites. |
| Strength | High (metallurgical bond). | Moderate (mechanical interlock). |
| Surface Finish | May require post-processing. | Clean, flush finish. |
| Reusability | Not reusable. | Not reusable. |
| Applications | Heavy-duty structural parts. | Thin-sheet assemblies (electronics, auto). |
When to Choose Each
- Weld Studs: High-strength, thick-metal applications where heat is acceptable (e.g., construction, industrial equipment).
- Clinch Studs: Thin, lightweight assemblies requiring clean finishes and no heat (e.g., consumer electronics, automotive panels).
Why Buy Self Clinching Studs from Manufacturer?

1. Cost Reduction and Elimination of Intermediaries
- No Middleman Markup: Direct procurement eliminates additional profit margins from distributors or agents, reducing bulk purchase costs.
- Volume Discounts: Manufacturers often offer discounts or tiered pricing for large orders, ideal for customers with long-term, fixed needs.
- Reduced Inventory Risk: On-demand custom production lowers the financial pressure of excess stock accumulation.
2. Strict Quality Control
- Source Control: Manufacturers have standardized production lines and inspection processes (such as ISO certification) to ensure every fastener meets uniform specifications (tolerance ±0.01mm).
- Material Traceability: Customers can specify materials (e.g., 304 stainless steel, aluminum alloys) and receive material certificates (Material Certificates).
- Quick Issue Resolution: Production defects are directly communicated to the manufacturer, avoiding third-party delays. For example, if coating is uneven, the process can be immediately adjusted.
3. Highly Customizable Services
- Flexible Specification Design: Custom thread sizes (e.g., M2 to M12), head shapes (e.g., round or flat), knurl depth, and more can be tailored to meet needs.
- Example: Custom fasteners with non-toxic passivation for medical devices.
- Special Materials and Processes: Options like corrosion-resistant passivated stainless steel, lightweight titanium alloys, and high-temperature plastic compatibility.
- Small Batch Prototyping: Initial samples can be produced to test design feasibility, avoiding excess inventory buildup.
4. Technical Support and Collaborative Innovation
- Installation Guidance: Manufacturers provide compression process manuals or on-site training to ensure proper tool usage (e.g., pressure tonnage range).
- Common Issues: A hole that is too large may lead to looseness, while one that is too small could cause sheet metal cracking.
- Joint R&D Capabilities: For unique applications (e.g., high-vibration environments), fastener structures can be jointly developed, such as increasing tensile strength for automotive battery panels.
- After-Sales Issue Resolution: If loosening occurs after installation, quick troubleshooting can address issues like hole diameter deviation or material hardness problems.
Building Sustainable Collaboration with Rivetfix

With 15+ years of experience in fastener manufacturing, Rivetfix has grown into a trusted global supplier. Today, we have a dedicated team of 200+ skilled production workers and 40+ professional sales representatives, ensuring seamless service and reliable supply.
Our vision is simple yet powerful: to provide the highest-quality fasteners at competitive prices to customers worldwide. By combining precision manufacturing, efficient operations, and exceptional customer support, we are committed to helping businesses build stronger, more cost-effective solutions.
Partnering with Rivetfix means stable supply, top-quality fasteners, and custom solutions. We help you cut costs, boost efficiency, and enhance durability. Expect on-time delivery, expert support, and innovation. Let’s grow together!
Get High Quality Rivet Nuts Quote!
Send Your Rivet Nut Request
For more than 20 years, Rivetfix has helped customers solve many rivet nuts sourcing needs and technical challenges.
Have a question? Contact us and we’ll provide you with the perfect solution.




